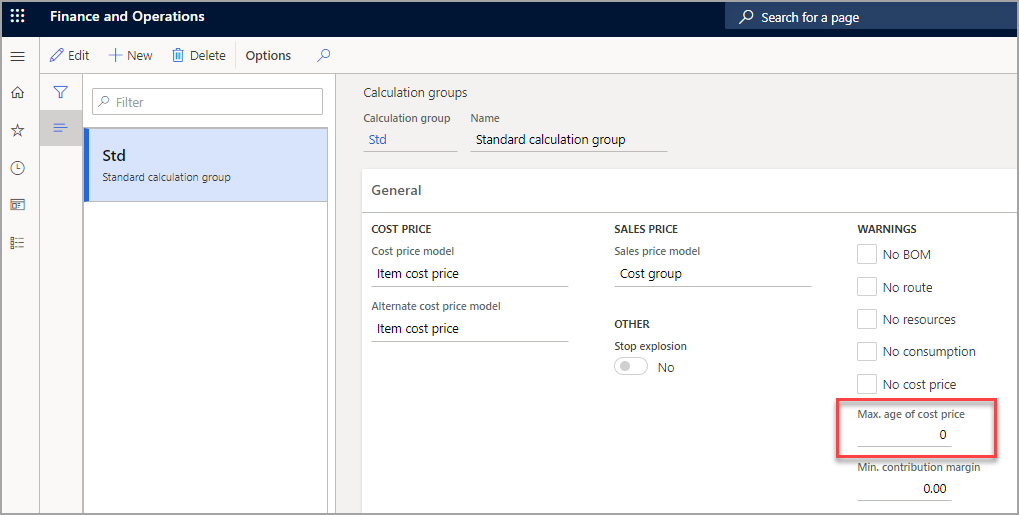
Calculation groups
You can define calculation groups in Cost management > Predetermined cost policies setup > Calculation groups.
Calculation groups that are assigned to items let you specify how the cost or sales price of components, as outlined by the calculation group, is sourced for the calculation. On the Calculation groups page, you can define a Cost price model, an Alternative cost price model, a Sales price model, and Warnings.
By assigning calculation groups to items, you can specify how a cost/sales price of a BOM component is calculated. You can also assign a BOM calculation group to items so that a BOM calculation will generate warning messages about potential sources of calculation errors.
To set up calculation groups, select Inventory and warehouse management > Setup > Costing > Calculation groups. Calculation groups contain the settings that are used in BOM calculations, including:
- Cost price model
- Sales price model
- Warnings
These settings determine how the cost and sales prices are calculated and whether warnings appear during the calculation process. When the elements of the calculation group are set up and assigned to a default value, BOM calculations can be run.
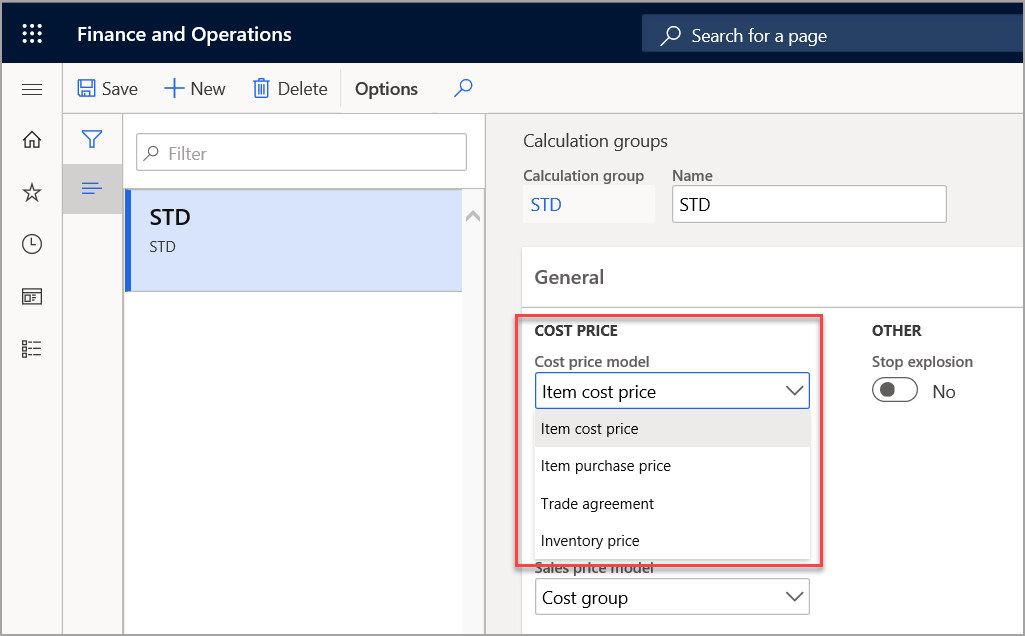
Cost price model
By setting the Cost price model field, you can indicate the source of a purchased component's cost contribution data during the calculation of the planned cost of a manufactured item. Some manufacturers calculate planned costs by using the purchase price trade agreements for purchased components or another basis, such as the purchase price records in a costing version.
The four options for the Cost price model field are:
Item cost price - The cost price from the Released product table is used, or the combination of item dimensions is used as the cost price.
Item purchase price - The purchase price from the Cost price field on the Purchase tab of the Released product list page is used.
Trade agreement - You can configure trade agreements for specific combinations of items and vendors or for specific sites. Then, when you select the Trade agreement option, the trade agreement that you created for the purchase price, together with the item and site, will be used.
Inventory price - The current inventory value for the item is used to calculate the unit cost in the BOM calculation. A unit cost price is calculated only if the posted quantity and the physical quantity are more than 0 (zero).
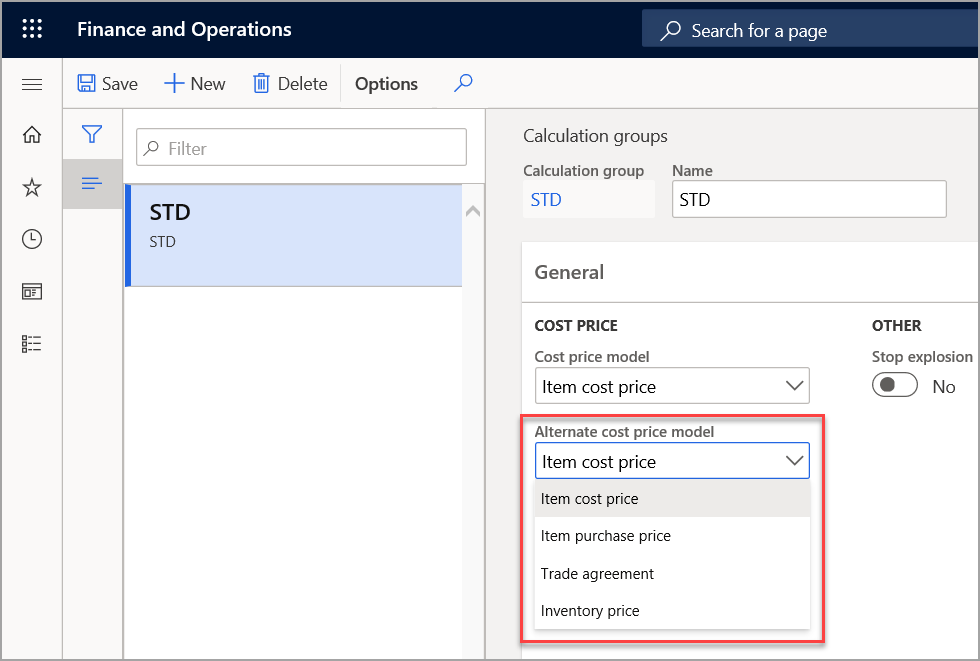
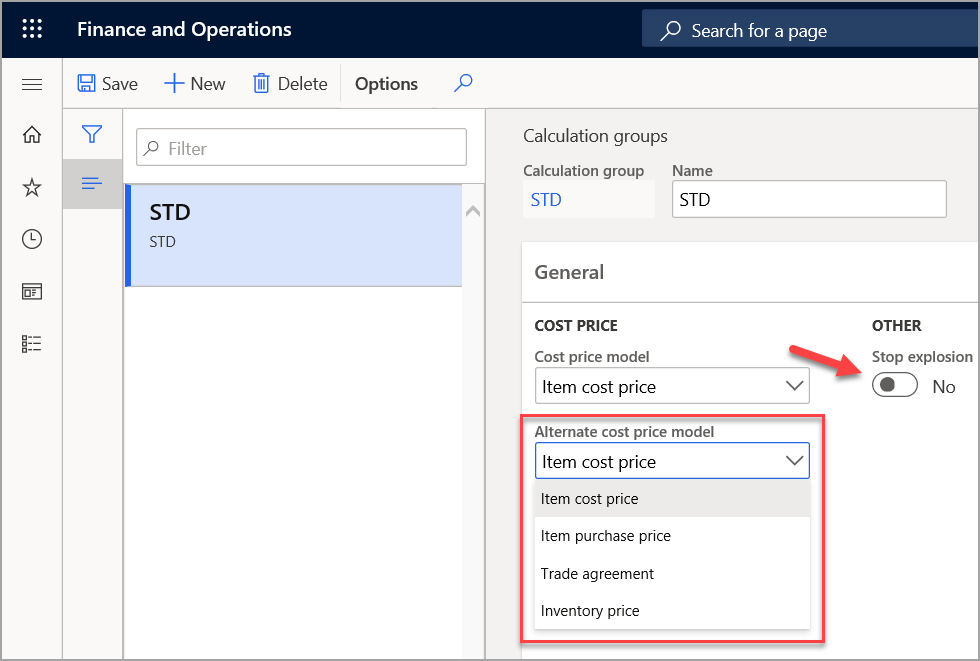
Alternate cost price model
The Alternate cost price model field has the same options as the Cost price model field. However, this field is used only when a price can't be found in the primary cost price model.
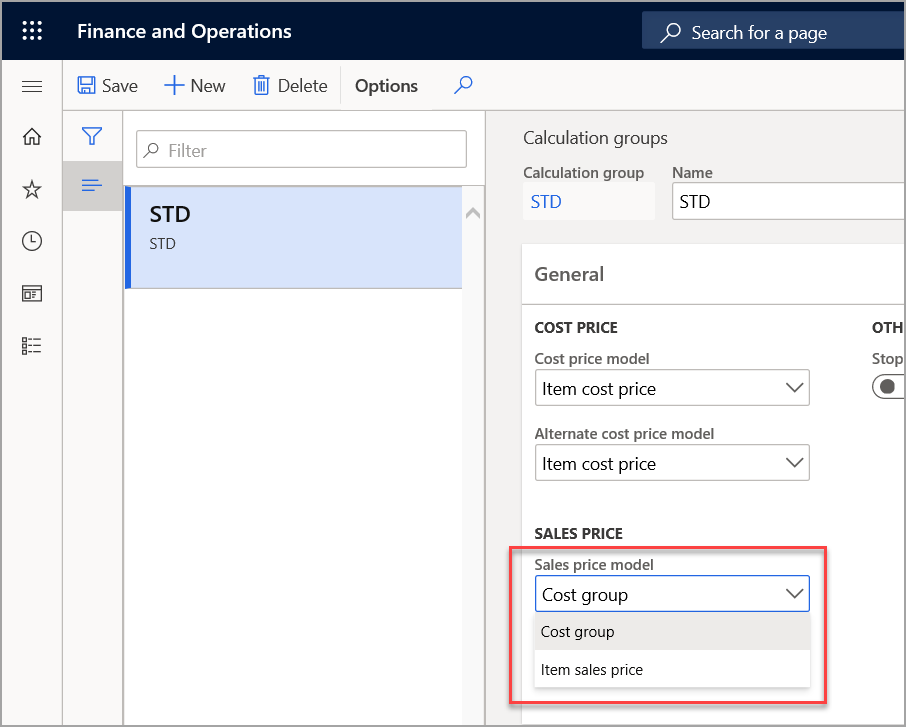
Sales price model
By setting the Sales price model field, you can indicate how the item's data is used to calculate a suggested sales price. You can specify either the item sales price or the cost group.
Some manufacturers want to calculate a suggested sales price for manufactured items. The calculated sales price can reflect a rolled-price approach that is based on the component's sales price record. Alternatively, the calculated sales price can reflect a cost-plus-markup approach that is based on the component's cost and applicable profit percentage, which is associated with the item's cost group.
The two options for the calculation of the Sales price model field are:
Cost group - When this option is selected, the sales price is calculated based on the cost price and the profit setting percentage from the cost group.
Item sales price - When this option is selected, the sales price on the Sell FastTab from the Released product table is used.
Stop explosion
By using the Stop explosion field, you can indicate that a manufactured item should be treated as a purchased item for cost roll-up purposes during BOM calculation.
Typical scenarios include a purchased item that is occasionally manufactured or a manufactured item that is now being purchased. The item is first designated as a manufactured item to define BOM and route information and to support production orders for the item. However, the Stop explosion flag prevents cost calculations from using the item's BOM and route. Instead, the BOM calculation uses the item's specified costs.
Typically, you will leave the value of Stop explosion as No.
Depending on the site, the item's cost can still be calculated by using BOM calculations. Explosion of planned purchase orders and production orders is stopped at the BOM whose components are associated with the calculation group that the Stop explosion option is selected for.
Master planning generates the planned orders on the BOM, not on the items that are included in the BOM. Basically, by selecting this option, you specify that a cost won't be added into the BOM calculation for items that have this calculation group.
Warnings
Under the Warnings section, you can select the options for any warning messages that users should receive when they perform BOM calculations.
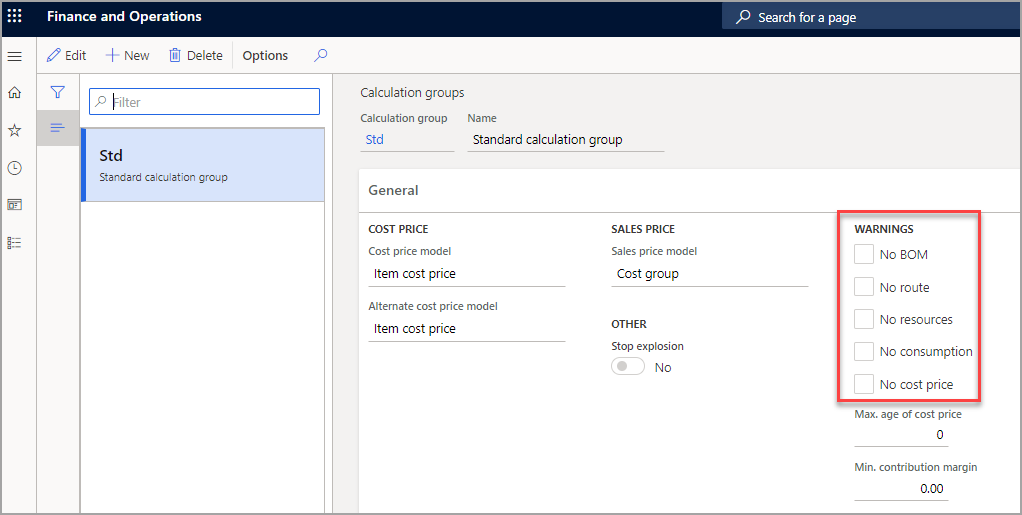
For example, if you select the No BOM check box, the user receives a warning if no active BOM version is found for one of the components or the parent item that the BOM calculation is run for.
If you select the No route check box, the user receives a warning if no active route version is found. If you're using resources on your routes and operations, you can instruct the system to check for those resources. Then, if a resource isn't found on every line in the active route, the user receives a warning.
You can also verify and check for consumption. Consumption is the quantity in a particular route. Typically, it represents the amount of time that is required to perform a specific operation for a production process. You can check whether an item has no cost price. If there is no active cost price for an item, no cost is added into the BOM calculation.
You can also check and verify the age of the cost price.
For example, you have entered 60 in the Max. age of cost price field to indicate that the unit cost price must be reevaluated after 60 days. If this limit is reached, the system generates a warning. For example, a cost price was entered for an item in January of this year. If it's now August, which is more than 60 days after the cost price was entered, the user receives a warning when the BOM calculation is run.
You can enter a percentage in the Minimum contribution margin field. This value indicates the point at which the minimum contribution margin isn't being met. If the contribution margin for a particular component isn't met, the user receives a warning. Therefore, this field helps guarantee that you don't undercut the costs and the additional carrying costs that might be required for your items.
Default setup in inventory and warehouse management parameters
To run a BOM calculation, you must either set up calculation groups and assign them to individual items or set a default calculation group. The calculation settings from the calculation group are then used as default values on the BOM calculation page at the time of BOM calculation. You can set up the default parameter in Inventory management > Setup > Inventory and warehouse parameters > Inventory accounting > Calculation group.
The default calculation group can also be listed on the Cost management > Inventory accounting policies setup > Parameters page, or a product-specific calculation group is required on the Released product details page.
The system first looks for the calculation group setup on the Released product details page. If the system doesn't find a calculation group there, it looks at the Parameters settings page.
If the system can't find a calculation group, the user receives an error message during calculation. A calculation group contains policies for the cost price model, the sales price model, and the warnings checklist. The calculation settings from the calculation group are used as default values on the BOM calculation page at the time of BOM calculation.
By setting up a default configuration group, you can also configure the warning conditions that prompt users during the BOM calculation process, if the selected components might cause calculation errors.
Because calculation groups are required to run calculations, you must set up a default calculation group in the Inventory management parameters. This setup enables companies to have a standard cost group and profit setting for all items. Then, if a particular item has special calculation requirements, the user can assign a different calculation group to that item.
Typically, you can set calculation groups on BOM component items instead of BOM items. However, when warning messages are shown, calculation groups can be applied. A calculation group that is assigned to items overrides the default value that is set up in the Inventory management parameters.