Deploy and configure Azure Monitor Agent using Azure Policy
This article covers how to deploy and configure the Azure Monitor Agent (AMA) to Arc-enabled servers through Azure Policy using a custom Policy definition. Using Azure Policy ensures that Azure Monitor is running on your selected Arc-enabled servers, and automatically install the Azure Monitor Agent on newly added Arc resources.
Deploying the Azure Monitor Agent through a custom Policy definition involves two main steps:
Selecting an existing or creating a new Data Collection Rule (DCR)
Creating and deploying the Policy definition
In this scenario, the Policy definition is used to verify that the AMA is installed on your Arc-enabled servers. It will also install the AMA on newly added machines or on existing machines that don't have the AMA installed.
In order for Azure Monitor to work on a machine, it needs to be associated with a Data Collection Rule. Therefore, you'll need to include the resource ID of the DCR when you create your Policy definition.
Select a Data Collection Rule
Data Collection Rules define the data collection process in Azure Monitor. They specify what data should be collected and where that data should be sent. You'll need to select or create a DCR to be associated with your Policy definition.
From your browser, go to the Azure portal.
Navigate to the Monitor | Overview page. Under Settings, select Data Collection Rules. A list of existing DCRs displays. You can filter this at the top of the window. If you need to create a new DCR, see Data collection rules in Azure Monitor for more information.
Select the DCR to apply to your ARM template to view its overview.
Select Resources to view a list of resources (such as Arc-enabled VMs) assigned to the DCR. To add more resources, select Add*. (You'll need to add resources if you created a new DCR.)
Select Overview, then select JSON View to view the JSON code for the DCR:
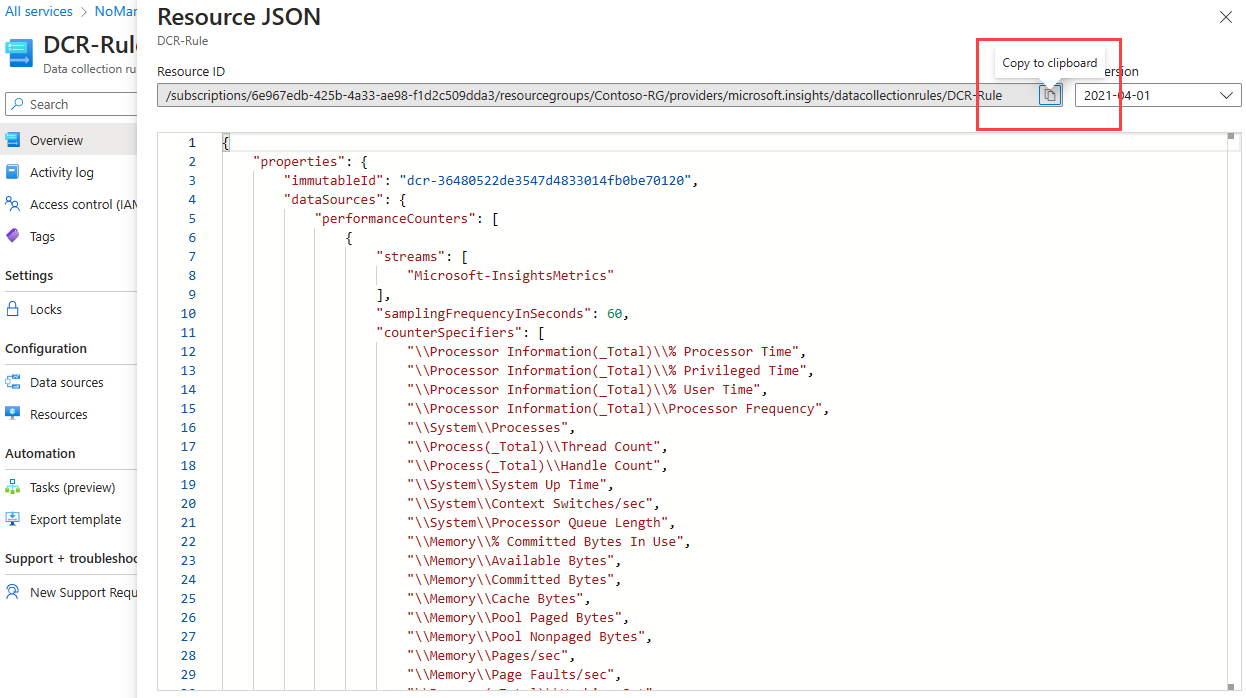
Locate the Resource ID field at the top of the window and select the button to copy the resource ID for the DCR to the clipboard. Save this resource ID; you'll need to use it when creating your Policy definition.
Create and deploy the Policy definition
In order for Azure Policy to check if AMA is installed on your Arc-enabled, you'll need to create a custom policy definition that does the following:
Evaluates if new VMs have the AMA installed and the association with the DCR.
Enforces a remediation task to install the AMA and create the association with the DCR on VMs that aren't compliant with the policy.
Select one of the following policy definition templates (that is, for Windows or Linux machines):
These templates are used to create a policy to configure machines to run Azure Monitor Agent and associate those machines to a DCR.
Select Assign to begin creating the policy definition. Enter the applicable information for each tab (that is, Basics, Advanced, etc.).
On the Parameters tab, paste the Data Collection Rule Resource ID that you copied during the previous procedure:
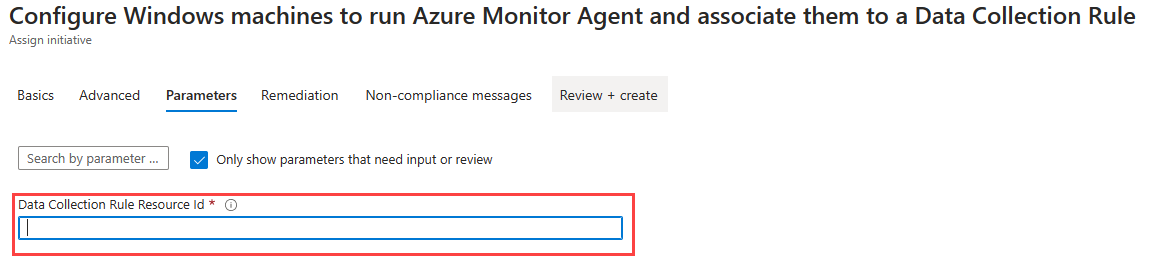
Complete the creation of the policy to deploy it for the applicable machines. Once Azure Monitor Agent is deployed, your Azure Arc-enabled servers can apply its services and use it for log collection.
Additional resources
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for