Recognize the importance of adapting to change
Your workshop includes people who want to incorporate technical skills into their jobs because their tasks are being computerized. They need to familiarize themselves with new software so they can continue doing their jobs by using technology. You want to work with them to ensure they feel comfortable with the technical complexities of their jobs.
Adapt to change
You might have found that change is the only constant and is an inevitable part of life. You encounter change in every aspect of your personal life and workplace. Even the best-designed plans can be thwarted. What happens when your plan is disrupted by something unexpected? Can you regroup to pivot and adapt? Can you try on different perspectives and generate multiple paths forward?

As you progress in your learning, change can introduce obstacles or setbacks. By learning how to react to and recover from unexpected disruptions or setbacks, you can overcome them. Instead of getting flustered and feeling overwhelmed, you should continue to improve your ability to persevere in the face of setbacks.
Tip
Developing cognitive flexibility gives you the ability to bounce back or pivot.
To better understand how cognitive flexibility helps you adapt to change, review the following video. It's about three minutes long.
Cognitive flexibility helps to reframe change as a positive thing. This process enables you to have an open mind to the various alternatives and possibilities that might reveal themselves. If you're apprehensive about change, you'll subconsciously try to block it, which might prevent you from making the most of the positive outcomes from that change.
Change can also prompt different responses in people depending on the type of mindset they have. People with a fixed mindset might approach a new technology with apprehension. By helping them improve their cognitive flexibility, you can help them shift from worry to a growth mindset.
Note
People with a fixed mindset believe they can only do certain things and that basic abilities like intelligence and talent are fixed traits that they're born with and can't change. People with a growth mindset believe they can learn anything they don't know and that they can improve their abilities through dedication and hard work.
The following table provides some examples of how cognitive flexibility can change a person's perception or confidence about a task or a new concept.
| Fixed mindset | Growth mindset with cognitive flexibility |
|---|---|
| I'll never get it. | If I keep at it, I'll get it. |
| I'm not a technology person, so this isn't for me. | I'm new to technology, and I'm on my way to becoming a tech person. |
| I'm not a hardware person. | I haven't worked much with hardware, but I'm eager to learn. |
| Unlike me, you're a natural. You were born to program. | This is unfamiliar to me, and I'm not yet sure how I feel about it. |
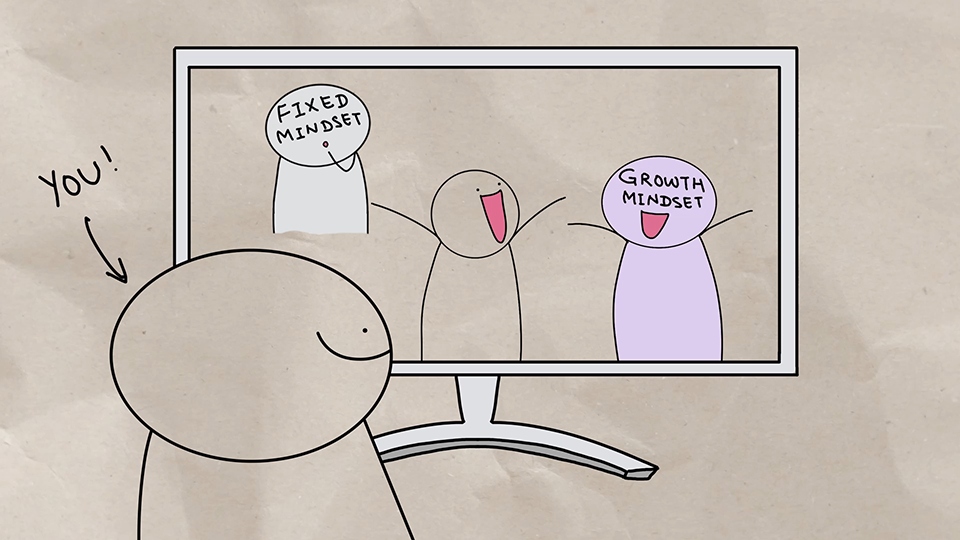
Use cognitive flexibility to adjust to change
When you improve your cognitive flexibility, you're more likely to:
Be open to attempting difficult problems.
Complete training sessions or programs that you initially find challenging.
Learn with a goal of mastering a skill instead of focusing only on performance.
Improve your confidence.
Recover from setbacks and mistakes.
Rethink your strategy and plan a different solution.
The inability to adapt to change leads to inflexibility, which can impede a person's enthusiasm, morale, and potential for progress. The following strategies can help you adapt to change:
Explore your different reactions to an unexpected setback or disruption.
Learn strategies for stretching what seems possible by expanding your perspectives and challenging your assumptions.
Recognize the importance of adapting to change.
Adjust your skills and mindset to include newer goals and requirements.
Practice active listening.
Note
Active listening is the process of listening with the purpose of understanding other people's perspectives by giving them your complete attention when they're communicating. To do this, you should:
- Change phrases from "It's" or "It must be" to "Could it be…?" to "Might it be…?"
- Articulate your approach. Explicitly name what's difficult, which might be the activity itself.
Remember, cognitive flexibility is all about stretching your approach and your thinking. It's not about finding what you think the right solution is. Can you think of other situations where a different vantage point has moved you past an obstacle?