Manage Azure DevTest Labs storage accounts
This article explains how to view and manage the Azure Storage accounts associated with Azure DevTest Labs.
View storage account contents
DevTest Labs automatically creates an Azure Storage account for every lab it creates. To see a lab's storage account and the information it holds:
On the lab's Overview page, select the Resource group.
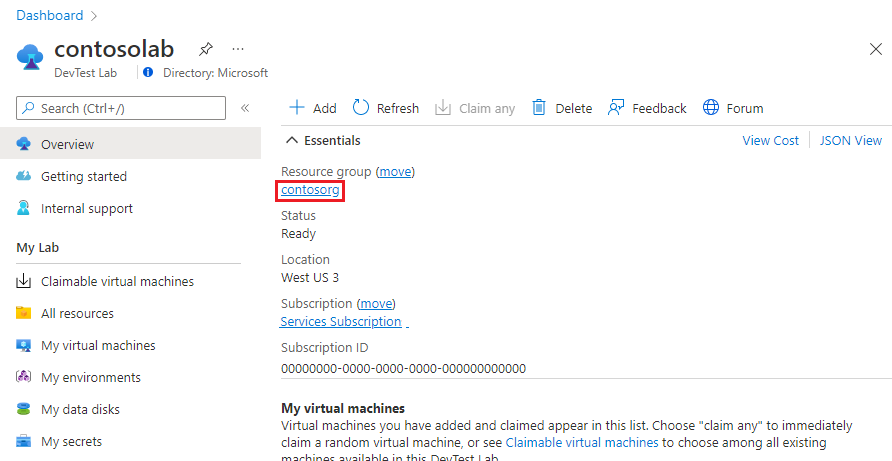
On the resource group's Overview page, select the lab's storage account. The naming convention for the lab storage account is:
a<labName><4-digit number>. For example, if the lab name iscontosolab, the storage account name could beacontosolab5237.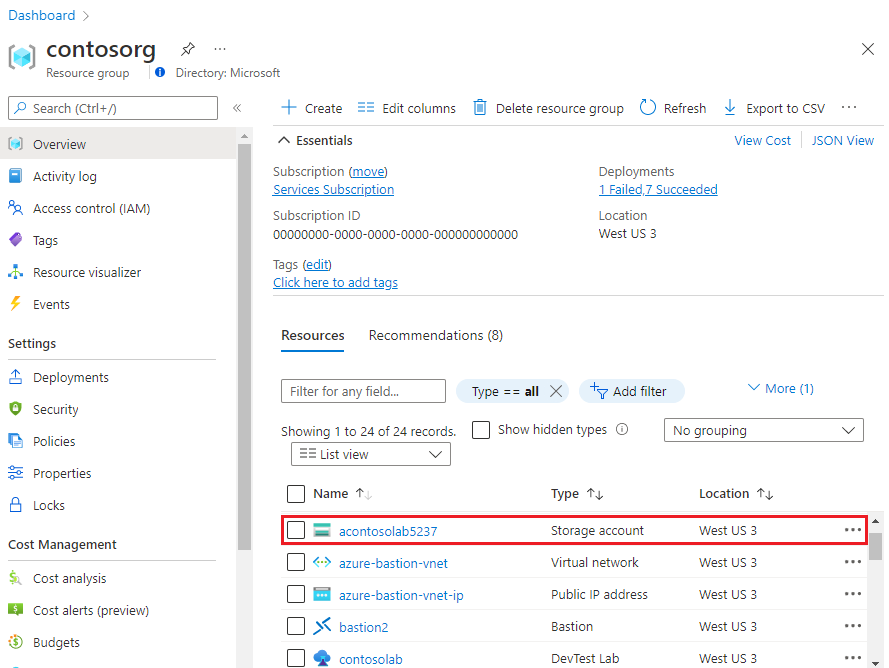
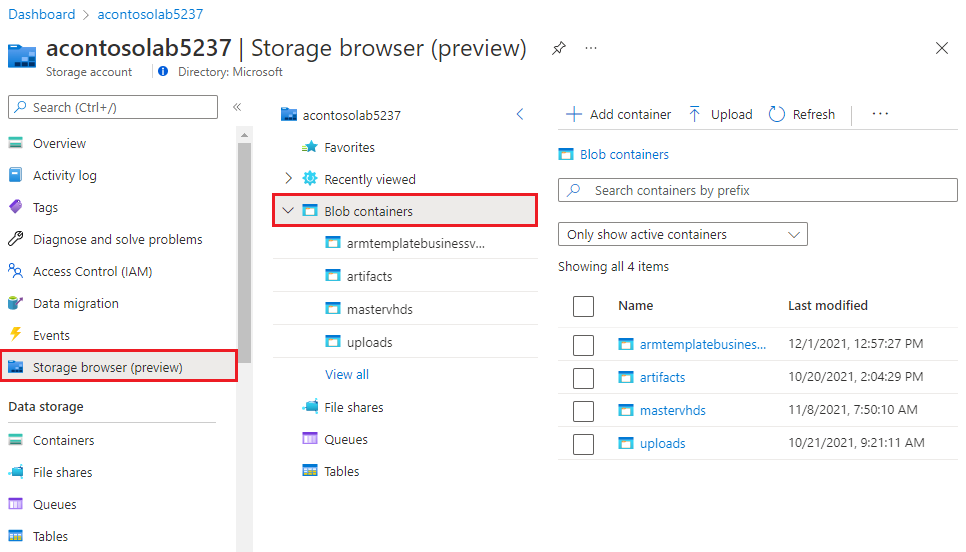
On the Storage account page, select Storage browser (preview) on the left menu, and then select Blob containers to see relevant lab-related content.
Manage Azure Storage lifecycle
The lab storage account stores:
- Formula documents to use for creating lab virtual machines (VMs).
- Uploaded virtual hard disks (VHDs) to use for creating custom VM images.
- Artifact and Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template caches, for faster retrieval during VM and environment creation.
- Artifact results, which are deployment and extension logs generated from applying artifacts.
The information in the lab storage account persists for the life of the lab and its resources, unless explicitly deleted. Most of this information is critical for the lab to operate. Manually deleting storage account information can cause data corruption or VM creation errors.
- Removing uploaded VHDs makes it no longer possible to create custom images from these VHDs.
- Deleting formula documents can lead to errors when creating VMs from formulas, updating formulas, or creating new formulas.
- DevTest Labs refreshes the artifact and ARM template caches whenever the lab connects to the artifact or template repositories. If you remove the caches manually, DevTest Labs recreates the caches the next time the lab connects to the repositories.
Set expiration for artifact results
The artifact results size can increase over time as artifacts are applied. You can set an expiration rule for artifact results to regularly delete older results from the storage account. This practice reduces storage account size and helps control costs.
The following rule sets a 90-day expiration specifically for artifact results:
{
"rules": [
{
"name": "expirationRule",
"enabled": true,
"type": "Lifecycle",
"definition": {
"filters": {
"blobTypes": [ "blockBlob" ],
"prefixMatch": [ "artifacts/results" ]
},
"actions": {
"baseBlob": {
"delete": { "daysAfterModificationGreaterThan": 90 }
},
"snapshot": {
"delete": { "daysAfterCreationGreaterThan": 90 }
}
}
}
}
]
}
Storage encryption and customer-managed keys
Azure Storage automatically encrypts all data in the lab storage account. Azure Storage encryption protects your data and helps meet organizational security and compliance commitments. For more information, see Azure Storage encryption for data at rest.
Azure Storage encrypts lab data with a Microsoft-managed key. Optionally, you can manage encryption with your own keys. If you choose to manage lab storage account encryption with your own key, you can use Azure Key Vault to specify a customer-managed key for encrypting and decrypting data.
For more information and instructions on configuring customer-managed keys for Azure Storage encryption, see:
- Use customer-managed keys with Azure Key Vault to manage Azure Storage encryption
- Configure encryption with customer-managed keys stored in Azure Key Vault
Next steps
For more information about managing Azure Storage, see Optimize costs by automatically managing the data lifecycle.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for