Create an application gateway that hosts multiple web sites using the Azure CLI
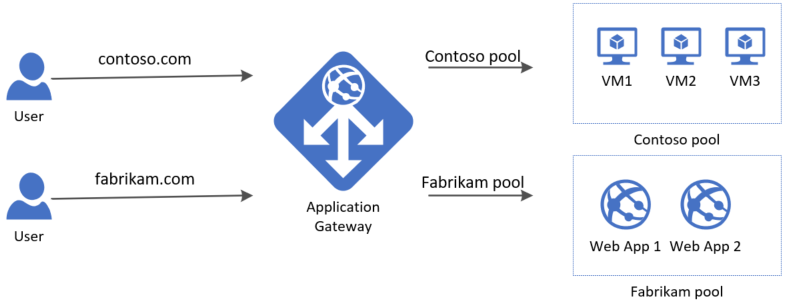
You can use the Azure CLI to configure the hosting of multiple web sites when you create an application gateway. In this article, you define backend address pools using virtual machines scale sets. You then configure listeners and rules based on domains that you own to make sure web traffic arrives at the appropriate servers in the pools. This article assumes that you own multiple domains and uses examples of www.contoso.com and www.fabrikam.com.
In this article, you learn how to:
- Set up the network
- Create an application gateway
- Create backend listeners
- Create routing rules
- Create Virtual Machine Scale Sets with the backend pools
- Create a CNAME record in your domain
If you prefer, you can complete this procedure using Azure PowerShell.
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create an Azure free account before you begin.
Prerequisites
Use the Bash environment in Azure Cloud Shell. For more information, see Quickstart for Bash in Azure Cloud Shell.
If you prefer to run CLI reference commands locally, install the Azure CLI. If you're running on Windows or macOS, consider running Azure CLI in a Docker container. For more information, see How to run the Azure CLI in a Docker container.
If you're using a local installation, sign in to the Azure CLI by using the az login command. To finish the authentication process, follow the steps displayed in your terminal. For other sign-in options, see Sign in with the Azure CLI.
When you're prompted, install the Azure CLI extension on first use. For more information about extensions, see Use extensions with the Azure CLI.
Run az version to find the version and dependent libraries that are installed. To upgrade to the latest version, run az upgrade.
- This tutorial requires version 2.0.4 or later of the Azure CLI. If using Azure Cloud Shell, the latest version is already installed.
Create a resource group
A resource group is a logical container into which Azure resources are deployed and managed. Create a resource group using az group create.
The following example creates a resource group named myResourceGroupAG in the eastus location.
az group create --name myResourceGroupAG --location eastus
Create network resources
Create the virtual network and the subnet named myAGSubnet using az network vnet create. You can then add the subnet that's needed by the backend servers using az network vnet subnet create. Create the public IP address named myAGPublicIPAddress using az network public-ip create.
az network vnet create \
--name myVNet \
--resource-group myResourceGroupAG \
--location eastus \
--address-prefix 10.0.0.0/16 \
--subnet-name myAGSubnet \
--subnet-prefix 10.0.1.0/24
az network vnet subnet create \
--name myBackendSubnet \
--resource-group myResourceGroupAG \
--vnet-name myVNet \
--address-prefix 10.0.2.0/24
az network public-ip create \
--resource-group myResourceGroupAG \
--name myAGPublicIPAddress \
--allocation-method Static \
--sku Standard
Create the application gateway
You can use az network application-gateway create to create the application gateway. When you create an application gateway using the Azure CLI, you specify configuration information, such as capacity, sku, and HTTP settings. The application gateway is assigned to myAGSubnet and myAGPublicIPAddress that you previously created.
az network application-gateway create \
--name myAppGateway \
--location eastus \
--resource-group myResourceGroupAG \
--vnet-name myVNet \
--subnet myAGsubnet \
--capacity 2 \
--sku Standard_v2 \
--http-settings-cookie-based-affinity Disabled \
--frontend-port 80 \
--http-settings-port 80 \
--http-settings-protocol Http \
--public-ip-address myAGPublicIPAddress \
--priority 10
It may take several minutes for the application gateway to be created. After the application gateway is created, you can see these new features of it:
- appGatewayBackendPool - An application gateway must have at least one backend address pool.
- appGatewayBackendHttpSettings - Specifies that port 80 and an HTTP protocol is used for communication.
- appGatewayHttpListener - The default listener associated with appGatewayBackendPool.
- appGatewayFrontendIP - Assigns myAGPublicIPAddress to appGatewayHttpListener.
- rule1 - The default routing rule that is associated with appGatewayHttpListener.
Add the backend pools
Add the backend pools that are needed to contain the backend servers using az network application-gateway address-pool create
az network application-gateway address-pool create \
--gateway-name myAppGateway \
--resource-group myResourceGroupAG \
--name contosoPool
az network application-gateway address-pool create \
--gateway-name myAppGateway \
--resource-group myResourceGroupAG \
--name fabrikamPool
Add listeners
Add listeners that are needed to route traffic using az network application-gateway http-listener create.
Note
With Application Gateway or WAF v2 SKU, you can also configure up to 5 host names per listener and you can use wildcard characters in the host name. See wildcard host names in listener for more information.
To use multiple host names and wildcard characters in a listener using Azure CLI, you must use --host-names instead of --host-name. With host-names, you can mention up to five host names as space-separated values. For example, --host-names "*.contoso.com *.fabrikam.com"
az network application-gateway http-listener create \
--name contosoListener \
--frontend-ip appGatewayFrontendIP \
--frontend-port appGatewayFrontendPort \
--resource-group myResourceGroupAG \
--gateway-name myAppGateway \
--host-name www.contoso.com
az network application-gateway http-listener create \
--name fabrikamListener \
--frontend-ip appGatewayFrontendIP \
--frontend-port appGatewayFrontendPort \
--resource-group myResourceGroupAG \
--gateway-name myAppGateway \
--host-name www.fabrikam.com
Add routing rules
Rules are processed in the order they're listed if rule priority field is not used. Traffic is directed using the first rule that matches regardless of specificity. For example, if you have a rule using a basic listener and a rule using a multi-site listener both on the same port, the rule with the multi-site listener must be listed before the rule with the basic listener in order for the multi-site rule to function as expected.
In this example, you create two new rules and delete the default rule created when you deployed the application gateway. You can add the rule using az network application-gateway rule create.
az network application-gateway rule create \
--gateway-name myAppGateway \
--name contosoRule \
--resource-group myResourceGroupAG \
--http-listener contosoListener \
--rule-type Basic \
--address-pool contosoPool \
--priority 200
az network application-gateway rule create \
--gateway-name myAppGateway \
--name fabrikamRule \
--resource-group myResourceGroupAG \
--http-listener fabrikamListener \
--rule-type Basic \
--address-pool fabrikamPool \
--priority 100
az network application-gateway rule delete \
--gateway-name myAppGateway \
--name rule1 \
--resource-group myResourceGroupAG
Add priority to routing rules
In order to ensure that more specific rules are processed first, use the rule priority field to ensure they have higher priority. Rule priority field must be set for all the existing request routing rules and any new rule that is created later must also have a rule priority value.
az network application-gateway rule create \
--gateway-name myAppGateway \
--name contosoRule \
--resource-group myResourceGroupAG \
--http-listener contosoListener \
--rule-type Basic \
--priority 200 \
--address-pool contosoPool
az network application-gateway rule create \
--gateway-name myAppGateway \
--name fabrikamRule \
--resource-group myResourceGroupAG \
--http-listener fabrikamListener \
--rule-type Basic \
--priority 100 \
--address-pool fabrikamPool
Create Virtual Machine Scale Sets
In this example, you create three Virtual Machine Scale Sets that support the three backend pools in the application gateway. The scale sets that you create are named myvmss1, myvmss2, and myvmss3. Each scale set contains two virtual machine instances on which you install IIS.
for i in `seq 1 2`; do
if [ $i -eq 1 ]
then
poolName="contosoPool"
fi
if [ $i -eq 2 ]
then
poolName="fabrikamPool"
fi
az vmss create \
--name myvmss$i \
--resource-group myResourceGroupAG \
--image Ubuntu2204 \
--admin-username azureuser \
--admin-password Azure123456! \
--instance-count 2 \
--vnet-name myVNet \
--subnet myBackendSubnet \
--vm-sku Standard_D1_v2 \
--upgrade-policy-mode Automatic \
--app-gateway myAppGateway \
--backend-pool-name $poolName
done
Install NGINX
for i in `seq 1 2`; do
az vmss extension set \
--publisher Microsoft.Azure.Extensions \
--version 2.0 \
--name CustomScript \
--resource-group myResourceGroupAG \
--vmss-name myvmss$i \
--settings '{ "fileUris": ["https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure/azure-docs-powershell-samples/master/application-gateway/iis/install_nginx.sh"],
"commandToExecute": "./install_nginx.sh" }'
done
Create a CNAME record in your domain
After the application gateway is created with its public IP address, you can get the DNS address and use it to create a CNAME record in your domain. You can use az network public-ip show to get the DNS address of the application gateway. Copy the fqdn value of the DNSSettings and use it as the value of the CNAME record that you create.
az network public-ip show \
--resource-group myResourceGroupAG \
--name myAGPublicIPAddress \
--query [dnsSettings.fqdn] \
--output tsv
The use of A-records isn't recommended because the VIP may change when the application gateway restarts.
Test the application gateway
Enter your domain name into the address bar of your browser. Such as, http://www.contoso.com.
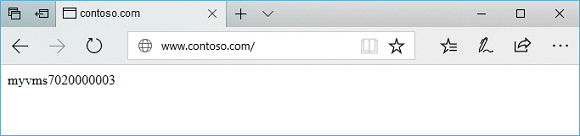
Change the address to your other domain and you should see something like the following example:

Clean up resources
When no longer needed, remove the resource group, application gateway, and all related resources.
az group delete --name myResourceGroupAG
Next steps
Create an application gateway with URL path-based routing rules
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for
