Rotate SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc customer-managed keytab
This article describes how to rotate customer-managed keytabs for SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc. These keytabs are used to enable Active Directory logins for the managed instance.
Prerequisites:
Before you proceed with this article, you must have an active directory connector in customer-managed keytab mode and a SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc created.
- Deploy a customer-managed keytab active directory connector
- Deploy and connect a SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc
How to rotate customer-managed keytabs in a managed instance
The following steps need to be followed to rotate the keytab:
- Get
kvnovalue for the current generation of credentials for the SQL MI Active Directory account. - Create a new keytab file with entries for the current generation of credentials. Specifically, the
kvnovalue should match from step (1.) above. - Update the new keytab file with new entries for the new credentials for the SQL MI Active Directory account.
- Create a kubernetes secret holding the new keytab file contents in the same namespace as the SQL MI.
- Edit the SQL MI spec to point the Active Directory keytab secret setting to this new secret.
- Change the password in the Active Directory domain.
We have provided the following PowerShell and bash scripts that will take care of steps 1-5 for you:
rotate-sqlmi-keytab.sh- This bash script usesktutiloradutil(if the--use-adutilflag is specified) to generate the new keytab for you.rotate-sqlmi-keytab.ps1- This PowerShell script usesktpass.exeto generate the new keytab for you.
Executing the above script would result in the following keytab file for the user arcsqlmi@CONTOSO.COM, secret sqlmi-keytab-secret-kvno-2-3 and namespace test:
KVNO Timestamp Principal
---- ------------------- ------------------------------------------------------
2 02/16/2023 17:12:05 arcsqlmiuser@CONTOSO.COM (aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96)
2 02/16/2023 17:12:05 arcsqlmiuser@CONTOSO.COM (arcfour-hmac)
2 02/16/2023 17:12:05 MSSQLSvc/arcsqlmi.contoso.com@CONTOSO.COM (aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96)
2 02/16/2023 17:12:05 MSSQLSvc/arcsqlmi.contoso.com@CONTOSO.COM (arcfour-hmac)
2 02/16/2023 17:12:05 MSSQLSvc/arcsqlmi.contoso.com:31433@CONTOSO.COM (aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96)
2 02/16/2023 17:12:05 MSSQLSvc/arcsqlmi.contoso.com:31433@CONTOSO.COM (arcfour-hmac)
3 02/16/2023 17:13:41 arcsqlmiuser@CONTOSO.COM (aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96)
3 02/16/2023 17:13:41 arcsqlmiuser@CONTOSO.COM (arcfour-hmac)
3 02/16/2023 17:13:41 MSSQLSvc/arcsqlmi.contoso.com@CONTOSO.COM (aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96)
3 02/16/2023 17:13:41 MSSQLSvc/arcsqlmi.contoso.com@CONTOSO.COM (arcfour-hmac)
3 02/16/2023 17:13:41 MSSQLSvc/arcsqlmi.contoso.com:31433@CONTOSO.COM (aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96)
3 02/16/2023 17:13:41 MSSQLSvc/arcsqlmi.contoso.com:31433@CONTOSO.COM (arcfour-hmac)
And the following updated-secret.yaml spec:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
type: Opaque
metadata:
name: sqlmi-keytab-secret-kvno-2-3
namespace: test
data:
keytab:
<keytab-contents>
Finally, change the password for arcsqlmi user account in the domain controller for the Active Directory domain contoso.com:
Open Server Manager on the domain controller for the Active Directory domain
contoso.com. You can either search for Server Manager or open it through the Start menu.Go to Tools > Active Directory Users and Computers
Select the user that you want to change password for. Right-click to select the user. Select Reset password:
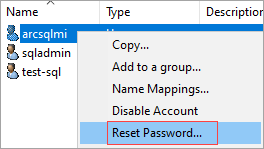
Enter new password and select
OK.
Troubleshooting errors after rotation
In case there are errors when trying to use Active Directory Authentication after completing keytab rotation, the following files in the arc-sqlmi container in the SQL MI pod are a good place to start investigating the root cause:
security.logfile located at/var/opt/mssql/log- This log file has logs for SQL's interactions with the Active Directory domain.errorlogfile located at/var/opt/mssql/log- This log file contains logs from the SQL Server running on the container.mssql.keytabfile located at/var/run/secrets/managed/keytabs/mssql- Verify that this keytab file contains the newly updated entries and matches the keytab file created by using the scripts provided above. The keytab file can be read using theklistcommand i.e.klist -k mssql.keytab -e
Additionally, after getting the kerberos Ticket-Granting Ticket (TGT) by using kinit command, verify the kvno of the SQL user matches the highest kvno in the mssql.keytab file in the arc-sqlmi container. For example, for arcsqlmi@CONTOSO.COM user:
- Get the kerberos TGT from the Active Directory domain by running
kinit arcsqlmi@CONTOSO.COM. This will prompt a user input for the password forarcsqlmiuser. - Once this succeeds, the
kvnocan be queried by runningkvno arcsqlmi@CONTOSO.COM.
We can also enable debug logging for the kinit command by running the following: KRB5_TRACE=/dev/stdout kinit -V arcsqlmi@CONTOSO.COM. This increases the verbosity and outputs the logs to stdout as the command is being executed.
Related content
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for