ATA capacity planning
Applies to: Advanced Threat Analytics version 1.9
This article helps you determine how many ATA servers are needed to monitor your network. It helps you estimate how many ATA Gateways and/or ATA Lightweight Gateways you need and the server capacity for your ATA Center and ATA Gateways.
Note
The ATA Center can be deployed on any IaaS vendor as long as the performance requirements described in this article are met.
Using the sizing tool
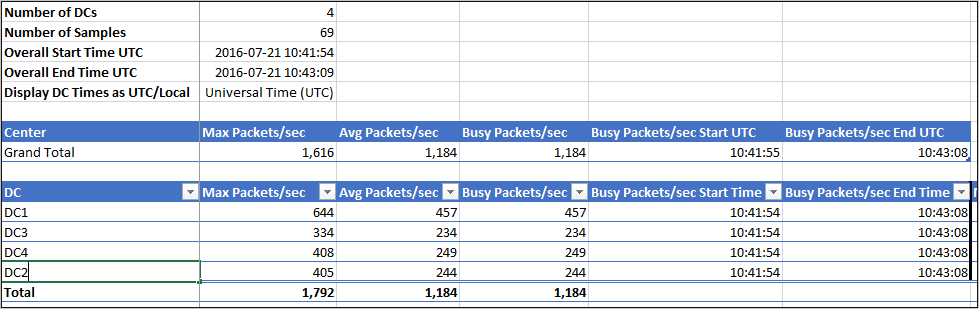
The recommended and simplest way to determine capacity for your ATA deployment is to use the ATA Sizing Tool. Run the ATA Sizing Tool and from the Excel file results, use the following fields to determine the ATA capacity you need:
ATA Center CPU and Memory: Match the Busy Packets/sec field in the ATA Center table results file to the PACKETS PER SECOND field in the ATA Center table.
ATA Center Storage: Match the Avg Packets/sec field in the ATA Center table results file to the PACKETS PER SECOND field in the ATA Center table.
ATA Gateway: Match the Busy Packets/sec field in the ATA Gateway table in the results file to the PACKETS PER SECOND field in the ATA Gateway table or the ATA Lightweight Gateway table, depending on the gateway type you choose.
Note
Because different environments vary and have multiple special and unexpected network traffic characteristics, after you initially deploy ATA and run the sizing tool, you may need to adjust and fine tune your deployment for capacity.
If you can't use the ATA Sizing Tool, manually gather the packet/sec counter information with a low collection interval (approximately 5 seconds) from all your Domain Controllers for 24 hours. Then, for each Domain Controller, calculate the daily average and the busiest period (15 minutes) average. The following sections provide instructions about how to collect the packets/sec counter from one Domain Controller.
Note
Because different environments vary and have multiple special and unexpected network traffic characteristics, after you initially deploy ATA and run the sizing tool, you may need to adjust and fine tune your deployment for capacity.
ATA Center Sizing
The ATA Center requires a recommended minimum of 30 days of data for user behavioral analytics.
| Packets per second from all DCs | CPU (cores*) | Memory (GB) | Database storage per day (GB) | Database storage per month (GB) | IOPS** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000 | 2 | 32 | 0.3 | 9 | 30 (100) |
| 40,000 | 4 | 48 | 12 | 360 | 500 (750) |
| 200,000 | 8 | 64 | 60 | 1,800 | 1,000 (1,500) |
| 400,000 | 12 | 96 | 120 | 3,600 | 2,000 (2,500) |
| 750,000 | 24 | 112 | 225 | 6,750 | 2,500 (3,000) |
| 1,000,000 | 40 | 128 | 300 | 9,000 | 4,000 (5,000) |
*This includes physical cores, not hyper-threaded cores.
**Average numbers (Peak numbers)
Note
- The ATA Center can handle an aggregated maximum of 1M packets per second from all monitored domain controllers. In some environments, the same ATA Center can handle overall traffic that is higher than 1M and some environments may exceed ATA capacity. Contact us at azureatpfeedback@microsoft.com for assistance in planning and estimating large environments.
- If your free space reaches a minimum of either 20% or 200 GB, the oldest collection of data is deleted. If it's not possible to successfully reduce the data collection to this level, an alert will be logged. ATA will continue functioning until the threshold of 5% or 50 GB free is reached. At this point, ATA will stop populating the database and an additional alert will be issued.
- You can deploy the ATA Center on any IaaS vendor if the performance requirements that are described in this article are met.
- The storage latency for read and write activities should be below 10 ms.
- The ratio between read and write activities is approximately 1:3 below 100,000 packets-per-second and 1:6 above 100,000 packets-per-second.
- When running the Center as a virtual machine (VM) the Center requires all memory be allocated to the VM, all the time. For more information on running ATA Center as a virtual machine, see ATA Center requirements.
- For optimal performance, set the Power Option of the ATA Center to High Performance.
- When working on a physical server, the ATA database needs you to disable Non-uniform memory access (NUMA) in the BIOS. Your system may refer to NUMA as Node Interleaving, in which case you have to enable Node Interleaving to disable NUMA. For more information, see your BIOS documentation. This isn't relevant when the ATA Center is running on a virtual server.
Choosing the right gateway type for your deployment
In an ATA deployment any combination of the ATA Gateway types is supported:
- Only ATA Gateways
- Only ATA Lightweight Gateways
- A combination of both
When deciding the Gateway deployment type, consider the following benefits:
| Gateway type | Benefits | Cost | Deployment topology | Domain controller use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATA Gateway | The Out of band deployment makes it harder for attackers to discover ATA is present | Higher | Installed alongside the domain controller (out of band) | Supports up to 50,000 packets per second |
| ATA Lightweight Gateway | Doesn't require a dedicated server and port-mirroring configuration | Lower | Installed on the domain controller | Supports up to 10,000 packets per second |
The following are examples of scenarios in which domain controllers should be covered by the ATA Lightweight Gateway:
Branch sites
Virtual domain controllers deployed in the cloud (IaaS)
The following are examples of scenarios in which domain controllers should be covered by the ATA Gateway:
- Headquarter data centers (having domain controllers with more than 10,000 packets per seconds)
ATA Lightweight Gateway Sizing
An ATA Lightweight Gateway can support the monitoring of one domain controller based on the amount of network traffic the domain controller generates.
| Packets per second* | CPU (cores**) | Memory (GB)*** |
|---|---|---|
| 1,000 | 2 | 6 |
| 5,000 | 6 | 16 |
| 10,000 | 10 | 24 |
*Total number of packets-per-second on the domain controller being monitored by the specific ATA Lightweight Gateway.
**Total number of non-hyper threaded cores that this domain controller has installed.
While hyper threading is acceptable for the ATA Lightweight Gateway, when planning for capacity, you should count actual cores and not hyper threaded cores.
***Total amount of memory that this domain controller has installed.
Note
- If the domain controller doesn't have the resources required by the ATA Lightweight Gateway, domain controller performance isn't affected, but the ATA Lightweight Gateway might not operate as expected.
- When running the Gateway as a virtual machine (VM) the Gateway requires all memory be allocated to the VM, all the time. For more information on running ATA Gateway as a virtual machine, see Dynamic memory requirements).
- For optimal performance, set the Power Option of the ATA Lightweight Gateway to High Performance.
- A minimum of 5 GB of space is required and 10 GB is recommended, including space needed for the ATA binaries, ATA logs, and performance logs.
ATA Gateway Sizing
Consider the following issues when deciding how many ATA Gateways to deploy.
- Active Directory forests and domains
ATA can monitor traffic from multiple domains from a single Active Directory forest. Monitoring multiple Active Directory forests requires separate ATA deployments. Don't configure a single ATA deployment to monitor network traffic of domain controllers from different forests. - Port Mirroring
Port mirroring considerations might require you to deploy multiple ATA Gateways per data Gateway or branch site. - Capacity
An ATA Gateway can support monitoring multiple domain controllers, depending on the amount of network traffic of the domain controllers being monitored.
| Packets per second* | CPU (cores**) | Memory (GB) |
|---|---|---|
| 1,000 | 1 | 6 |
| 5,000 | 2 | 10 |
| 10,000 | 3 | 12 |
| 20,000 | 6 | 24 |
| 50,000 | 16 | 48 |
*Total average number of packets-per-second from all domain controllers being monitored by the specific ATA Gateway during their busiest hour of the day.
*The total amount of domain controller port-mirrored traffic can't exceed the capacity of the capture NIC on the ATA Gateway.
**Hyper-threading must be disabled.
Note
- When running the Gateway as a virtual machine (VM) the Gateway requires all memory be allocated to the VM, all the time. For more information on running ATA Gateway as a virtual machine, see Dynamic memory requirements.
- For optimal performance, set the Power Option of the ATA Gateway to High Performance.
- A minimum of 5 GB of space is required and 10 GB is recommended, including space needed for the ATA binaries, ATA logs, and performance logs.
See Also
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for