Leverage virtual TPMs in Azure confidential VMs
Applies to: ✔️ Linux VMs
This "how to" shows you how to use some benefits provided by a virtual Trusted Platform Module (TPM) in a confidential VM.
Prerequisites
To see how vTPMs work in confidential VMs, read the concept page.
Some of the steps mentioned use the tpm2-tools library that is source repository for the Trusted Platform Module (TPM2.0). Follow the steps here to build and install the library.
How to get the direct AMD SEV-SNP hardware report
The guest attestation feature helps you to confirm that a confidential VM runs on a hardware-based trusted execution environment (TEE) with security features enabled for isolation and integrity. When a confidential VM boots it generates a SEV-SNP hardware report containing a signed report issued by AMD SEV-SNP, platform boot settings, and platform measurements. This report is stored in a predefined nonvolatile index (NVIndex) of the vTPM, where data can be securely and persistently stored. Today our guest attestation library can be used to access and retrieve the SEV-SNP hardware report. Customers can use Microsoft Azure Attestation to verify the reports or verify the raw AMD SEV-SNP report on their own by following steps here.
How to extend a measurement to a PCR and validate it through the vTPM
Currently confidential VMs generate a SEV-SNP report at boot that is accessible through the virtual trusted platform module (vTPM). This report also includes the vTPM’s public attestation key (AKPub). The AKPub can be used to generate an attestation of the vTPM runtime state including the platform configuration register (PCR) state. Therefore, the AKPub can be used to link the vTPM PCR measurements that are signed by the private attestation key (AKPri), to SEV-SNP attestation.
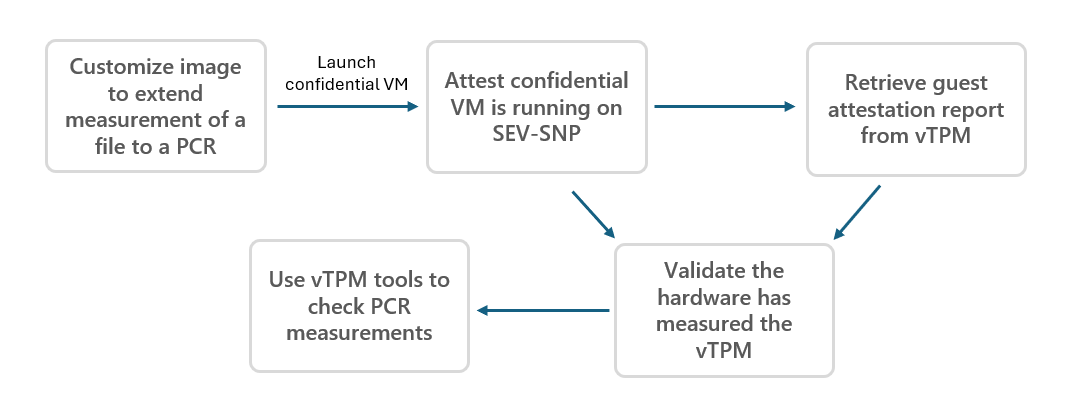
These steps list out which artifacts you need and how to get them:
Extend a measurement to a PCR.
There are multiple ways to extend a measurement to a PCR using the tpm2-tools library. This command shows how to hash a file using sha256 bank and then extend it to a PCR.
sha256sum <any file> tpm2_pcrextend <pcr_number>:sha256=<result from first command>Retrieve the AMD’s VCEK certificate.
The AMD Versioned Chip Endorsement Key (VCEK) is used to sign the AMD SEV-SNP report. The VCEK certificate allows you to verify that the report was signed by a genuine AMD CPU key. There are two ways retrieve the certificate:
a. Obtain the VCEK certificate by running the following command – it obtains the cert from a well-known Azure Instance Metadata Service (IMDS) endpoint:
curl -H Metadata:true http://169.254.169.254/metadata/THIM/amd/certification > vcek cat ./vcek | jq -r '.vcekCert , .certificateChain' > ./vcek.pemb. To retrieve the certificate, use the AMD VCEK Certificate tool and the steps mentioned in the specification.
Retrieve the public attestation key (AKpub) from the attestation report.
AMD's SEV-SNP guest attestation report is signed using the VCEK. The report data JSON in the guest attestation report is measured and the hash is reflected in the SEV-SNP report. The report data JSON includes a VM configuration section that contains attestation claims supplied to the AMD processor by the guest firmware. The claims in this section relate to the state of the Microsoft boot loader and operating system i.e whether the secure boot is enabled, whether Windows serial console is enabled etc. These claims also include the "HCLAkPub" signing key that is the attestation key (AKPub) for the TPM.
These steps extract the SNP report from a set NVIndex and dump the report data JSON. The guest_report.bin file is used in the following step.
tpm2_nvread -C o 0x01400001 > ./snp_report.bin dd skip=32 bs=1 count=1184 if=./snp_report.bin of=./guest_report.binHere's an example of how the report data JSON looks like:
"keys": [ { "kid": "HCLAkPub", "key_ops": [ "encrypt" ], "kty": "RSA", "e": "AQAB", "n": "2I-ayAABWYhQU-D81quVW4i1sH14-Offul2U2LwsgtihxykIzXY_5YzQAY4e56GMZSpm5r6telRr5rnFJa8iklzol7ecYZEX1nc1WK51a68E2kZNyomFVSIlDPJCn14NpRoxuipIfhe16zWVYZ8dpYbpelyzHZZpskdBLnUKldffUYliWSXLBpjPb89VV0FYxKPi_bSGviBXWOiRtcITRcXfpjlfD3DgZqlK4gj11RChqaEYG_GAPlxceu5h1pusgLuPEULWzvkKuGw7j8ZrxdYEUNB-uHU0nxuQvYxtksPs3zX6ELcV2GjwJupzYUUAu95OQUGI-soDWKvIXM4epw" } ], "vm-configuration": { "console-enabled": true, "secure-boot": true, "tpm-enabled": true, "vmUniqueId": "A80B7FE7-5B93-4027-9971-6CCEE468C2B3" }Validate the VCEK certificate and guest attestation report.
Once we have retrieved the VCEK certificate and guest attestation report, we can check that the VCEK has signed the guest attestation report. This step ensures the vTPM is properly measured by the AMD SEV-SNP hardware and that we can trust the vTPM. There are multiple ways to do verification, the following example uses the open-source AMD SEV Tool.
sudo ./sevtool –-ofolder <location of vcek.pem & guest_report.bin> --validate_guest_reportUse vTPM tools to get PCR measurements.
After you have established trust in the vTPM, then you can go get a quote using the AKpub and reflect PCR measurements.
a. Retrieve the public attestation key. 0x81000003 is the location of the AKpub.
tpm2_readpublic -c 0x81000003 -f pem -o <outputfile.pem>b. Generate a TPM quote using the options mentioned here. This example shows how to get the quote and reflect PCRs 15, 16 and 22. The nonce is added to protect against replay attacks. The message output file records the quote message that makes up the data that is signed by the TPM. Finally the PCR values are stored in the PCR_output_file. Refer to the tpm2_quote link to learn more about the options used.
tpm2_quote -c 0x81000003 -l sha256:15,16,22 -q <nonce> -m <message_output_file.msg> -s <signature_output_file.sig> -o <PCR_output_file.pcrs> -g sha256c. The following command can be used on a remote machine to verify the confidential VM generated quote in the previous step. Use the AKpub retrieved from step a as an input here.
tpm2_checkquote -u <outputfile.pem> -m <message_output_file.msg> -s <signature_output_file.sig> -f <PCR_output_file.pcrs> -g sha256 -q <nonce>
Using the tpm2_checkquote command, a relying party can cryptographically verify the entire chain including all boot time and runtime extended PCRs. We recommend you use PCR23 to extend measurements of user mode components or runtime data.
Using the steps mentioned in this document allows you to extend any arbitrary runtime attestation data, configuration, or application into vTPM PCRs. Therefore, you can have a chain of measurements of all components (per your choice) provided by the vTPM that is rooted to the AMD SEV-SNP report.
Next steps
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for