Run an application by using Fortanix Confidential Computing Manager
Learn how to run your application in Azure confidential computing by using Fortanix Confidential Computing Manager and Node Agent from Fortanix.
Fortanix is a third-party software vendor that provides products and services that work with the Azure infrastructure. There are other third-party providers that offer similar confidential computing services for Azure.
Note
Some of the products referenced in this document aren't provided by Microsoft. Microsoft is providing this information only as a convenience. References to these non-Microsoft products doesn't imply endorsement by Microsoft.
This tutorial shows you how to convert your application image into a confidential compute-protected image. The environment uses Fortanix software, powered by Azure DCsv2-series Intel SGX-enabled virtual machines. The solution orchestrates critical security policies like identity verification and data access control.
For Fortanix support, join the Fortanix Slack community. Use the #enclavemanager channel.
Prerequisites
- If you don't have a Fortanix Confidential Computing Manager account, sign up before you start.
- You need a private Docker registry to push converted application images.
- If you don't have an Azure subscription, create an account before you start.
Note
Free trial accounts don't have access to the virtual machines used in this tutorial. To complete the tutorial, you need a pay-as-you-go subscription.
Add an application to Fortanix Confidential Computing Manager
Sign in to Fortanix Confidential Computing Manager (Fortanix CCM).
Go to the Accounts page and select ADD ACCOUNT to create a new account:
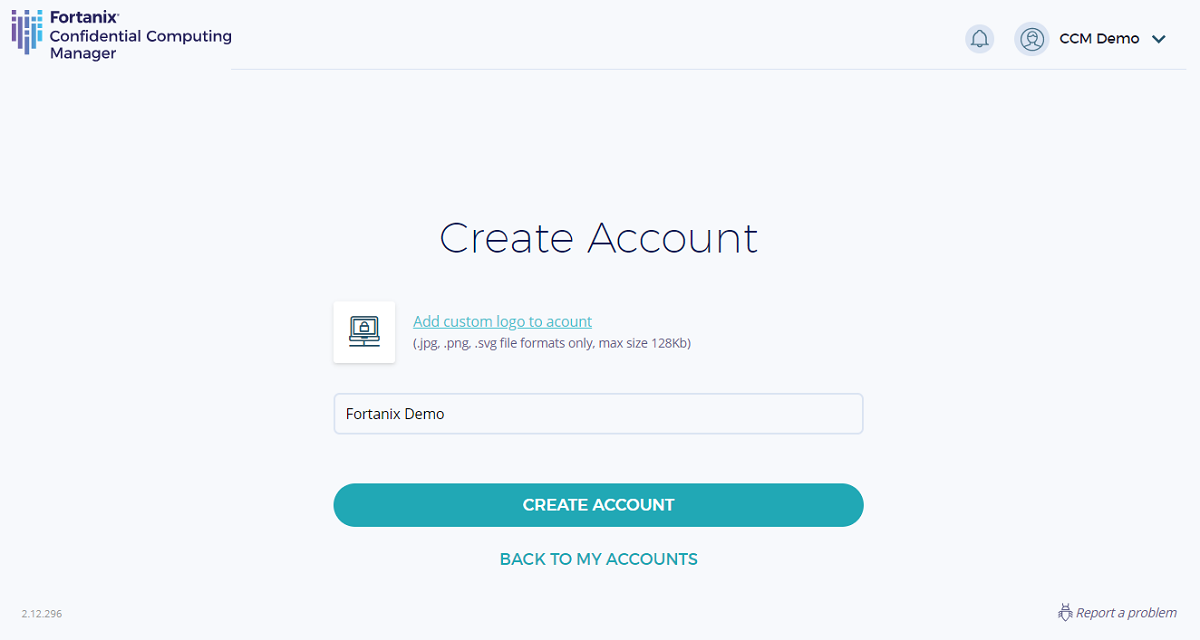
After your account is created, click SELECT ACCOUNT to select the newly created account. You can now start enrolling compute nodes and creating applications.
On the Applications tab, select + APPLICATION to add an application. In this example, we'll add an Enclave OS application that runs a Python Flask server.
Select the ADD button for the Enclave OS Application:

Note
This tutorial covers adding only Enclave OS applications. For information about adding EDP Rust Applications, see Bringing EDP Rust Apps to Confidential Computing Manager.
In this tutorial, we'll use the Fortanix Docker registry for the sample application. Enter the specified values for the following settings. Use your private Docker registry to store the output image.
Application name: Python Application Server
Description: Python Flask Server
Input image name: fortanix/python-flask
Output image name: fortanix-private/python-flask-sgx (Replace with your own registry.)
ISVPRODID: 1
ISVSVM: 1
Memory size: 1 GB
Thread count: 128
Optional: Run the non-converted application.
Docker Hub: https://hub.docker.com/u/fortanix
App: fortanix/python-flask
Run the following command:
sudo docker run fortanix/python-flaskNote
We don't recommend that you use your private Docker registry to store the output image.
Add a certificate. Enter the following values, and then select NEXT:
- Domain: myapp.domain.com
- Type: Certificate Issued by Confidential Computing Manager
- Key path: /run/key.pem
- Key type: RSA
- Certificate path: /run/cert.pem
- RSA Key Size: 2048 Bits
Create an image
A Fortanix CCM Image is a software release or version of an application. Each image is associated with one enclave hash (MRENCLAVE).
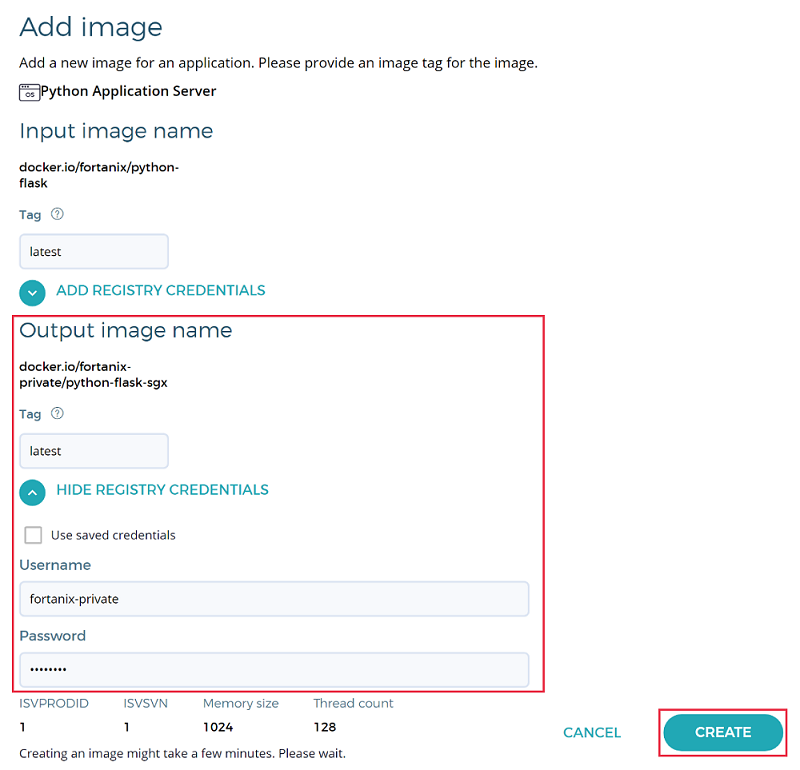
On the Add image page, enter the registry credentials for Output image name. These credentials are used to access the private Docker registry where the image will be pushed. Because the input image is stored in a public registry, you don't need to provide credentials for the input image.
Enter the image tag and select CREATE:
Domain and image allowlist
An application whose domain is added to the allowlist will get a TLS certificate from the Fortanix Confidential Computing Manager. When an Enclave OS application starts, it will contact the Fortanix Confidential Computing Manager to receive that TLS certificate.
On the Tasks tab on the left side of the screen, approve the pending requests to allow the domain and image.
Enroll the compute node agent in Azure
Create and copy a join token
You'll now create a token in Fortanix Confidential Computing Manager. This token allows a compute node in Azure to authenticate itself. Your Azure virtual machine will need this token.
- On the Compute Nodes tab, select ENROLL NODE.
- Select the COPY button to copy the join token. The compute node uses this join token to authenticate itself.
Enroll nodes into Fortanix Node Agent
Creating a Fortanix node agent will deploy a virtual machine, network interface, virtual network, network security group, and public IP address in your Azure resource group. Your Azure subscription will be billed hourly for the virtual machine. Before you create a Fortanix node agent, review the Azure virtual machine pricing page for DCsv2-series. Delete any Azure resources that you're not using.
Go to the Azure Marketplace and sign in with your Azure credentials.
In the search box, enter Fortanix Confidential Computing Node Agent. In the search results, select Fortanix Confidential Computing Node Agent to go to the app's home page:
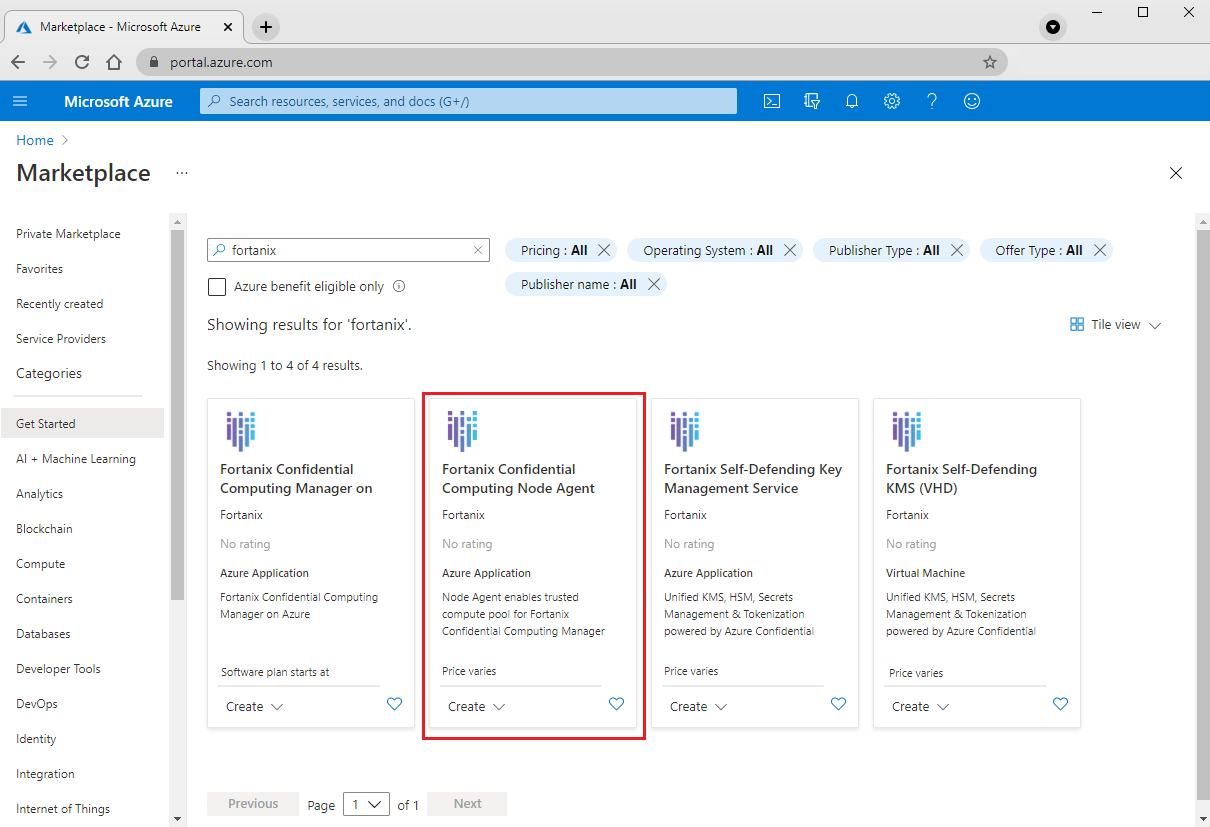
Select Get It Now, provide your information if necessary, and then select Continue. You'll be redirected to the Azure portal.
Select Create to go to the Fortanix Confidential Computing Node Agent deployment page.
On this page, you'll enter information to deploy a virtual machine. The VM is a DCsv2-series Intel SGX-enabled virtual machine from Azure that has Fortanix Node Agent software installed on it. The node agent will allow your converted image to run with increased security on Intel SGX nodes in Azure. Select the subscription and resource group where you want to deploy the virtual machine and associated resources.
Note
Constraints apply when you deploy DCsv2-series virtual machines in Azure. You might need to request quota for additional cores. Read about confidential computing solutions on Azure VMs for more information.
Select an available region.
In the Node Name box, enter a name for your virtual machine.
Enter a user name and password (or SSH key) for authenticating into the virtual machine.
Leave the default OS Disk Size of 200. Select a VM Size. (Standard_DC4s_v2 will work for this tutorial.)
In the Join Token box, paste in the token that you created earlier in this tutorial:

Select Review + create. Make sure the validation passes, and then select Create. When all the resources deploy, the compute node is enrolled in Fortanix Confidential Computing Manager.
Run the application image on the compute node
Run the application by running the following command. Be sure to change the node IP, port, and converted image name to the values for your application.
For this tutorial, here's the command to run:
sudo docker run \
--device /dev/isgx:/dev/isgx \
--device /dev/gsgx:/dev/gsgx \
-v /var/run/aesmd/aesm.socket:/var/run/aesmd/aesm.socket \
-e NODE_AGENT_BASE_URL=http://52.152.206.164:9092/v1/ fortanix-private/python-flask-sgx
In this command:
52.152.206.164is the node agent host IP.9092is the default port that Node Agent listens to.fortanix-private/python-flask-sgxis the converted app. You can find it in the Fortanix Confidential Computing Manager Web Portal. It's on the Images tab, in the Image Name column of the Images table.
Verify and monitor the running application
- Return to Fortanix Confidential Computing Manager.
- Be sure you're working in the Account where you enrolled the node.
- On the Applications tab, verify that there's a running application with an associated compute node.
Clean up resources
If you no longer need them, you can delete the resource group, virtual machine, and associated resources. Deleting the resource group will unenroll the nodes associated with your converted image.
Select the resource group for the virtual machine, and then select Delete. Confirm the name of the resource group to finish deleting the resources.
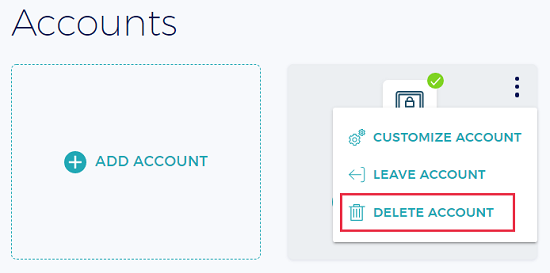
To delete the Fortanix Confidential Computing Manager account you created, go to the Accounts page in the Fortanix Confidential Computing Manager. Hover over the account you want to delete. Select the vertical black dots in the upper-right corner and then select DELETE ACCOUNT.
Next steps
In this tutorial, you used Fortanix tools to convert your application image to run on top of a confidential computing virtual machine. For more information about confidential computing virtual machines on Azure, see Solutions on virtual machines.
To learn more about Azure confidential computing offerings, see Azure confidential computing overview.
You can also learn how to complete similar tasks by using other third-party offerings on Azure, like Anjuna and Scone.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for