Remote Share Provider
APPLIES TO:  2013
2013  2016
2016  2019
2019  Subscription Edition
Subscription Edition  SharePoint in Microsoft 365
SharePoint in Microsoft 365
With organizations increasingly using SharePoint for rich contents rather than normal documents, the storage requirements have grown multifold. Administrators must regularly review and clean up contents in the SharePoint. By default, all the structured content such as metadata, or unstructured content such as files, are stored in content databases in the SQL server attached to SharePoint Server. Unstructured data in SharePoint are stored in content database as Binary Large Object (BLOB) and they are immutable.
In SharePoint 2013, Remote BLOB Storage (RBS) technology was created in SQL server to offload BLOBs from content database and SQL FILESTREAM provider was provided at that time. In SharePoint Server Subscription, new Remote Share Provider was created for IT administrators to lower down the overall cost of SharePoint deployment in on-premise environments as reasonable and easy to use storage solution by offloading content from SQL server to network SMB storage.
Key features of Remote Share Provider
In SharePoint Server Subscription Edition, we provide a new RBS provider Remote Share Provider.
Following are the key features of Remote Share Provider:
- This provider supports Binary Large Object (BLOB) storage offload to remote SMB system and totally enables content database storage in SQL server side. Therefore, with the same amount of limitation of content database, as in 200-GB size, more file volumes can be stored in one content database. Hence, it helps not only to reduce the cost for storage but also for the maintenance.
- There is a PowerShell Cmdlet to check the data completeness to figure out storage problem.
- By applying the existing backup and restore methodology of SMB system, it provides relatively reasonable disaster recovery.
Limitations of Remote Share Provider
Remote Share Provider introduces the new storage system into SharePoint. Any other system can introduce complexity and reliability downgrade in some circumstances. As it is based on RBS, following are some of the limitations that are also applicable to Remote Share Provider:
- Encryption is not supported on BLOBs, even if transparent data encryption is enabled.
- RBS does not support using data compression.
- As content database and BLOB storages are separated, backup and restore from farm and content database level are not enough for disaster recovering. BLOB storages need to be backed up and recovered at the same time when performing farm and content database level backup and recovery.
Advantages and disadvantages of Remote Share Provider
When compared with storing BLOBs inside SQL server, there are advantages and disadvantages to use Remote Share Provider.
Advantages:
- Improve SQL performance by moving unstructured data outside of SQL.
- Lower down storage cost by using low-cost SMB storage.
- Stores large number of files.
Disadvantages:
- Requires other backup and restore step for remote storage (SMB).
- Requires separate configuration of security and data protection in the remote storage (SMB).
- Another storage layer reduces availability and reliability of the overall system that is High availability and Disaster Recovery (HADR) will not work by default until you set up HADR for SMB storage.
Planning Remote Share Provider
Remote Share Provider is suitable for the scenarios when you need:
- Huge volume of contents in site collection, which can cause a problem in storage cost and system performance.
- Site collection is not for time-critical business. If the site collection is down, you can take time to restore content database and remote BLOB storage. Service downtime for this specific site collection will not have significant impact to organization business.
- More READ operations than WRITE operations on that site collection.
Backup and restore methodology must be planned for remote storage system as SharePoint as SQL server backup or restore might not be able to cover BLOBs stored in the remote storage system. It is recommended to use System Center Data Protection Manager (DPM) to manage backup and restore so that content database and remote BLOB storage can be backed up at the same time.
In DPM, you can create protection group for both SharePoint content database and remote SMB storage so that these data sets can be backed up/managed together by DPM. For more information, see
If you do not use DPM to manage backup and restore, you can follow the two steps to back up SharePoint in sequence:
- Back up farm or content database by using Backup-SPFarm PowerShell cmdlet.
- Backup remote SMB storage by using your existing backup tool.
To restore SharePoint back, reverse the sequence to:
- Restore the SMB storage from backup storage.
- Restore content database or farm by using Restore-SPFarm PS cmdlet.
Remote Share Provider does not provide encryption to ensure the data security. It relies on the security and access control provided by SMB storage. Hence, to keep your BLOB data safe from threats, proper actions must be taken at the storage level.
- Enable SMB encryption to ensure BLOBs are transferred safely through network and storage.
- Enable access control so that only limited users can access BLOBs in the SMB storage.
- Enable BitLocker to strengthen the data safety.
Considering high availability
By using previous FILESTREAM provider, which is default shipped with SQL server, High availability and Disaster Recovery (HADR) is handled by SQL Server HADR cluster.
By moving to new Remote Share Provider, this SQL Server level HADR cannot cover the BLOBs inside SMB storage. Hence, Remote Share Provider cannot support same as SQL server HADR by default. It requires more cost and effort to set up a HADR-ready SMB storage and integrate with SharePoint and SQL server with layer HADR system.
High availability was supported by setting up a failover SharePoint farm in the past. With Remote Share Provider, it can still work.
There are two different configurations for failover farm with Remote Share Provider.
Share same SMB BLOB storage between active the SharePoint farm and the failover farm.

For this configuration, there are two sets of SharePoint servers and SQL servers, however, they share the same SMB storage for BLOBs. Real-time database synchronization is set up to stream changes from active SQL server in active SharePoint farm to failover SQL server in fail over SharePoint farm. So if there is any problem in active SharePoint farm, admin can immediately switch to fail over SharePoint farm.
Share same SMB BLOB storage between active SharePoint farm and failover farm with SMB BLOB storage failover backup.
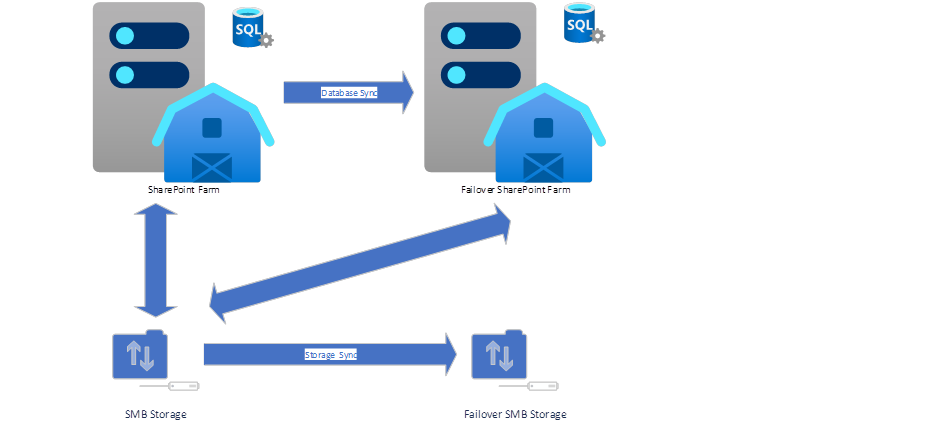
This configuration is exactly the same as configuration #1 except there is a failover backup for SMB BLOB storage. Not only database is synced but SMB storage is also backed up. In this situation, when active SharePoint farm has problem, it can switch to fail over farm with other setting to change the SMB storage UNC path to failover SMB storage.
Security and permission
Remote Share Provider does not provide encryption to ensure the data security. It relies on the security and access control provided by SMB storage. Therefore, to keep the BLOB data safe from threats, proper actions must be taken at the storage level:
- Enable SMB encryption to ensure BLOBs are transferred safely through network and storage.
- Enable access control so that only limited users can access BLOBs in the SMB storage.
- Enable BitLocker to strengthen the data safety, if possible.
- The user account used to perform the steps in the Provision a BLOB store for each content database section must be a member of the
db_ownerfixed database role on each database that you are configuring RBS for. - The user account installing the client library in the steps in the Install the RBS client library on SQL Server and each front-end or application server section must be a member of the administrators' group on all of the computers where you are installing the library.
- The user account enabling RBS in the Enable RBS for each content database section must have sufficient permissions to run Microsoft PowerShell.
Setting up Remote Share Provider
Install RBS library to evert SharePoint front end and application server
Install RBS library to every SharePoint frontend and Application server in SharePoint farm using the following command line:
Msiexec /qn /lvx* rbs_install_log.txt /I RBS.msi ADDLOCAL="Client"
Note
Do not install RBS library through the GUI.
Enable RBS feature in specific content database
RBS is applied to specific content database. Hence, every time when a new content database needs to use RBS, it needs to be set up. Then RBS providers can be registered on the content database.
Ensure that there is a master key for this content database for which you want to apply RBS. If the master key does not exist, create a new one for the content database.
To create master key for specific content database:
- Confirm that the user account performing these steps is a member of the
db_ownerfixed database role on each database that you are configuring for RBS. - Open SQL Server Management Studio.
- Connect to the instance of SQL Server that hosts the content database.
- Expand Databases.
- Select the content database for which you want to create a BLOB store, and then click New Query.
- Paste the following SQL queries in Query pane, and then run them in the sequence listed. In each case, replace
[WSS_Content]with the content database name, and replacec:\BlobStorewith thevolume\directoryin which you want the BLOB store created. The provisioning process creates a folder in the location that you specify. You can provision a BLOB store only once. If you attempt to provision the same BLOB store multiple times, you will receive an error.
#Replace with <your content database>
use [<Your content database>]
#Replace with your <Your SQL database instance>
if not exists
(select * from sys.symmetric_keys
where name = N'##MS_DatabaseMasterKey##')
create master key encryption by password = N'<Admin Key Password>'
You can set up RBS for each content database by using below command line. Replace DBNAME and DBINSTANCE with your specific content database name and database instance name.
msiexec /qn /lvc* rbs.log /i rbs.msi TRUSTSERVERCERTIFICATE=true DBNAME="Your content database" ADDLOCAL="ServerScript,EnableRBS" DBINSTANCE="Your SQL database instance"
Setting up credentials for Remote Share Provider
To access restricted SMB storage, it is recommended that specific domain account is assigned to Remote Share Provider to READ/WRITE BLOB files in SMB storage. The provider is using PSCredential object to sign-in remote RBS storage with this specific account credential.
See Get-Credential to get PSCredential object for the RBS provider.
Registering BLOB store with Remote Share Provider
To offload BLOB storage from content database to SMB storage, you need to create and register a new remote share BLOB store by using Remote Share Provider to a given content database.
You can use Register-SPRemoteShareBlobStore cmdlet to register a new BLOB store for specific content database.
Register-SPRemoteShareBlobStore -ContentDatabase <SPContentDatabasePipeBind> -Name <BlobStoreName[ValidateLength(8, 128)]> -Location <UNCPath> [-BlobStoreCredential <PSCredential>][- PoolCapacity <Int>]
The cmdlet parameters are:
-ContentDatabase <SPContentDatabasePipeBind>
The content database, the new BLOB store will be applied to, can either be the content database object or the content database name.
-Name <BlobStoreName[ValidateLength(8, 128)]>
The name of new created BLOB store.
-Location<UNCPath[ValidateLength(5, 256)]>
The UNC path of the SMB storage this BLOB store will use.
[-BlobStoreCredential] <PSCredential>
The PSCredential object, which is used to access the SMB storage. If this parameter is not specified, it will use the service account, which is applied to the current web application.
[-PoolCapacity] <Int [ValidateRange(1000, 10000)]>
The number of BLOB trunks in each BLOB pool. If this parameter is not specified, it will be set to 1000.
Example cmdlet syntax:
Register-SPRemoteShareBlobStore -ContentDatabase $db -Name "RemoteBlob" -Location "\\SPVNEXT\blobstore"
Switching and activating BLOB store
The registered remote share BLOB store will not take effect until it is activated. Switch-SPBlobStorage cmdlet needs to be run after Register-SPRemoteShareBlobStore, so that new contents to the content database will be routed to the newly created remote share BLOB store.
Switch-SPBlobStorage -RemoteShareBlobStore <SPRemoteShareBlobStorePipeBind>
This cmdlet will switch default BLOB storage of the content database to the given remote share BLOB store. Since BLOB store is unique in farm and linked to specific content database, there is no need to specify the content database in this cmdlet.
The remote share BLOB store, which will be active, can either be a remote share BLOB store object or the remote share BLOB store name.
Syntax example:
$blobstore = Register-SPRemoteShareBlobStore -ContentDatabase $db -Name "RemoteBlob" -Location \\SPVNEXT\blobstore
Switch-SPBlobStorage -RemoteShareBlobStore $blobstore
Switch-SPBlobStorage -ContentDatabase <SPContentDatabasePipeBind> -SQL
This cmdlet will switch default BLOB storage back to content database in SQL.
-ContentDatabase <SPContentDatabasePipeBind
The content database, which will need to set back to SQL. It can either be a content database object or content database name.
SQL
Indicates that the content database will use SQL for BLOB storage for new contents.
Syntax example:
Switch-SPBlobStorage -ContentDatabase $db -SQL
Grant permission to web application pool account and SharePoint service application pool account
After the RBS setup, new schema mssqlrbs is created in the content database. Hence, the access permission for this new schema must be granted to Web Application Pool Account and SharePoint Service Application Pool Account, so that the web application and the service application can access RBS in the content database.
Use the below sample SQL command in SQL server to grant the permission.
ALTER AUTHORIZATION ON SCHEMA::mssqlrbs to [web_app_pool_account];
ALTER AUTHORIZATION ON SCHEMA::mssqlrbs to [service app_pool_account];
Resetting IIS
After remote share BLOB store becomes the default BLOB storage to the content database, you need to run iisreset in every SharePoint front-end server and SharePoint application server. Then any new content will be written to the external SMB storage using Remote Share Provider.
Managing and configuring remote share BLOB store
You can use Get-SPRemoteShareBlobStore cmdlet to get the remote share BLOB stores in the farm.
Get-SPRemoteShareBlobStore -RemoteShareBlobStore <SPRemoteShareBlobStorePipeBind>
This cmdlet will get a remote share BLOB store object by remote share BLOB store name.
Get-SPRemoteShareBlobStore -ContentDatabase <SPContentDatabasePipeBind>
This cmdlet will get all the remote share BLOB store objects for the given content database.
Get-SPRemoteShareBlobStore
This cmdlet will get all the remote share BLOB store objects for the current farm.
You can change the configuration of remote share BLOB store at any time.
Set-SPRemoteShareBlobStore -RemoteShareBlobStore <SPRemoteShareBlobStorePipeBind> [-Location <String>] [-BlobStoreCredential <PSCredential>] [-PoolCapacity <int>]
The cmdlet parameters are:
-RemoteShareBlobStore <SPRemoteShareBlobStorePipeBind>
The remote share BLOB store needs to be changed. It can either be the remote share BLOB store object or be the remote share BLOB store name.
[-Location <String>]
The UNC path, which the BLOB storage needs to switch to. This parameter changes the UNC path of the SMB storage used. It will not move the BLOBs from the old SMB storage to the new SMB storage.
[-BlobStoreCredential <PSCredential>]
The PSCredential object, which the BLOB storage needs to switch to apply.
[-PoolCapacity <int>]
The capacity of each pool that is used in the BLOB store.
Migrating BLOBs from one remote share BLOB store to another
One content database can have several BLOB stores, and at any time only one of these BLOB stores can be active for WRITE while others are just for READ. Sometimes, there is a need to move BLOBs from one BLOB store to another. For example, you may need to set up a new SMB storage and move all BLOBs to the new SMB storage. In this situation, you need to migrate data from SQL or old BLOB stores to the new BLOB store.
By following the below sample, you can migrate your BLOBs from old BLOB storage to a new active BLOB store created by committing Migrate().
$db = Get-SPContentDatabase $YourDatabaseName
$rbss = $db.RemoteBlobStorageSettings
$rbss.SetActiveProviderName($YourBlobStoreName)
$rbss.Migrate()
If you want to migrate your BLOBs from BLOB stores back to SQL content database, you can follow below example by setting active provider to empty.
$db = Get-SPContentDatabase $YourDatabaseName
$rbss = $db.RemoteBlobStorageSettings
$rbss.SetActiveProviderName()
$rbss.Migrate()
Unregistering remote share BLOB store
You can unregister remote share BLOB store by using cmdlet Unregister-SPRemoteShareBlobStore.
Unregister-SPRemoteShareBlobStore -RemoteShareBlobStore <SPRemoteShareBlobStorePipeBind> [-Force]
The cmdlet parameters are:
RemoteShareBlobStore <SPRemoteShareBlobStorePipeBind>
The remote share BLOB store needs to be unregistered. It can either be the remote share BLOB store object or be the remote share BLOB store name. If the RemoteShareBlobStore is active in the content database, or there are still BLOBs in use in this blob store, this cmdlet will throw exception.
[-Force]
This switch forces unregistration even when the RemoteShareBLOBStore is not active but the BLOBs are still in use. If there's need to unregister such BLOB store, you can run the cmdlet with this switch to ignore the detection of in-use BLOBs in the BLOB store. If the blob store is active in the content database, this cmdlet will throw an exception to prevent unintentional unregistering of a BLOB store in-use.
We do not recommend using this -Force switch because it will leave BLOBs in the SMB storage behind and make your SharePoint contents unaccessible. We recommend migrating BLOBs firstly and then unregister remote share BLOB store.
Validating data consistency of remote share BLOB store
You can validate remote share BLOB store used by the content database by cmdlet Test-SPRemoteShareBlobStore.
Test-SPRemoteShareBlobSotore -ContentDatabase <SPContentDatabasePipeBind> [-LogPath <String>]
The cmdlet parameters are:
-ContentDatabase <SPContentDatabasePipeBind>
The content database needs to be validated against
[-LogPath <String>]
The path of the validation log.