Secure your networks with Azure Firewall Manager
Working with Azure Firewall Manager
Azure Firewall Manager is a security management service that provides central security policy and route management for cloud-based security perimeters.

Azure Firewall Manager simplifies the process of centrally defining network and application-level rules for traffic filtering across multiple Azure Firewall instances. You can span different Azure regions and subscriptions in hub and spoke architectures for traffic governance and protection.
If you manage multiple firewalls, you know that continuously changing firewall rules make it difficult to keep them in sync. Central IT teams need a way to define base firewall policies and enforce them across multiple business units. At the same time, DevOps teams want to create their own local derived firewall policies that are implemented across organizations. Azure Firewall Manager can help solve these problems.
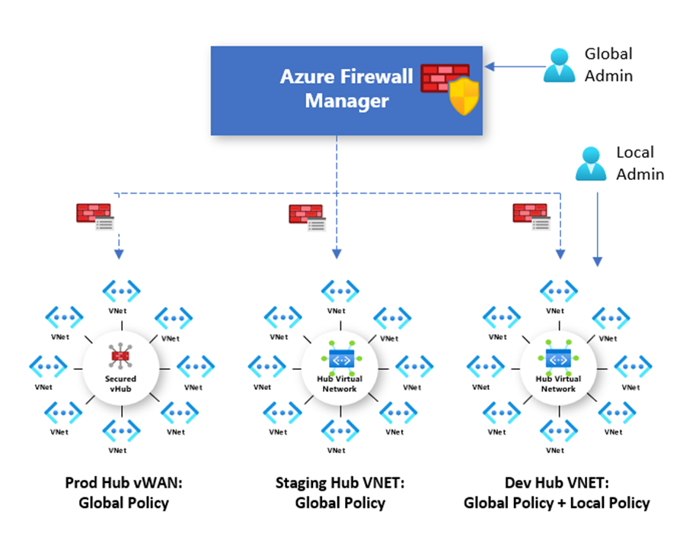
Firewall Manager can provide security management for two network architecture types:
- Secured Virtual Hub - This is the name given to any Azure Virtual WAN Hub when security and routing policies have been associated with it. An Azure Virtual WAN Hub is a Microsoft-managed resource that lets you easily create hub and spoke architectures.
- Hub Virtual Network - This is the name given to any standard Azure virtual network when security policies are associated with it. A standard Azure virtual network is a resource that you create and manage yourself. At this time, only Azure Firewall Policy is supported. You can peer spoke virtual networks that contain your workload servers and services. You can also manage firewalls in standalone virtual networks that are not peered to any spoke.
Azure Firewall Manager features
The key features offered by Azure Firewall Manager are:
Central Azure Firewall deployment and configuration
You can centrally deploy and configure multiple Azure Firewall instances that span different Azure regions and subscriptions.
Hierarchical policies (global and local)
You can use Azure Firewall Manager to centrally manage Azure Firewall policies across multiple secured virtual hubs. Your central IT teams can author global firewall policies to enforce organization wide firewall policy across teams. Locally authored firewall policies allow a DevOps self-service model for better agility.
Integrated with third-party security-as-a-service for advanced security
In addition to Azure Firewall, you can integrate third-party security-as-a-service providers to provide additional network protection for your VNet and branch Internet connections. This feature is available only with secured virtual hub deployments (see above).
Centralized route management
You can easily route traffic to your secured hub for filtering and logging without the need to manually set up User Defined Routes (UDR) on spoke virtual networks. This feature is available only with secured virtual hub deployments (see above).
Region availability
You can use Azure Firewall Policies across regions. For example, you can create a policy in the West US region, and still use it in the East US region.
DDoS protection plan
You can associate your virtual networks with a DDoS protection plan within Azure Firewall Manager.
Manage Web Application Firewall policies
You can centrally create and associate Web Application Firewall (WAF) policies for your application delivery platforms, including Azure Front Door and Azure Application Gateway.
Azure Firewall Manager policies
A Firewall policy is an Azure resource that contains NAT, network, and application rule collections and Threat Intelligence settings. It is a global resource that can be used across multiple Azure Firewall instances in Secured Virtual Hubs and Hub Virtual Networks. New policies can be created from scratch or inherited from existing policies. Inheritance allows DevOps to create local firewall policies on top of organization mandated base policy. Policies work across regions and subscriptions.
You can create Firewall Policy and associations with Azure Firewall Manager. However, you can also create and manage a policy using REST API, templates, Azure PowerShell, and the Azure CLI. Once you create a policy, you can associate it with a firewall in a virtual WAN hub making it a Secured Virtual Hub and/or associate it with a firewall in a standard Azure virtual network making it a Hub Virtual Network.
Deploying Azure Firewall Manager for Hub Virtual Networks
The recommended process to deploy Azure Firewall Manager for Hub Virtual Networks is as follows:
Create a firewall policy
You can either create a new policy, derive a base policy, and customize a local policy, or import rules from an existing Azure Firewall. Ensure you remove NAT rules from policies that should be applied across multiple firewalls.
Create your hub and spoke architecture
Do this either by creating a Hub Virtual Network using Azure Firewall Manager and peering spoke virtual networks to it using virtual network peering, or by creating a virtual network and adding virtual network connections and peering spoke virtual networks to it using virtual network peering.
Select security providers and associate firewall policy
Currently, only Azure Firewall is a supported provider. This can be done while creating a Hub Virtual Network, or by converting an existing virtual network to a Hub Virtual Network. It is also possible to convert multiple virtual networks.
Configure User Defined Routes to route traffic to your Hub Virtual Network firewall
Deploying Azure Firewall Manager for Secured Virtual Hubs
The recommended process to deploy Azure Firewall Manager for Secured Virtual Hubs is as follows:
Create your hub and spoke architecture
Do this either by creating a Secured Virtual Hub using Azure Firewall Manager and adding virtual network connections, or by creating a Virtual WAN Hub and adding virtual network connections.
Select security providers
This can be done while creating a Secured Virtual Hub, or by converting an existing Virtual WAN Hub to a Secure Virtual Hub.
Create a firewall policy and associate it with your hub
This is applicable only if you are using Azure Firewall. Third-party security-as-a-service policies are configured via the partners management experience.
Configure route settings to route traffic to your Secured Virtual Hub
You can easily route traffic to your secured hub for filtering and logging without User Defined Routes (UDR) on spoke Virtual Networks by using the Secured Virtual Hub Route Setting page.
You cannot have more than one hub per virtual WAN per region, however you can add multiple virtual WANs in the region to achieve this.
You cannot have overlapping IP spaces for hubs in a vWAN.
Your hub VNet connections must be in the same region as the hub.