How to manage your data relationships
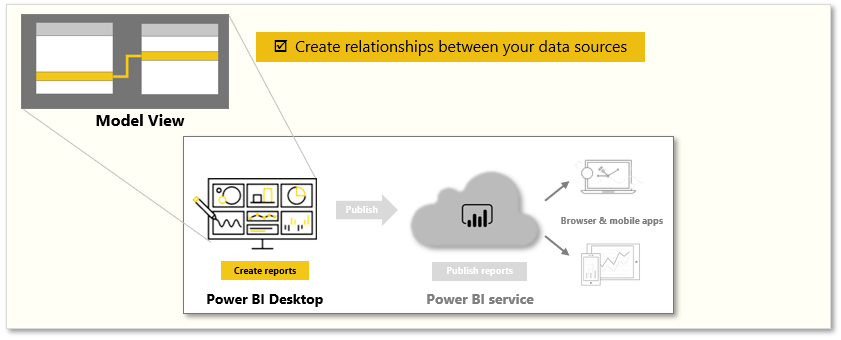
The Model view in Power BI Desktop allows you to visually set the relationship between tables or elements. A relationship is where two or more tables are linked together because they contain related data. This enables users to run queries for related data across multiple tables. Use the Model view to see a diagrammatic view of your data.
Tasks in this unit include:
Note
To follow along with the examples on this page, download the sample Access database here and import all the tables into Power BI Desktop (Get Data > Database > Access database). If you have any issues loading the Access database, please read this article.
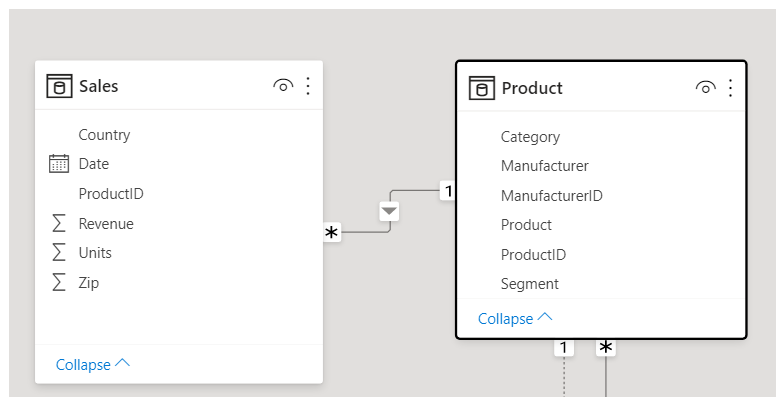
In the Model view, notice that a block represents each table and the lines between them represent relationships.
Adding and removing relationships is straightforward. To remove a relationship, right-click the relationship and select Delete. To create a relationship, drag the field from one table and drop the field on the field of the other table that you want to link.
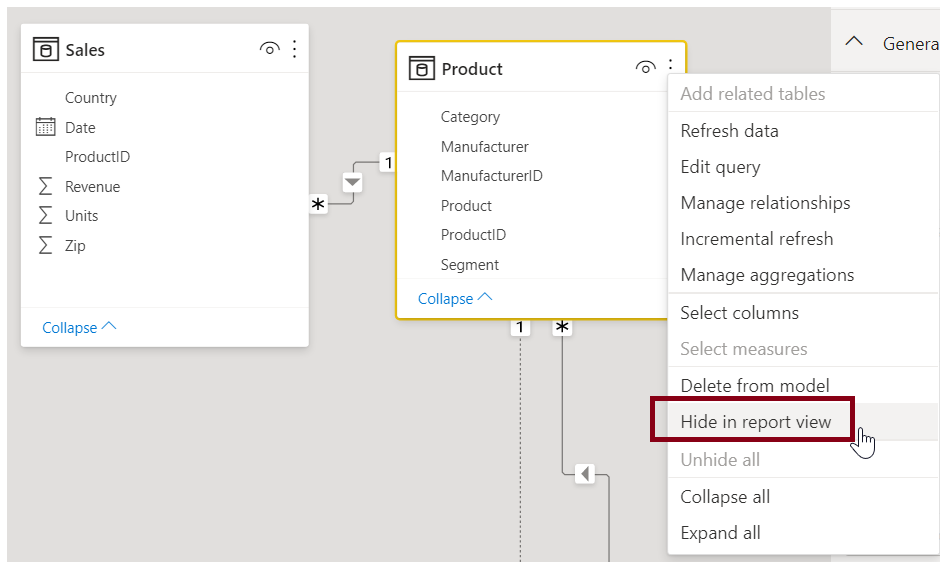
To hide a table or individual column from your report, right-click the table or column in the Model view and select Hide in report view.
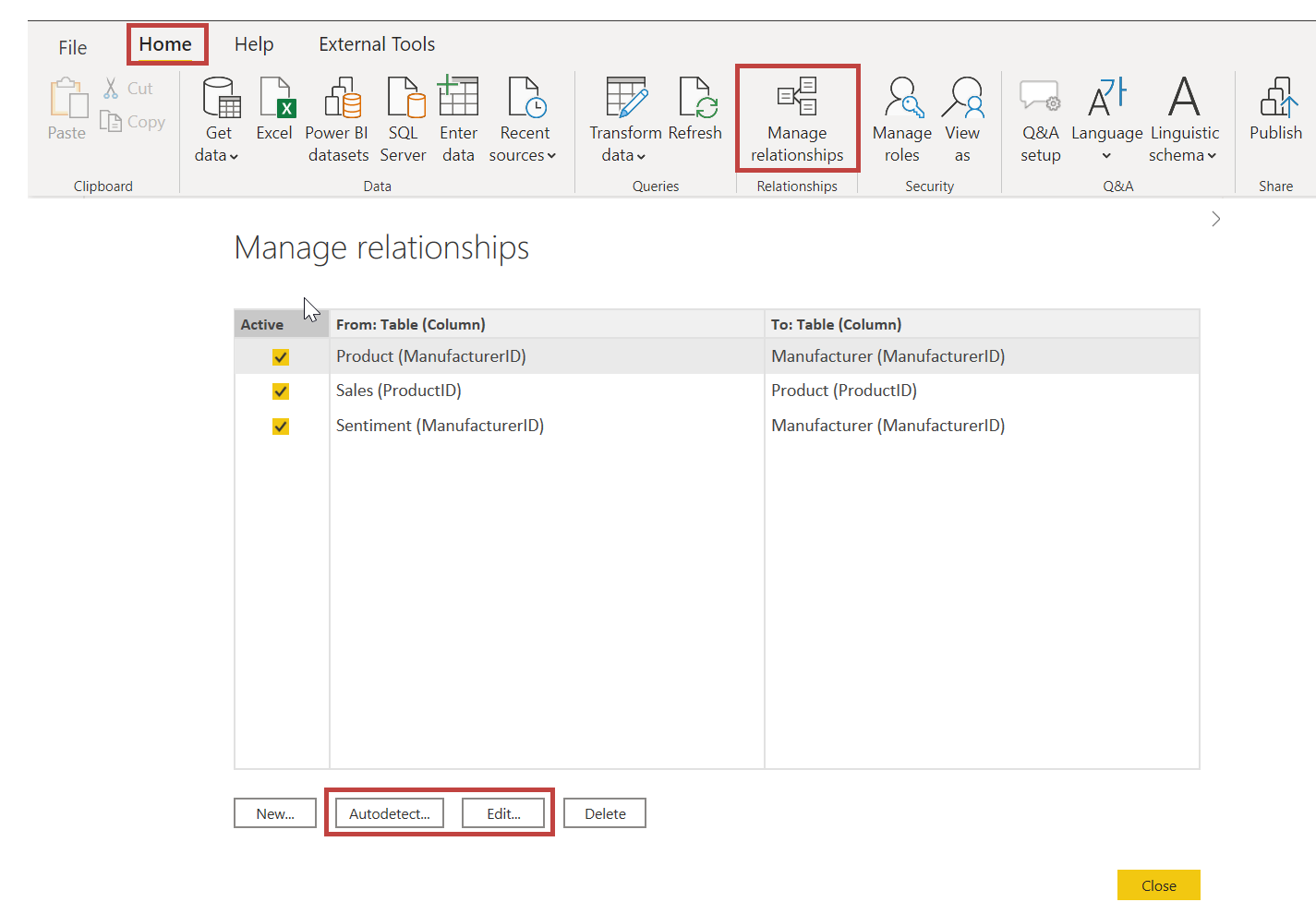
For a more detailed view of your data relationships, on the Home tab, select Manage Relationships. The Manage Relationships dialog box displays your relationships as a list instead of as a visual diagram. From the dialog box, you can select Autodetect to find relationships in new or updated data. Select Edit to manually edit your relationships. You'll find advanced options in the Edit section to set the Cardinality and Cross-filter direction of your relationships.
Your options for Cardinality are explained in the following table.
| Cardinality options | Example |
|---|---|
| Many to One | The most common default relationship. The column in one table can have more than one instance of a value. The related table (or lookup table) has only one instance of a value. |
| One to One | The column in one table has only one instance of a particular value, and the other related table has only one instance of a particular value. |
Generally, we recommend minimizing the use of bi-directional relationships. They can negatively impact model query performance, and possibly deliver confusing experiences for your report users.
Setting accurate relationships between your data allows you to create complex calculations across multiple data elements.
For more information, see: Create and manage relationships in Power BI Desktop and Bi-directional relationship guidance.