Connect to AD-integrated SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc
This article describes how to connect to SQL Managed Instance endpoint using Active Directory (AD) authentication. Before you proceed, make sure you have an AD-integrated SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc deployed already.
See Tutorial – Deploy AD-integrated SQL Managed Instance to deploy SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc with Active Directory authentication enabled.
Note
Ensure that a DNS record for the SQL endpoint is created in Active Directory DNS servers before continuing on this page.
Create Active Directory logins in SQL Managed Instance
Once SQL Managed Instance is successfully deployed, you will need to provision Active Directory logins in SQL Server.
To provision logins, first connect to the SQL Managed Instance using the SQL login with administrative privileges and run the following T-SQL:
CREATE LOGIN [<NetBIOS domain name>\<AD account name>] FROM WINDOWS;
GO
The following example creates a login for an Active Directory account named admin, in the domain named contoso.local, with NetBIOS domain name as CONTOSO:
CREATE LOGIN [CONTOSO\admin] FROM WINDOWS;
GO
Connect to SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc
From your domain joined Windows-based client machine or a Linux-based domain aware machine, you can use sqlcmd utility, or open SQL Server Management Studio or Azure Data Studio (ADS) to connect to the instance with AD authentication.
A domain-aware Linux-based machine is one where you are able to use Kerberos authentication using kinit. Such machine should have /etc/krb5.conf file set to point to the Active Directory domain (realm) being used. It should also have /etc/resolv.conf file set such that one can run DNS lookups against the Active Directory domain.
Connect from Linux/Mac OS
To connect from a Linux/Mac OS client, authenticate to Active Directory using the kinit command and then use sqlcmd tool to connect to the SQL Managed Instance.
kinit <username>@<REALM>
sqlcmd -S <Endpoint DNS name>,<Endpoint port number> -E
For example, to connect with the CONTOSO\admin account to the SQL managed instance with endpoint sqlmi.contoso.local at port 31433, use the following command:
kinit admin@CONTOSO.LOCAL
sqlcmd -S sqlmi.contoso.local,31433 -E
In the example, -E specifies Active Directory integrated authentication.
Connect SQL Managed Instance from Windows
To log in to SQL Managed Instance with your current Windows Active Directory login, run the following command:
sqlcmd -S <DNS name for master instance>,31433 -E
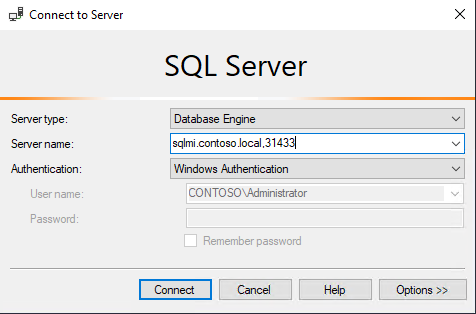
Connect to SQL Managed Instance from SSMS
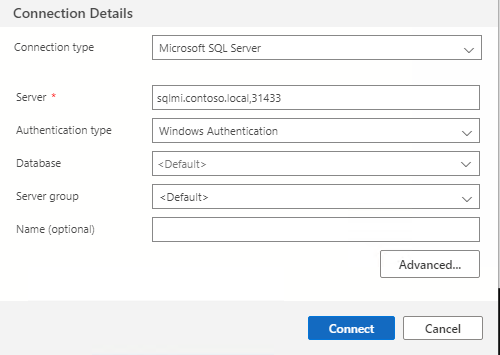
Connect to SQL Managed Instance from ADS
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for