Remote Monitoring architectural choices
The Azure IoT Remote Monitoring solution accelerator is an open-source, MIT licensed, solution accelerator. To help you speed up your IoT development process, it shows common IoT scenarios such as:
- Device connectivity
- Device management
- Stream processing
The Remote Monitoring solution follows the recommended Azure IoT reference architecture.
This article describes the key architectural and technical choices made in each of the Remote Monitoring subsystems. However, the technical choices Microsoft made in the Remote Monitoring solution aren't the only way to implement a remote monitoring IoT solution. You should regard the technical implementation as a baseline for building a successful application and you should modify it to:
- Fit the available skills and experience in your organization.
- Meet your vertical application needs.
Architectural choices
The architecture that Microsoft recommends for an IoT application is cloud native, microservice, and serverless based. You should build the different subsystems of an IoT application as discrete services that you can deploy and scale independently. These attributes enable greater scale, more flexibility in updating individual subsystems, and provide the flexibility to choose an appropriate technology for each subsystem.
You can implement microservices using more than one technology. For example, you could choose either of the following options to implement a microservice:
- Use a container technology such as Docker with serverless technology such as Azure Functions.
- Host your microservices in PaaS services such as Azure App Services.
Technology choices
This section details the technology choices made in the Remote Monitoring solution for each of the core subsystems.
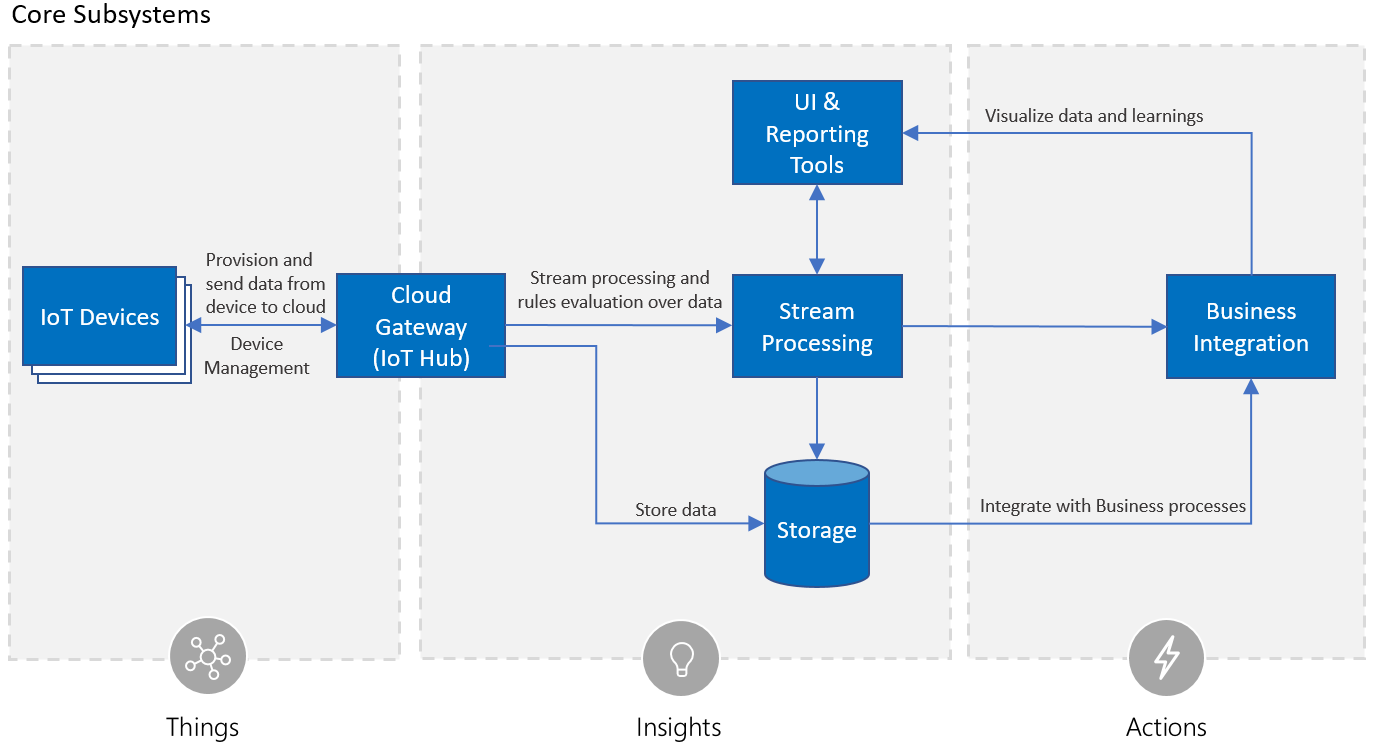
Cloud Gateway
Azure IoT Hub is used as the Remote Monitoring solution cloud gateway. IoT Hub offers secure, bi-directional communication with devices.
For IoT device connectivity, you can use:
- The IoT Hub device SDKs to implement a native client application for your device. The SDKs offer wrappers around the IoT Hub REST API and handle scenarios such as retries.
- The integration with Azure IoT Edge to deploy and manage custom modules running in containers on your devices.
- The integration with automatic device management in IoT Hub to manage connected devices in bulk.
Stream processing
For stream processing, the Remote Monitoring solution uses Azure Stream Analytics for complex rule processing. If you want to use simpler rules, there's a custom microservice with support for simple rule processing, although this set-up not part of the out-of-the-box deployment. The reference architecture recommends Azure Functions for simple rule processing and Azure Stream Analytics for complex rule processing.
Storage
For storage, the Remote Monitoring solution accelerator uses both Azure Time Series Insights and Azure Cosmos DB. Azure Time Series Insights stores the messages coming through IoT Hub from your connected devices. The solution accelerator uses Azure Cosmos DB for all other storage such as cold storage, rules definitions, alerts, and configuration settings.
Azure Cosmos DB is the recommended general-purpose warm storage solution for IoT applications. However, solutions such as Azure Time Series Insights and Azure Data Lake are appropriate for many use cases. With Azure Time Series Insights, you can gain deeper insights into your time-series sensor data by spotting trends and anomalies. This feature lets you conduct root-cause analyses and avoid costly downtime.
Note
Time Series Insights is not currently available in the Azure China cloud. New Remote Monitoring solution accelerator deployments in the Azure China cloud use Cosmos DB for all storage.
Business integration
Business integration in the Remote Monitoring solution is limited to the generation of alerts, which are placed in warm storage. Connect the solution with Azure Logic Apps to implement deeper business integration scenarios.
User Interface
The web UI is built with JavaScript React. React offers a commonly used industry web UI framework and is similar to other popular frameworks such as Angular.
Runtime and orchestration
The Remote Monitoring solution uses Docker containers to run the subsystems with Kubernetes as the orchestrator for horizontal scale. This architecture enables individual scale definitions for each subsystem. However, this architecture does incur DevOps costs to keep the virtual machines and containers up-to-date and secure.
Alternatives to Docker include hosting microservices in PaaS services such as Azure App Service. Alternatives to Kubernetes include orchestrators such as Service Fabric, DC/OS, or Swarm.