Graph search query syntax
In this article, you learn about the graph search functionality in Azure Machine Learning.
Graph search lets you fast navigate a node when you are debugging or building a pipeline. You can either type the key word or query in the input box in the toolbar, or under search tab in the left panel to trigger search. All matched result will be highlighted in yellow in canvas, and if you select a result in the left panel, the node in canvas will be highlighted in red.
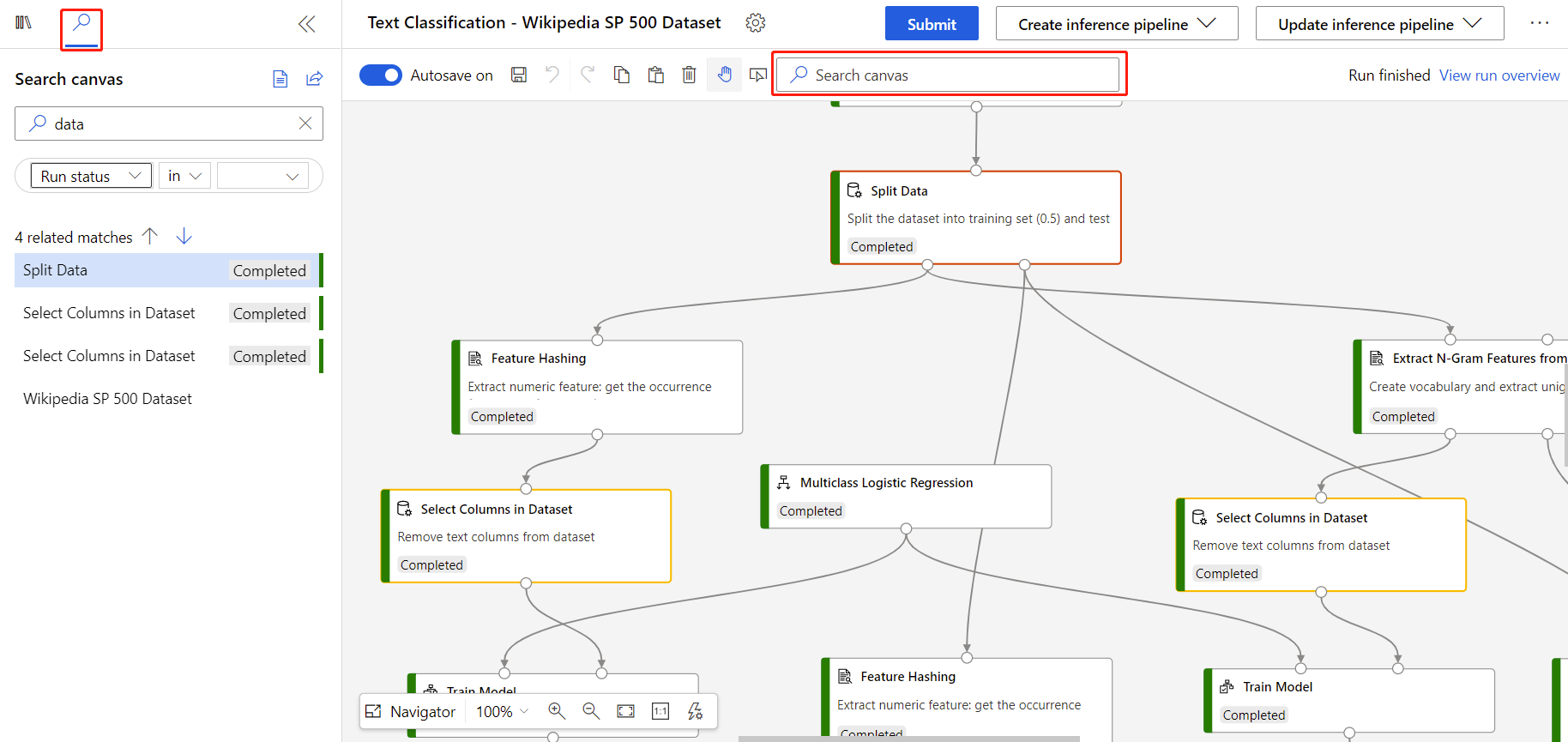
Graph search supports full-text keyword search on node name and comments. You can also filter on node property like runStatus, duration, computeTarget. The keyword search is based on Lucene query. A complete search query looks like this:
[[lucene query] | [filter query]]
You can use either Lucene query or filter query. To use both, use the | separator. The syntax of the filter query is more strict than Lucene query. So if customer input can be parsed as both, the filter query will be applied.
For example, data OR model | compute in {cpucluster}, this is to search nodes of which name or comment contains data or model, and compute is cpucluster.
Lucene query
Graph search uses Lucene simple query as full-text search syntax on node "name" and "comment". The following Lucene operators are supported:
- AND/OR
- Wildcard matching with ? and * operators.
Examples
Simple search:
JSON DataAND/OR:
JSON AND ValidationMultiple AND/OR:
(JSON AND Validation) OR (TSV AND Training)Wildcard matching:
machi?e learningmach*ing
Note
You cannot start a Lucene query with a "*" character.
Filter query
Filter queries use the following pattern:
[key1] [operator1] [value1]; [key2] [operator1] [value2];
You can use the following node properties as keys:
- runStatus
- compute
- duration
- reuse
- publish
- tags
And use the following operators:
- Greater or equal:
>= - Less or equal:
<= - Greater:
> - Less:
< - Equal:
== - Contain:
= - NotEqual:
!= - In:
in
Example
- duration > 100;
- status in { Failed,NotStarted}
- compute in {gpu-cluster}; runStatus in {Completed}
Technical notes
- The relationship between multiple filters is "AND"
- If
>=, >, <, or <=is chosen, values will automatically be converted to number type. Otherwise, string types are used for comparison. - For all string type values, case is insensitive in comparison.
- Operator "In" expects a collection as value, collection syntax is
{name1, name2, name3} - Space will be ignored between keywords
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for