This guide shows how Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps and Microsoft Sentinel can help secure and protect Amazon Web Services (AWS) account access and environments.
AWS organizations that use Microsoft Entra ID for Microsoft 365 or hybrid cloud identity and access protection can quickly and easily deploy Microsoft Entra ID for AWS accounts, often without additional cost.
Architecture
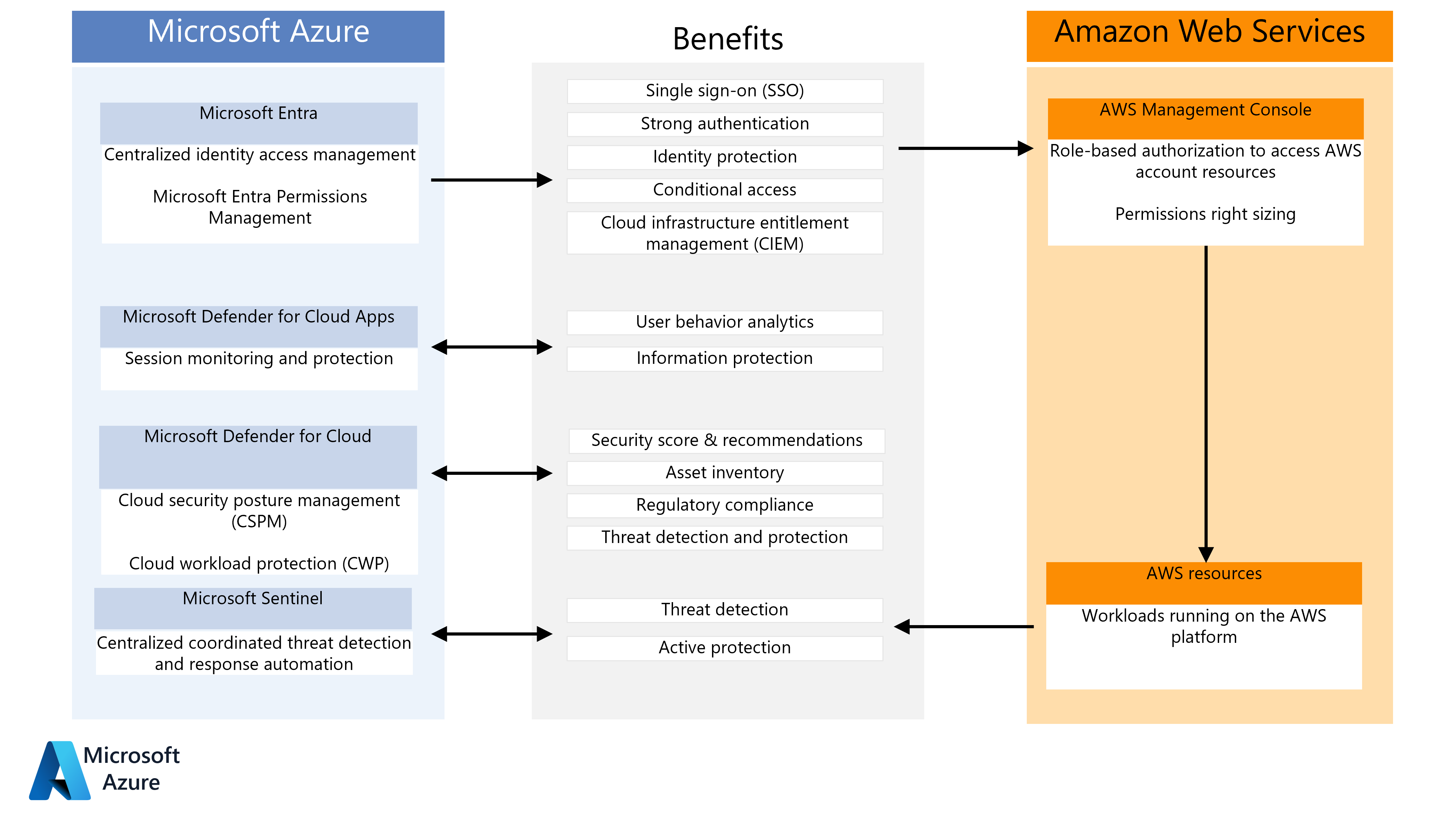
This diagram summarizes how AWS installations can benefit from key Microsoft security components:
Download a PowerPoint file of this architecture.
Workflow
Microsoft Entra ID provides centralized single sign-on (SSO) and strong authentication through multifactor authentication and the conditional access feature. Microsoft Entra ID supports AWS role-based identities and authorization for access to AWS resources. For more information and detailed instructions, see Microsoft Entra identity and access management for AWS. Microsoft Entra Permissions Management is a cloud infrastructure entitlement management (CIEM) product that provides comprehensive visibility and control over permissions for any AWS identity or resource. You can use Microsoft Entra Permissions Management to:
- Get a multi-dimensional view of your risk by assessing identities, permissions, and resources.
- Automate the enforcement of the least privilege policy in your entire multicloud infrastructure.
- Use anomaly and outlier detection to prevent data breaches that are caused by misuse and malicious exploitation of permissions.
For more information and detailed onboarding instructions, see Onboard an Amazon Web Services (AWS) account.
Defender for Cloud Apps:
- Integrates with the Microsoft Entra Conditional Access feature to enforce additional restrictions.
- Helps monitor and protect sessions after sign-in.
- Uses user behavior analytics (UBA) and other AWS APIs to monitor sessions and users and to support information protection.
Microsoft Defender for Cloud displays AWS security recommendations in the Defender for Cloud portal together with Azure recommendations. Defender for Cloud offers more than 160 out-of-the-box recommendations for infrastructure as a service (IaaS) and platform as a service (PaaS) services. It also provides support for regulatory standards, including Center for Internet Security (CIS) and payment card industry (PCI) standards, and for the AWS Foundational Security Best Practices standard. Defender for Cloud also provides cloud workload protection (CWP) for Amazon EKS clusters, AWS EC2 instances, and SQL servers that run on AWS EC2.
Microsoft Sentinel integrates with Defender for Cloud Apps and AWS to detect and automatically respond to threats. Microsoft Sentinel monitors the AWS environment for misconfiguration, potential malware, and advanced threats to AWS identities, devices, applications, and data.
Components
- Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps
- Microsoft Defender for Cloud
- Microsoft Sentinel
- Microsoft Entra ID
Defender for Cloud Apps for visibility and control
When several users or roles make administrative changes, a consequence can be configuration drift away from intended security architecture and standards. Security standards can also change over time. Security personnel must constantly and consistently detect new risks, evaluate mitigation options, and update security architecture to prevent potential breaches. Security management across multiple public cloud and private infrastructure environments can become burdensome.
Defender for Cloud Apps is a cloud access security broker (CASB) platform with cloud security posture management (CSPM) capabilities. Defender for Cloud Apps can connect to multiple cloud services and applications to collect security logs, monitor user behavior, and impose restrictions that the platforms themselves might not offer.
Defender for Cloud Apps provides several capabilities that can integrate with AWS for immediate benefits:
- The Defender for Cloud Apps app connector uses several AWS APIs, including UBA, to search for configuration issues and threats on the AWS platform.
- AWS Access Controls can enforce sign-in restrictions that are based on application, device, IP address, location, registered ISP, and specific user attributes.
- Session Controls for AWS block potential malware uploads or downloads based on Microsoft Defender Threat Intelligence or real-time content inspection.
- Session controls can also use real-time content inspection and sensitive data detection to impose data loss prevention (DLP) rules that prevent cut, copy, paste, or print operations.
Defender for Cloud Apps is available standalone, or as part of Microsoft Enterprise Mobility + Security E5, which includes Microsoft Entra ID P2. For pricing and licensing information, see Enterprise Mobility + Security pricing options.
Defender for Cloud for CSPM and CWP platforms (CWPP)
With cloud workloads commonly spanning multiple cloud platforms, cloud security services must do the same. Defender for Cloud helps protect workloads in Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Defender for Cloud provides an agentless connection to your AWS account. Defender for Cloud also offers plans to secure your AWS resources:
- The Defender for Cloud overview page displays CSPM metrics, alerts, and insights. Defender for Cloud assesses your AWS resources according to AWS-specific security recommendations and incorporates your security posture into your secure score. The asset inventory provides a single place to view all your protected AWS resources. The regulatory compliance dashboard reflects the status of your compliance with built-in standards that are specific to AWS. Examples include AWS CIS standards, PCI data security standards (PCI-DSS), and the AWS Foundational Security Best Practices standard.
- Microsoft Defender for Servers brings threat detection and advanced defenses to supported Windows and Linux EC2 instances.
- Microsoft Defender for Containers brings threat detection and advanced defenses to supported Amazon EKS clusters.
- Microsoft Defender for SQL brings threat detection and advanced defenses to your SQL servers that run on AWS EC2 and AWS RDS Custom for SQL Server.
Microsoft Sentinel for advanced threat detection
Threats can come from a wide range of devices, applications, locations, and user types. DLP requires inspecting content during upload or download, because post-mortem review might be too late. AWS doesn't have native capabilities for device and application management, risk-based conditional access, session-based controls, or inline UBA.
It's critical that security solutions reduce complexity and deliver comprehensive protection regardless of whether resources are in multicloud, on-premises, or hybrid environments. Defender for Cloud provides CSPM and CWP. Defender for Cloud identifies configuration weak spots across AWS to help strengthen your overall security posture. It also helps provide threat protection for Amazon EKS Linux clusters, AWS EC2 instances, and SQL servers in AWS EC2.
Microsoft Sentinel is a security information and event management (SIEM) and security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) solution that centralizes and coordinates threat detection and response automation for modern security operations. Microsoft Sentinel can monitor AWS accounts to compare events across multiple firewalls, network devices, and servers. Microsoft Sentinel combines monitoring data with threat intelligence, analytics rules, and machine learning to discover and respond to advanced attack techniques.
You can connect AWS and Defender for Cloud Apps with Microsoft Sentinel. Then you can see Defender for Cloud Apps alerts and run additional threat checks that use multiple Defender Threat Intelligence feeds. Microsoft Sentinel can initiate a coordinated response that's outside Defender for Cloud Apps. Microsoft Sentinel can also integrate with IT service management (ITSM) solutions and retain data on a long-term basis for compliance purposes.
Scenario details
Microsoft offers several security solutions that can help secure and protect AWS accounts and environments.
Other Microsoft security components can integrate with Microsoft Entra ID to provide additional security for AWS accounts:
- Defender for Cloud Apps backs up Microsoft Entra ID with session protection and user-behavior monitoring.
- Defender for Cloud provides threat protection to AWS workloads. It also helps proactively strengthen security for AWS environments and uses an agentless approach to connect to those environments.
- Microsoft Sentinel integrates with Microsoft Entra ID and Defender for Cloud Apps to detect and automatically respond to threats against AWS environments.
These Microsoft security solutions are extensible and offer multiple levels of protection. You can implement one or more of these solutions along with other types of protection for a full-security architecture that helps protect current and future AWS deployments.
Potential use cases
This article provides AWS identity architects, administrators, and security analysts with immediate insights and detailed guidance for deploying several Microsoft security solutions.
Recommendations
Keep the following points in mind when you develop a security solution.
Security recommendations
The following principles and guidelines are important for any cloud security solution:
- Ensure that the organization can monitor, detect, and automatically protect user and programmatic access into cloud environments.
- Continually review current accounts to ensure identity and permission governance and control.
- Follow least privilege and zero trust principles. Make sure that users can access only the specific resources that they require, from trusted devices and known locations. Reduce the permissions of every administrator and developer to provide only the rights that they need for the role that they perform. Review regularly.
- Continuously monitor platform configuration changes, especially if they provide opportunities for privilege escalation or attack persistence.
- Prevent unauthorized data exfiltration by actively inspecting and controlling content.
- Take advantage of solutions that you might already own, like Microsoft Entra ID P2, that can increase security without additional expense.
Basic AWS account security
To ensure basic security hygiene for AWS accounts and resources:
- Review the AWS security guidance at Best practices for securing AWS accounts and resources.
- Reduce the risk of uploading and downloading malware and other malicious content by actively inspecting all data transfers through the AWS Management Console. Content that you upload or download directly to resources within the AWS platform, such as web servers or databases, might need additional protection.
- Consider protecting access to other resources, including:
- Resources created within the AWS account.
- Specific workload platforms, like Windows Server, Linux Server, or containers.
- Devices that administrators and developers use to access the AWS Management Console.
Deploy this scenario
Take the steps in the following sections to implement a security solution.
Plan and prepare
To prepare for deployment of Azure security solutions, review and record current AWS and Microsoft Entra account information. If you've deployed more than one AWS account, repeat these steps for each account.
In the AWS Billing Management Console, record the following current AWS account information:
- AWS Account ID, a unique identifier
- Account name, or root user
- Payment method, whether assigned to a credit card or a company billing agreement
- Alternate contacts who have access to AWS account information
- Security questions, securely updated and recorded for emergency access
- AWS regions that are enabled or disabled to comply with data security policy
In the Azure portal, review the Microsoft Entra tenant:
- Assess Tenant information to see whether the tenant has a Microsoft Entra ID P1 or P2 license. A P2 license provides advanced Microsoft Entra identity management features.
- Assess Enterprise applications to see whether any existing applications use the AWS application type, as shown by
http://aws.amazon.com/in the Homepage URL column.
Deploy Defender for Cloud Apps
After you deploy the central management and strong authentication that modern identity and access management require, you can implement Defender for Cloud Apps to:
- Collect security data and carry out threat detections for AWS accounts.
- Implement advanced controls to mitigate risk and prevent data loss.
To deploy Defender for Cloud Apps:
- Add a Defender for Cloud Apps app connector for AWS.
- Configure Defender for Cloud Apps monitoring policies for AWS activities.
- Create an enterprise application for SSO to AWS.
- Create a conditional access app control application in Defender for Cloud Apps.
- Configure Microsoft Entra session policies for AWS activities.
- Test Defender for Cloud Apps policies for AWS.
Add an AWS app connector
In the Defender for Cloud Apps portal, expand Investigate and then select Connected apps.
On the App connectors page, select the Plus Sign (+) and then select Amazon Web Services from the list.
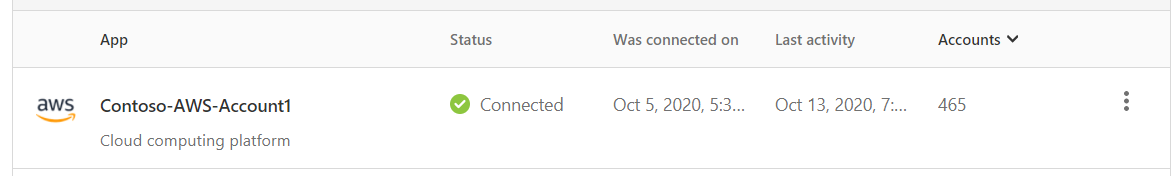
Use a unique name for the connector. In the name, include an identifier for the company and specific AWS account, for example Contoso-AWS-Account1.
Follow the instructions at Connect AWS to Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps to create an appropriate AWS identity and access management (IAM) user.
- Define a policy for restricted permissions.
- Create a service account to use those permissions on behalf of the Defender for Cloud Apps service.
- Provide the credentials to the app connector.
The time it takes to establish the initial connection depends on the AWS account log sizes. When the connection is complete, you see a connection confirmation:
Configure Defender for Cloud Apps monitoring policies for AWS activities
After you turn on the app connector, Defender for Cloud Apps shows new templates and options in the policy configuration builder. You can create policies directly from the templates and modify them for your needs. You can also develop a policy without using the templates.
To implement policies by using the templates:
In the Defender for Cloud Apps left navigation window, expand Control and then select Templates.
Search for aws and review the available policy templates for AWS.
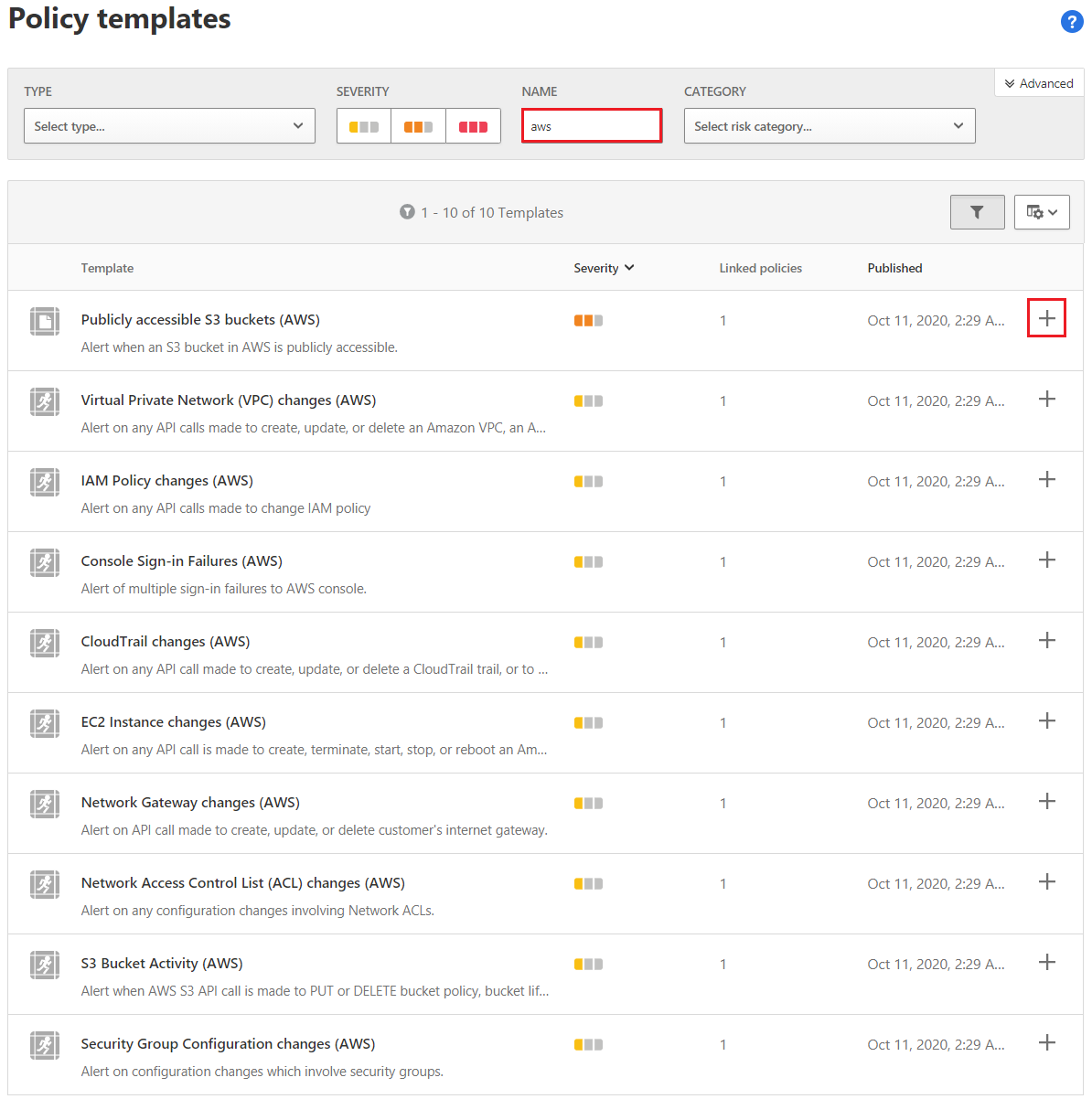
To use a template, select the Plus Sign (+) to the right of the template item.
Each policy type has different options. Review the configuration settings and save the policy. Repeat this step for each template.
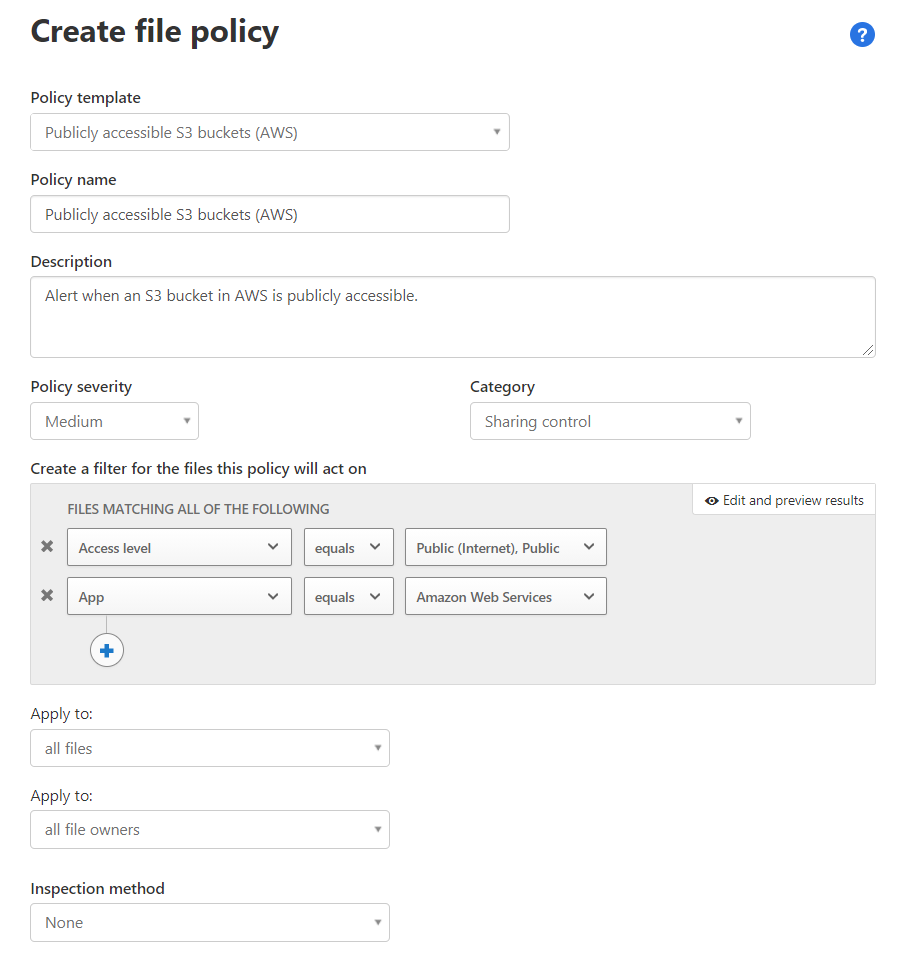
To use file policies, make sure the file monitoring setting is turned on in Defender for Cloud Apps settings:
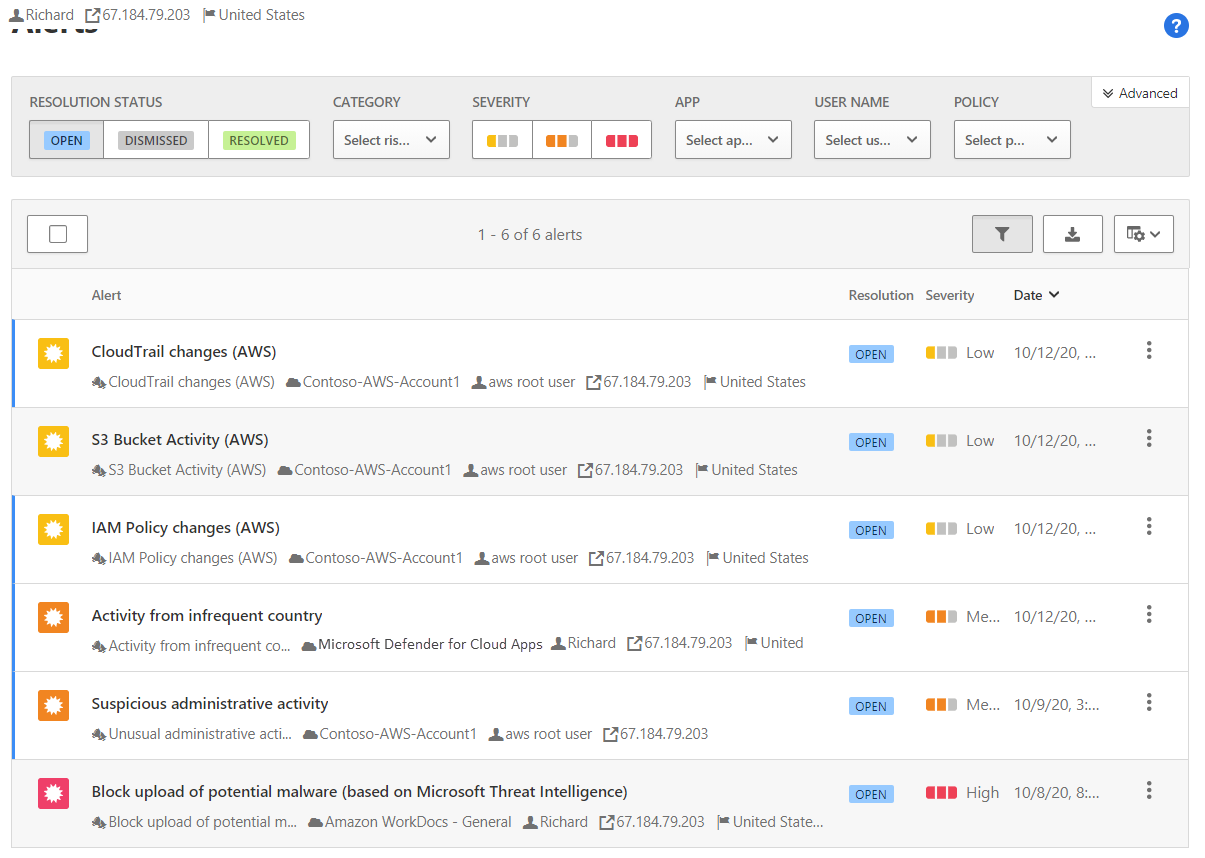
As Defender for Cloud Apps detects alerts, it displays them on the Alerts page in the Defender for Cloud Apps portal:
Create an enterprise application for SSO to AWS
Follow the instructions at Tutorial: Microsoft Entra single sign-on (SSO) integration with AWS single sign-on to create an enterprise application for SSO to AWS. Here's a summary of the procedure:
- Add AWS SSO from the gallery.
- Configure and test Microsoft Entra SSO for AWS SSO:
- Configure Microsoft Entra SSO.
- Configure AWS SSO.
- Create an AWS SSO test user.
- Test SSO.
Create a conditional access app control application in Defender for Cloud Apps
Go to the Defender for Cloud Apps portal, select Investigate, and then select Connected apps.
Select Conditional Access App Control apps, and then select Add.
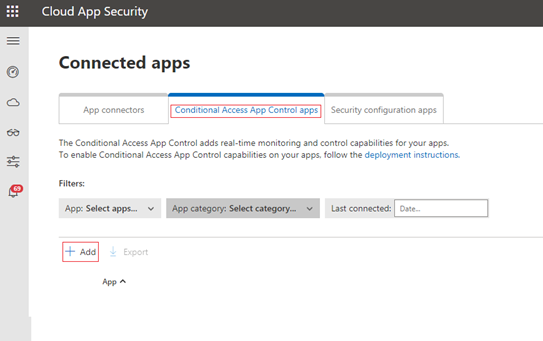
In the Search for an app box, enter Amazon Web Services, and then select the application. Select Start wizard.
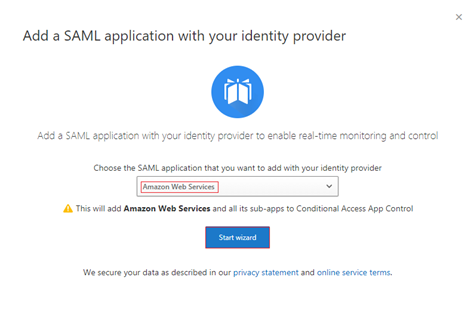
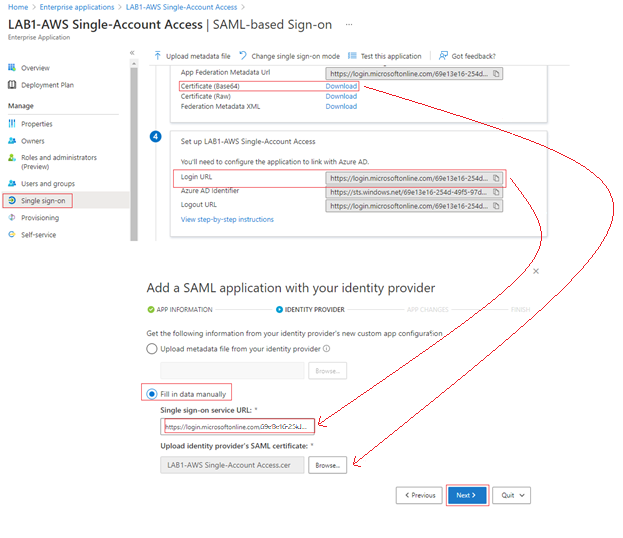
Select Fill in data manually. Enter the Assertion consumer service URL value that's shown in the following screenshot, and then select Next.
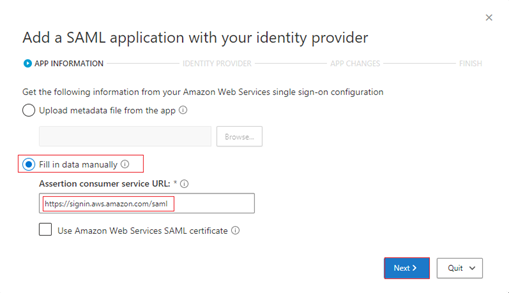
On the next page, ignore the External configuration steps. Select Next.
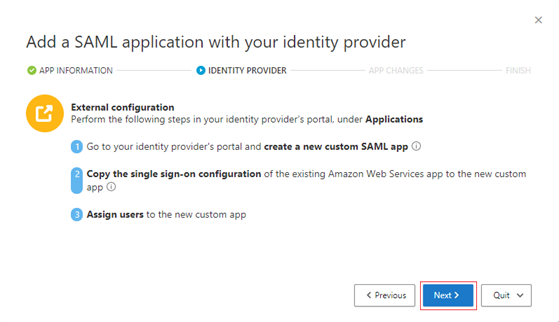
Select Fill in data manually, and then take the following steps to enter the data:
- Under Single sign-on service URL, enter the Login URL value for the enterprise application that you created for AWS.
- Under Upload identity provider's SAML certificate, select Browse.
- Locate the certificate for the enterprise application that you created.
- Download the certificate to your local device, and then upload it to the wizard.
- Select Next.
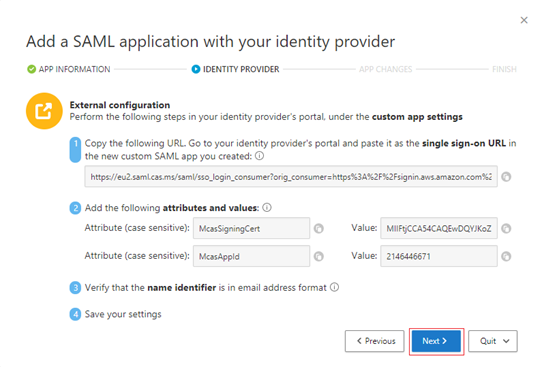
On the next page, ignore the External configuration steps. Select Next.
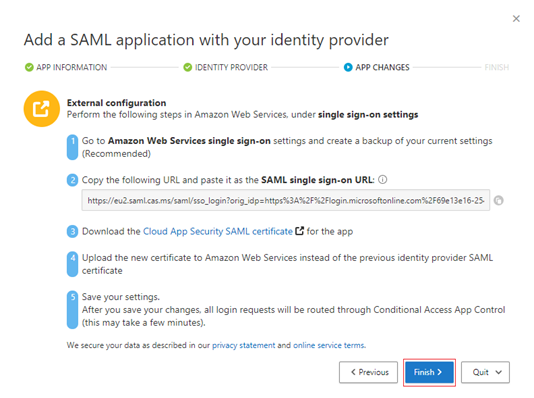
On the next page, ignore the External configuration steps. Select Finish.
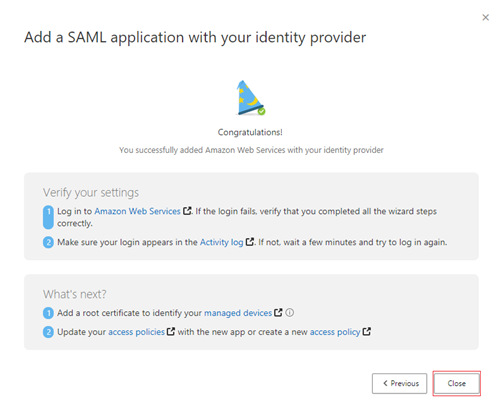
On the next page, ignore the Verify your settings steps. Select Close.
Configure Microsoft Entra session policies for AWS activities
Session policies are a powerful combination of Microsoft Entra Conditional Access policies and the reverse proxy capability of Defender for Cloud Apps. These policies provide real-time suspicious behavior monitoring and control.
In Microsoft Entra ID, create a new conditional access policy with the following settings:
- Under Name, enter AWS Console – Session Controls.
- Under Users and Groups, select the two role groups that you created earlier:
- AWS-Account1-Administrators
- AWS-Account1-Developers
- Under Cloud apps or actions, select the enterprise application that you created earlier, such as Contoso-AWS-Account 1.
- Under Session, select Use Conditional Access App Control.
Under Enable policy, select On.
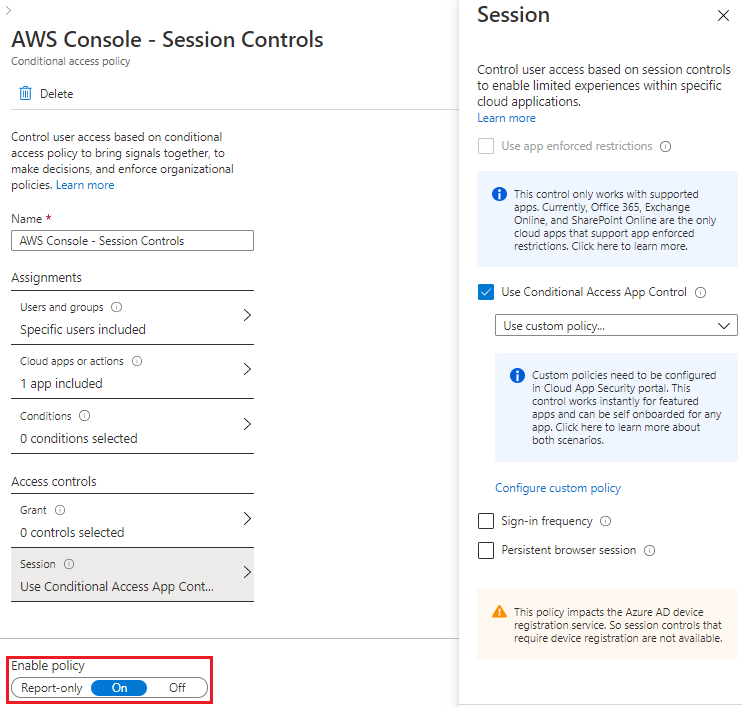
Select Create.
After you create the Microsoft Entra Conditional Access policy, set up a Defender for Cloud Apps session policy to control user behavior during AWS sessions.
In the Defender for Cloud Apps portal, expand Control and then select Policies.
On the Policies page, select Create policy and then select Session policy from the list.
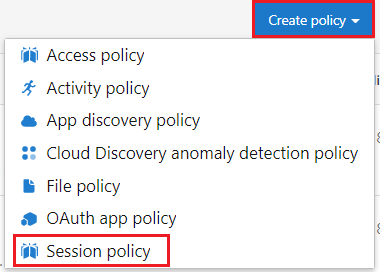
On the Create session policy page, under Policy template, select Block upload of potential malware (based on Microsoft Threat Intelligence).
Under Activities matching all of the following, modify the activity filter to include App, equals, and Amazon Web Services. Remove the default device selection.
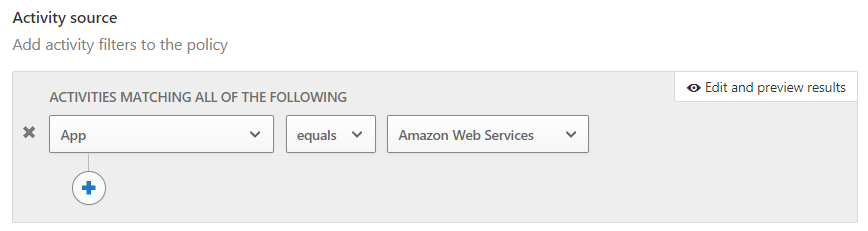
Review the other settings, and then select Create.
Test Defender for Cloud Apps policies for AWS
Test all policies regularly to ensure that they're still effective and relevant. Here are a few recommended tests:
IAM policy changes: This policy is triggered each time that you attempt to modify the settings within AWS IAM. For instance, when you follow the procedure later in this deployment section to create a new IAM policy and account, you see an alert.
Console sign-in failures: Any failed attempts to sign in to one of the test accounts trigger this policy. The alert details show that the attempt came from one of the Azure regional datacenters.
S3 bucket activity policy: When you attempt to create a new AWS S3 storage account and set it to be publicly available, you trigger this policy.
Malware detection policy: If you configure malware detection as a session policy, you can test it by following these steps:
- Download a safe test file from the European Institute for Computer Anti-Virus Research (EICAR).
- Try to upload that file to an AWS S3 storage account.
The policy immediately blocks the upload attempt, and an alert appears in the Defender for Cloud Apps portal.
Deploy Defender for Cloud
You can use a native cloud connector to connect an AWS account to Defender for Cloud. The connector provides an agentless connection to your AWS account. You can use this connection to gather CSPM recommendations. By using Defender for Cloud plans, you can secure your AWS resources with CWP.
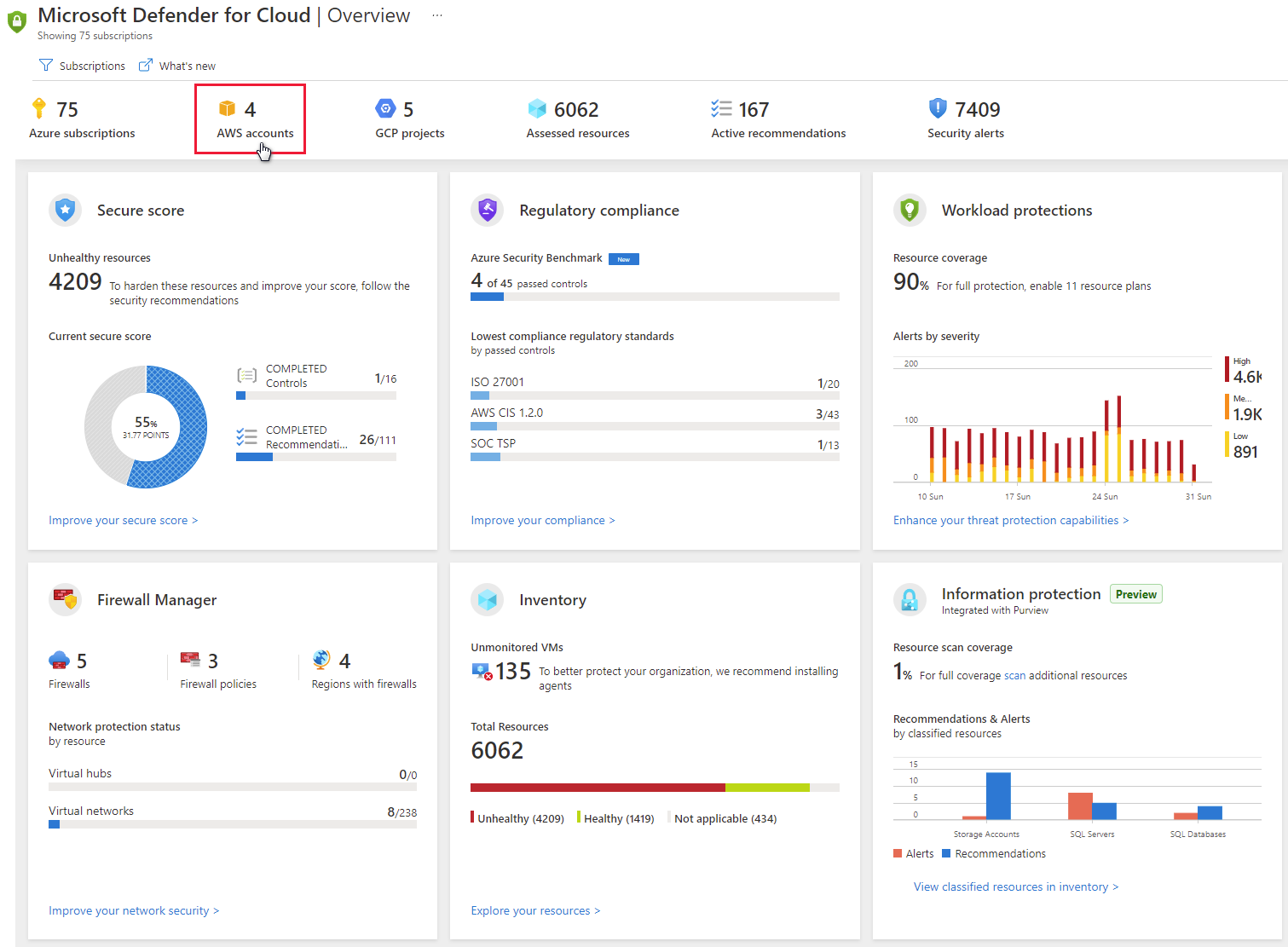
To protect your AWS-based resources, take these steps, which the following sections describe in detail:
- Connect an AWS account.
- Monitor AWS.
Connect your AWS account
To connect your AWS account to Defender for Cloud by using a native connector, follow these steps:
Review the prerequisites for connecting an AWS account. Ensure that you complete them before you proceed.
If you have any classic connectors, remove them by following the steps in Remove classic connectors. Using both the classic and native connectors can produce duplicate recommendations.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Select Microsoft Defender for Cloud, and then select Environment settings.
Select Add environment > Amazon Web Services.

Enter the details of the AWS account, including the storage location of the connector resource. Optionally, select Management account to create a connector to a management account. Connectors are created for each member account that's discovered under the provided management account. Auto-provisioning is turned on for all newly onboarded accounts.
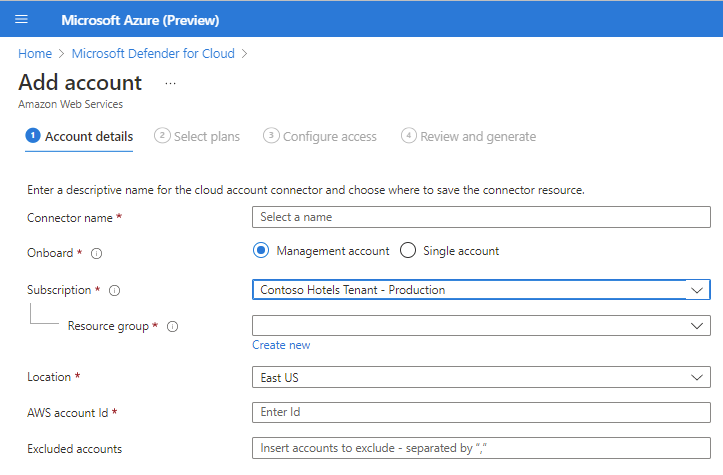
Select Next: Select plans.
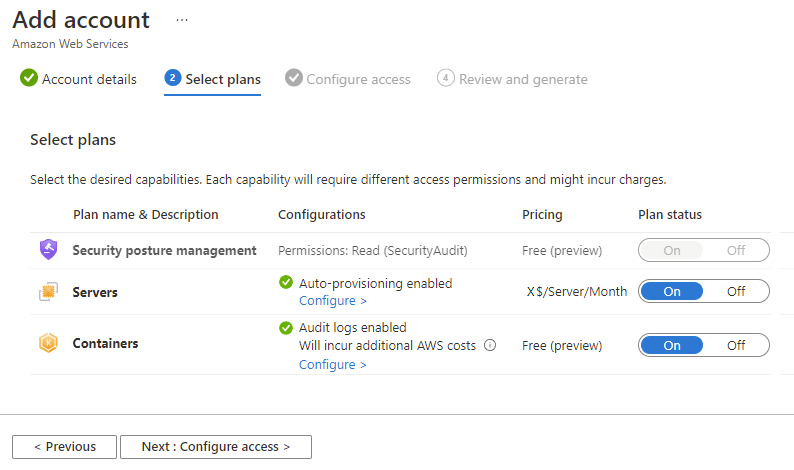
By default, the servers plan is turned on. This setting is necessary to extend Defender for Servers coverage to your AWS EC2. Ensure you've fulfilled the network requirements for Azure Arc. Optionally, to edit the configuration, select Configure.
By default, the containers plan is turned on. This setting is necessary to have Defender for Containers protection for your AWS EKS clusters. Ensure you've fulfilled the network requirements for the Defender for Containers plan. Optionally, to edit the configuration, select Configure. If you disable this configuration, the threat detection feature for the control plane is disabled. To view a list of features, see Defender for Containers feature availability.
By default, the databases plan is turned on. This setting is necessary to extend Defender for SQL coverage to your AWS EC2 and RDS Custom for SQL Server. Optionally, to edit the configuration, select Configure. We recommend that you use the default configuration.
Select Next: Configure access.
Download the CloudFormation template.
Follow the on-screen instructions to use the downloaded CloudFormation template to create the stack in AWS. If you onboard a management account, you need to run the CloudFormation template as Stack and as StackSet. Connectors are created for the member accounts within 24 hours of onboarding.
Select Next: Review and generate.
Select Create.
Defender for Cloud immediately starts scanning your AWS resources. Within a few hours, you see security recommendations. For a list of all the recommendations Defender for Cloud can provide for AWS resources, see Security recommendations for AWS resources - a reference guide.
Monitor your AWS resources
The Defender for Cloud security recommendations page displays your AWS resources. You can use the environments filter to take advantage of the multicloud capabilities of Defender for Cloud, such as viewing the recommendations for Azure, AWS, and GCP resources together.
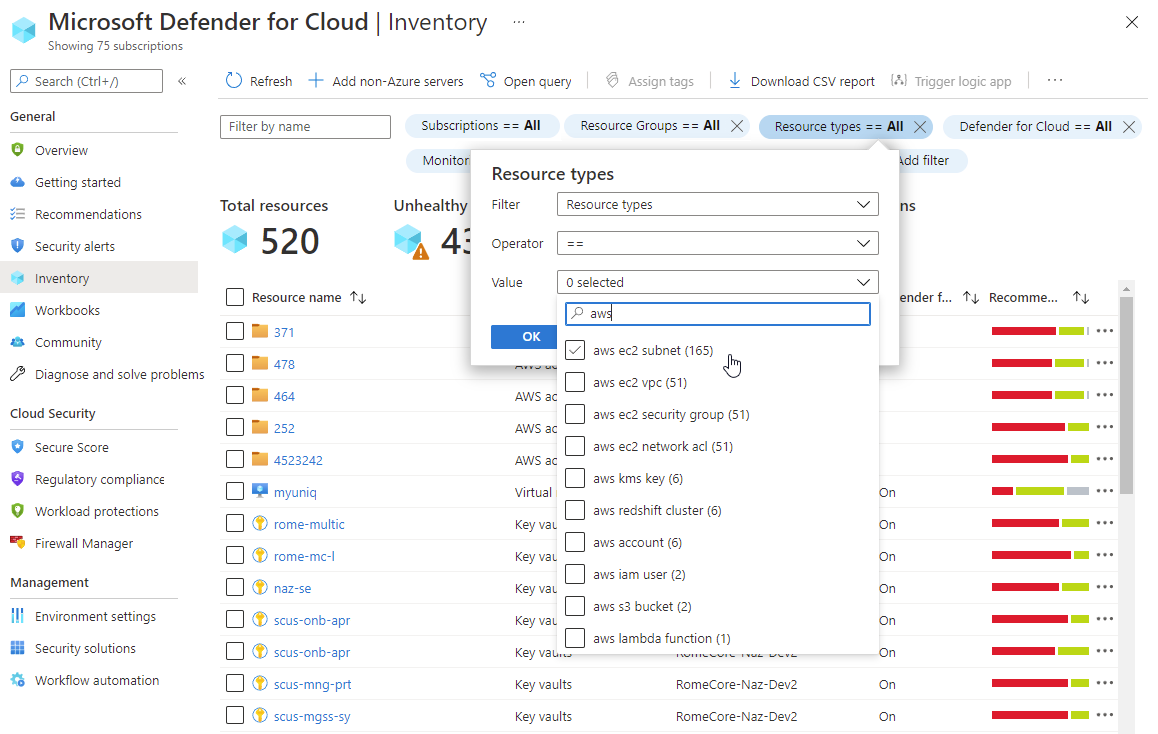
To view all the active recommendations for your resources by resource type, use the Defender for Cloud asset inventory page. Set the filter to display the AWS resource type that you're interested in.
Deploy Microsoft Sentinel
If you connect an AWS account and Defender for Cloud Apps to Microsoft Sentinel, you can use monitoring capabilities that compare events across multiple firewalls, network devices, and servers.
Enable the Microsoft Sentinel AWS connector
After you enable the Microsoft Sentinel connector for AWS, you can monitor AWS incidents and data ingestion.
As with the Defender for Cloud Apps configuration, this connection requires configuring AWS IAM to provide credentials and permissions.
In AWS IAM, follow the steps at Connect Microsoft Sentinel to AWS CloudTrail.
To complete the configuration in the Azure portal, under Microsoft Sentinel > Data connectors, select the Amazon Web Services connector.
Select Open connector page.
Under Configuration, enter the Role ARN value from the AWS IAM configuration in the Role to add field, and select Add.
Select Next steps, and then select the AWS Network Activities and AWS User Activities activities to monitor.
Under Relevant analytic templates, select Create rule next to the AWS analytic templates that you want to turn on.
Set up each rule, and select Create.
The following table shows the rule templates that are available for checking AWS entity behaviors and threat indicators. The rule names describe their purpose, and the potential data sources list the data sources that each rule can use.
| Analytic template name | Data sources |
|---|---|
| Known IRIDIUM IP | DNS, Azure Monitor, Cisco ASA, Palo Alto Networks, Microsoft Entra ID, Azure Activity, AWS |
| Full Admin policy created and then attached to Roles, Users, or Groups | AWS |
| Failed AzureAD logons but success logon to AWS Console | Microsoft Entra ID, AWS |
| Failed AWS Console logons but success logon to AzureAD | Microsoft Entra ID, AWS |
| Multifactor authentication disabled for a user | Microsoft Entra ID, AWS |
| Changes to AWS Security Group ingress and egress settings | AWS |
| Monitor AWS Credential abuse or hijacking | AWS |
| Changes to AWS Elastic Load Balancer security groups | AWS |
| Changes to Amazon VPC settings | AWS |
| New UserAgent observed in last 24 hours | Microsoft 365, Azure Monitor, AWS |
| Login to AWS Management Console without multifactor authentication | AWS |
| Changes to internet facing AWS RDS Database instances | AWS |
| Changes made to AWS CloudTrail logs | AWS |
| Defender Threat Intelligence map IP entity to AWS CloudTrail | Defender Threat Intelligence Platforms, AWS |
Enabled templates have an IN USE indicator on the connector details page.

Monitor AWS incidents
Microsoft Sentinel creates incidents based on the analyses and detections that you turn on. Each incident can include one or more events, which reduces the overall number of investigations that are necessary to detect and respond to potential threats.
Microsoft Sentinel shows incidents that Defender for Cloud Apps generates, if it's connected, and incidents that Microsoft Sentinel creates. The Product names column shows the incident source.
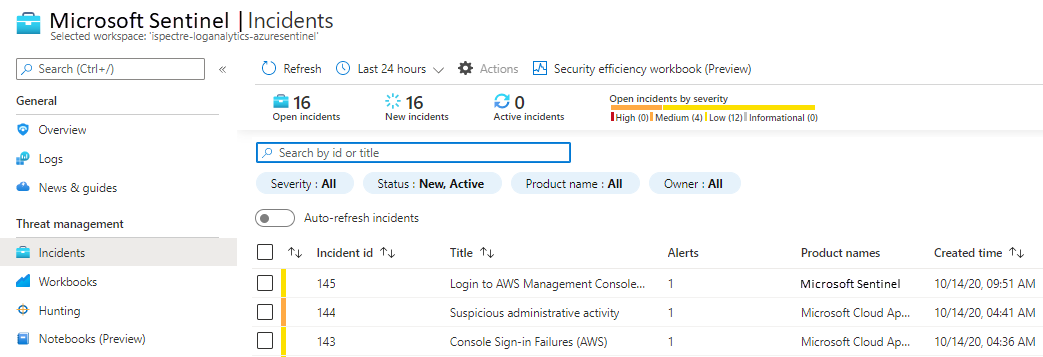
Check data ingestion
Check that data is continuously ingested into Microsoft Sentinel by regularly viewing the connector details. The following chart shows a new connection.
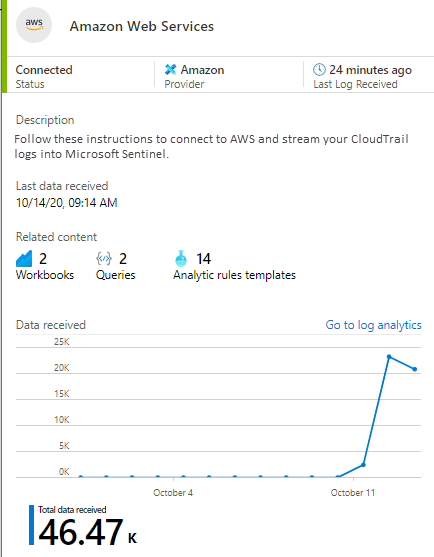
If the connector stops ingesting data and the line chart value drops, check the credentials that you use to connect to the AWS account. Also check that AWS CloudTrail can still collect the events.
Contributors
This article is maintained by Microsoft. It was originally written by the following contributor.
Principal author:
- Lavanya Murthy | Senior Cloud Solution Architect
To see non-public LinkedIn profiles, sign in to LinkedIn.
Next steps
- For security guidance from AWS, see Best practices for securing AWS accounts and resources.
- For the latest Microsoft security information, see Microsoft Security.
- For full details of how to implement and manage Microsoft Entra ID, see Securing Azure environments with Microsoft Entra ID.
- For an overview of AWS asset threats and corresponding protective measures, see How Defender for Cloud Apps helps protect your Amazon Web Services (AWS) environment.
- For information about connectors and how to establish connections, see these resources:
Related resources
- For in-depth coverage and comparison of Azure and AWS features, see the Azure for AWS professionals content set.
- For guidance for deploying Microsoft Entra identity and access solutions for AWS, see Microsoft Entra identity and access management for AWS.