Use Resource Health to troubleshoot connectivity for Azure SQL Managed Instance
Applies to:
Azure SQL Managed Instance
Resource Health for Azure SQL Managed Instance helps you diagnose and get support when an Azure issue impacts your resources. It informs you about the current and past health of your resources and helps you mitigate issues. The Resource health page provides technical support when you need help with Azure service issues.
Health checks
Resource health determines the health of your SQL managed instance by examining the success and failure of logins to the resource. Currently, Resource health for your SQL managed instance only examines login failures due to system error and not user error. The health status is updated every 1 to 2 minutes.
Health states
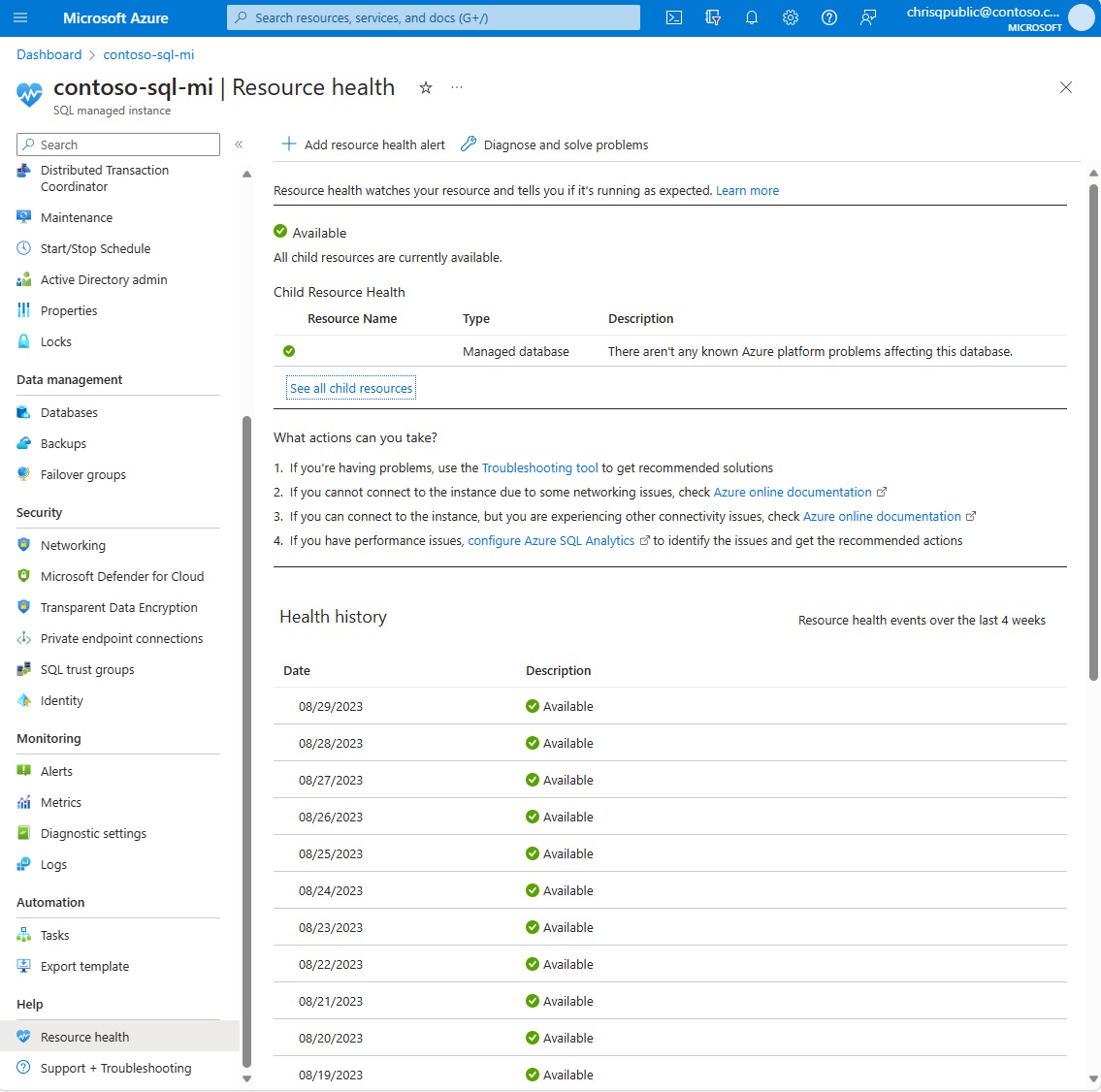
Available
A status of Available means that Resource health has not detected login failures due to system errors on your SQL managed instance.
Degraded
A status of Degraded means that Resource health has detected a majority of successful logins, but some failures as well. These are most likely transient login errors. To reduce the impact of connection issues caused by transient login errors, implement retry logic in your code.
Unavailable
A status of Unavailable means that Resource health has detected consistent login failures to your SQL managed instance. If your resource remains in this state for an extended period of time, contact support.
Unknown
The health status of Unknown indicates that Resource health hasn't received information about this resource for more than 10 minutes. Although this status isn't a definitive indication of the state of the resource, it is an important data point in the troubleshooting process. If the resource is running as expected, the status of the resource will change to Available after a few minutes. If you're experiencing problems with the resource, the Unknown health status might suggest that an event in the platform is affecting the resource.
Historical information
You can access up to 30 days of health history in the Health history section of Resource health. The section will also contain the reason (when available) for downtimes. Currently, Azure shows the downtime for your resource at a two-minute granularity. The actual downtime is likely less than a minute. The average is 8 seconds.
Downtime reasons
When your SQL managed instance experiences downtime, analysis is performed to determine a reason. When available, the downtime reason is reported in the Health history section of Resource health. Downtime reasons are typically published within 45 minutes after an event.
Select a maintenance window
You can configure your maintenance window to make impactful maintenance events predictable and less disruptive for your workload. The maintenance window feature helps you plan around predictable upgrades or scheduled maintenance. Advance notifications are available for all SQL managed instances. Advance notifications enable customers to configure notifications to be sent up to 24 hours in advance of any planned event.
Planned maintenance
The Azure infrastructure periodically performs planned maintenance – the upgrade of hardware or software components in the datacenter. While the database undergoes maintenance, Azure SQL may terminate some existing connections and refuse new ones. The login failures experienced during planned maintenance are typically transient, and retry logic for occasional network errors helps reduce the impact. If you continue to experience login errors, contact support.
Reconfiguration
Reconfigurations are considered transient conditions and are expected from time to time. These events can be triggered by load balancing or software/hardware failures. Any client production application that connects to a cloud database should implement a robust connection retry logic for transient errors, as it would help mitigate these situations and should generally make the errors transparent to the end user.
Next steps
- Learn more about retry logic for transient errors.
- Troubleshoot, diagnose, and prevent SQL connection errors.
- Learn more about configuring Resource Health alerts.
- Get an overview of Resource Health.
- Review Resource Health FAQ.
- Configure a maintenance window and advance notifications.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for