Optimization goals in Resource Scheduling Optimization
An optimization goal defines conditions and expectations that Resource Scheduling Optimization should consider when performing an optimization.
The Resource Scheduling Optimization engine processes a list of resources and a list of resource requirements and existing bookings. It creates the optimal route or list of bookings for the resources. Bookings are considered optimally scheduled if they meet all constraints respect the importance of the listed objectives in the defined order.
Create a scheduling optimization goal
Using the elements of a goal, you define how bookings should be optimized.
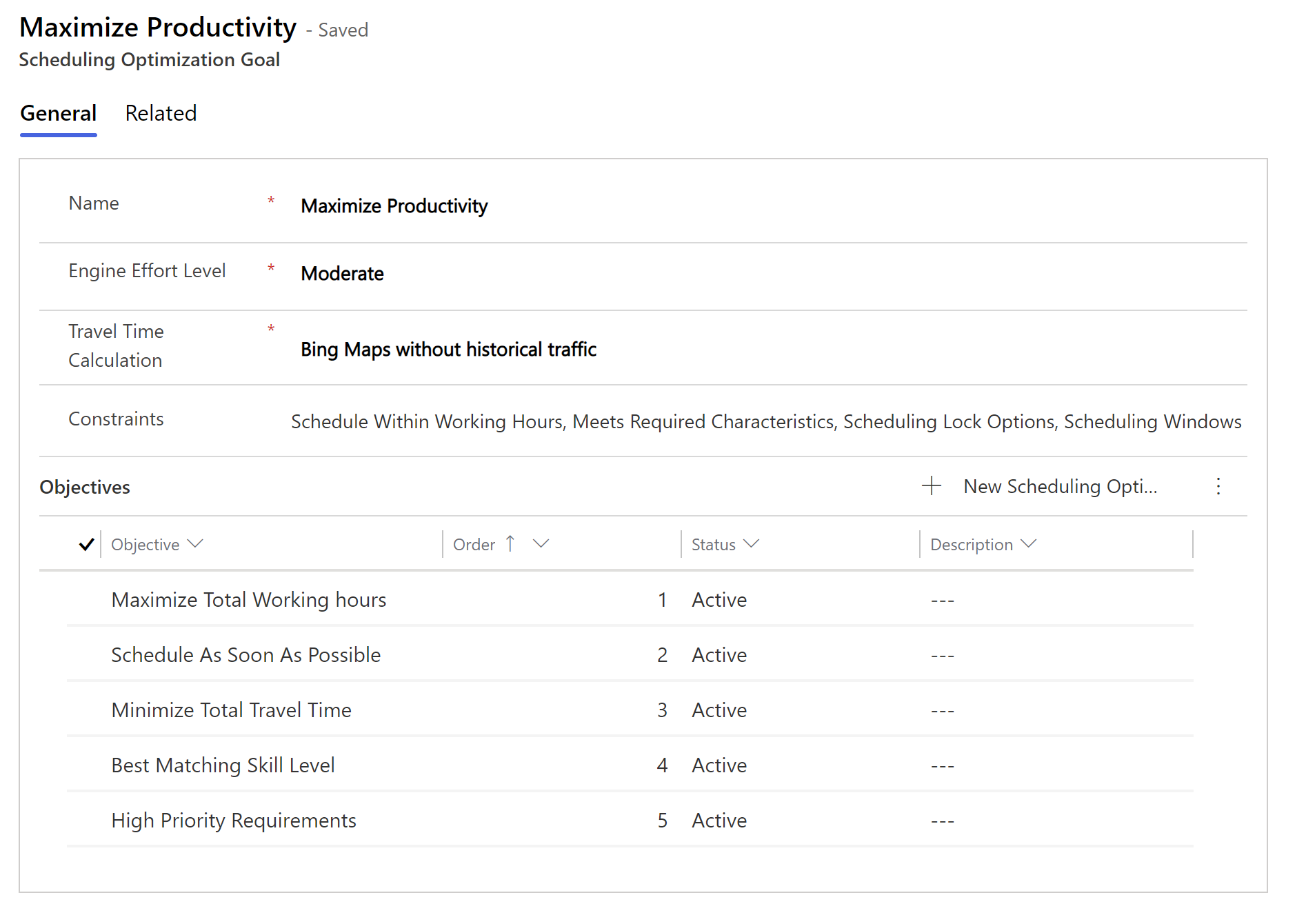
In Resource Scheduling Optimization, in the Settings section, go to Optimization Goals.
Enter a Name for the optimization goal.
Choose an Engine Effort Level. It defined the amount of effort that the system puts in to find the best combination of resources, route, and day or time. Higher effort levels mean that the optimization engine considers more possible combinations. The more combinations the system considers, the longer it takes to complete the calculations.
Choose the Travel Time Calculation option to specify the method of calculating travel distance between resources and requirements.
Select all Constraints for the optimization goal. Constraints are restrictions that are imposed on the bookings that the system creates.
Select Save to create the Scheduling Optimization Goal record.
In the Objectives section of the record, select an objective to change its properties. Select New Scheduling Optimization Objective to add more. All objectives are explained in detail below.
Select Save & Close to apply your changes.
Default optimization goal
When Resource Scheduling Optimization is deployed, the system automatically creates a default goal with some constraints and objectives. You can modify it as needed or create a new optimization goal and set it as default.
The default goal is used when single resource optimization is selected from the schedule board.
Go to Resource Scheduling > Settings > Administration > Scheduling Parameter > Resource Scheduling Optimization to set the default goal.
Understand constraints
Resource Scheduling Optimization works with a set of constraints that you can use to define an optimization goal.
Schedule Within Working Hours
Creates the booking if the travel time to the work location and the work itself fit in a resource's working hours. It also includes travel time from the last booking to the resource's end location. However, the travel time at the end of the day isn't represented on the schedule board.
If the constraint is removed from the goal, work will still be scheduled within working hours, but travel to and from bookings can happen outside of the resource's working hours. It might not leave time at the end of the day to travel to the resource's end location. All bookings will end within a resource's working hours. For more information, go to Allow travel time outside of working hours.
Meets Required Characteristics
Ensures that a resource has all the required characteristics and proficiency to complete a resource requirement.
Meets Required Roles
Ensures that a bookable resource has the required roles to complete a resource requirement. If the resource requirement lists more than one role, the system will ensure one of the roles matches.
Scheduling Lock Options (deprecated)
The Scheduling Lock constraint is deprecated and will soon be removed as a constraint option. Selecting this option won't have any effect on subsequent Resource Scheduling Optimization runs. For more information on using and troubleshooting the updated booking lock options, go to Understand the booking lock option in Resource Scheduling Optimization.
Scheduling Windows
This constraint ensures that Resource Scheduling Optimization creates a booking within the time window of the resource requirement or booking record.
From/To Date or Date Window Start/End set to the same date: Resource Scheduling Optimization schedules the booking on that day but the time of day doesn't matter.
Time Window Start and Time Window End define a time frame: Resource Scheduling Optimization schedules the booking in that time frame but the date doesn't matter.
Time From Promised and Time To Promised are set to a date and a time frame: Resource Scheduling Optimization schedules a booking on the selected date in the selected time range.
Date Window Start/End and Time Window Start/End are set to a time frame on the same day: Resource Scheduling Optimization schedules a booking on the selected date in the selected time range.
Empty time values (v3.0+): Resource Scheduling Optimization will respect scenarios where either the start or end time isn't defined.
For example, if a requirement has only a time window start value, the system schedules the requirement after that time, regardless of date.
This logic applies to the following fields on the Resource Requirement and Resource Booking entity:
- Time Window Start and Time Window End
- Time From Promised and Time To Promised
- From Date and To Date
Note
If time and date fields contain conflicting information, Resource Scheduling Optimization uses Time From/To Promised first.
Meets Resource Preferences
You can add preferred resources to the requirement entity. For more information, go to Resource preferences. Resource Scheduling Optimization respects three different types of resource preferences:
- Preferred: Scheduling preference for the defined resource, if available, but not guaranteed if a different resource better fits the optimal schedule.
- Restricted: The system won't schedule to the resources added to requirements with this resource preference.
- Must choose from: The defined resource gets scheduled if available during the time range. For multiple resources, the system will schedule the first that is available. If none of them are available, the requirement won't get scheduled.
Matches Territories
Respect the Territory field values on the requirement and resource records, and schedule bookings only when the territory values on both records match. A requirement can only belong to one territory, but resources can belong to multiple territories.
Matches Resource Type
Resource types define how the resource relates to the organization. The system considers the Resource Type field values on the requirement and resource records. It schedules bookings only when the resource type values on both records match.
The following resource types are considered for optimization:
- Users
- Contacts
- Accounts
- Equipment
- Facility
Understand objectives
Add and rank the objectives of the Resource Scheduling Optimization goal. You can select multiple objectives, but the order matters. The higher it is on the list, the more preference the system gives to the objective.
Maximize Total Working Hours
The most aggregate work time best meets this objective. Aggregate work is calculated by taking all bookings that were created or updated during the optimization process.
Minimize Total Travel Time
Iteration with the total lowest aggregate travel time best meets this objective. It considers the travel time for the resource to get back to their end location after their last booking, although this travel time isn't shown on the schedule board.
Note
This can't be the first objective in the list because to truly minimize travel time, Resource Scheduling Optimization might not schedule any requirement that requires travel time to meet the first objective.
Locked Bookings (deprecated)
The Locked bookings objective is deprecated and will soon be removed as a goal option. Selecting this option won't have any effect on subsequent Resource Scheduling Optimization runs. For more information on using and troubleshooting the updated booking lock options, go to Understand the booking lock option in Resource Scheduling Optimization.
High Priority Requirements
Prioritize bookings for requirements with the highest score for priority. The priority is set on the Resource Requirement record and is an option set with weighted values. Resource Scheduling Optimization checks Level of Importance on priority to determine how important that priority is. Example: The Level of Importance is 10 for urgent priority and 1 for low priority. Mathematically speaking, Resource Scheduling Optimization looks at the importance of one urgent requirement (Level of Importance: 10 x Number of requirements: 1) same as that of 10 low-priority requirements (Level of Importance: 1 x Number of requirements: 10).
Note
This objective doesn't optimize to book all high priority requirements ahead of the others within the day. It only optimizes to ensure that the high priority requirements are booked to the earliest possible day, not the earliest possible time slot within the day.
Maximize Preferred Resources
Consider the list of preferred resources noted on related requirements. The system will try to assign bookings to preferred resources first while meeting other constraints and objectives.
Best Matching Skill Level
Resource Scheduling Optimization will consider the proficiency rating when matching characteristics required by requirements and the resources who possess those characteristics. If all required characteristics match, the system prioritizes resources with fewer skills first to keep resources available with more or unique skills for emergency work.
This objective depends on the Meets Required Characteristics constraint within the optimization goal.
Meets Required Characteristics constraint selected:
- Resources without the characteristic (skill) or lower-than-required proficiency ratings aren't considered.
- Resources with the exact skill level are the best match and get the highest score.
- The more overqualified a resource is, the lower their score will be.
Meets Required Characteristics constraint not selected:
- Less qualified resources and resources without the skill can still be booked.
- Overqualified resources get a higher score than less qualified resources.
- The more overqualified a resource is, the lower their score will be.
- The less qualified a resource is, the lower their score will be.
- Resources without the skill get the lowest score.
The following graphic shows the score distribution, depending on the skill level for a characteristic rating model that ranges from 1 to 10. The desired skill level is 4, which gets the highest score.

Schedule as soon as possible
Occasionally, there may be more resource capacity than demand for resources. To effectively front-load optimized bookings, add the Schedule As Soon As Possible objective into your optimization goal.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for