View logs for a Service Fabric container service
Azure Service Fabric is a container orchestrator and supports both Linux and Windows containers. This article describes how to view container logs of a running container service or a dead container so that you can diagnose and troubleshoot problems.
Access the logs of a running container
Container logs can be accessed using Service Fabric Explorer. In a web browser, open Service Fabric Explorer from the cluster's management endpoint by navigating to http://mycluster.region.cloudapp.azure.com:19080/Explorer.
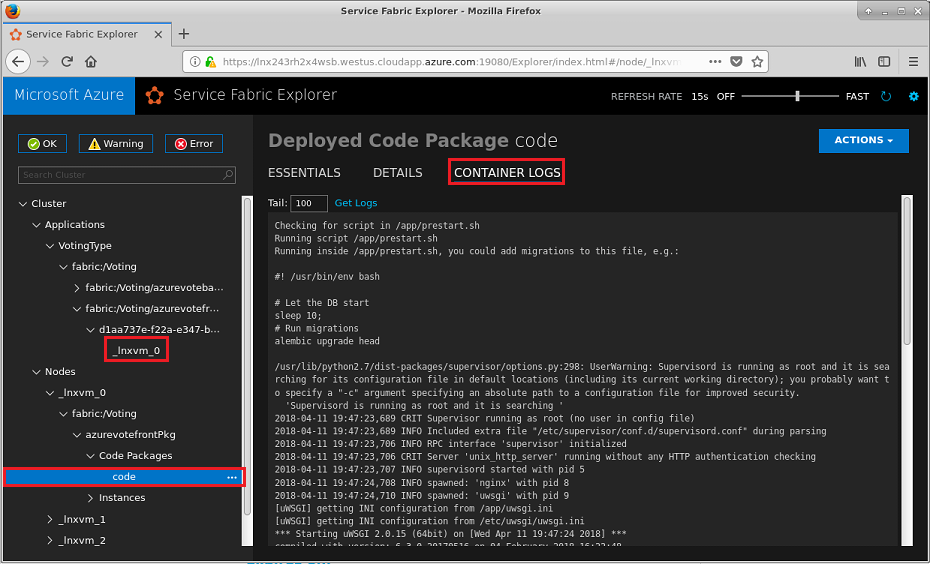
Container logs are located on the cluster node that the container service instance is running on. As an example, get the logs of the web front-end container of the Linux Voting sample application. In the tree view, expand Cluster>Applications>VotingType>fabric:/Voting/azurevotefront. Then expand the partition (d1aa737e-f22a-e347-be16-eec90be24bc1, in this example) and see that the container is running on cluster node _lnxvm_0.
In the tree view, find the code package on the _lnxvm_0 node by expanding Nodes>_lnxvm_0>fabric:/Voting>azurevotfrontPkg>Code Packages>code. Then select the Container Logs option to display the container logs.
Access the logs of a dead or crashed container
Starting in v6.2, you can also fetch the logs for a dead or crashed container using REST APIs or Service Fabric CLI (SFCTL) commands.
Set container retention policy
To assist with diagnosing container startup failures, Service Fabric (version 6.1 or higher) supports retaining containers that terminated or failed to start. This policy can be set in the ApplicationManifest.xml file as shown in the following snippet:
<ContainerHostPolicies CodePackageRef="NodeService.Code" Isolation="process" ContainersRetentionCount="2" RunInteractive="true">
The setting ContainersRetentionCount specifies the number of containers to retain when they fail. If a negative value is specified, all failing containers will be retained. When the ContainersRetentionCount attribute is not specified, no containers will be retained. The attribute ContainersRetentionCount also supports Application Parameters so users can specify different values for test and production clusters. Use placement constraints to target the container service to a particular node when using this feature to prevent the container service from moving to other nodes. Any containers retained using this feature must be manually removed.
The setting RunInteractive corresponds to Docker's --interactive and tty flags. When this setting is set to true in the manifest file, these flags are used to start the container.
REST
Use the Get Container Logs Deployed On Node operation to get the logs for a crashed container. Specify the name of the node that the container was running on, application name, service manifest name, and the code package name. Specify &Previous=true. The response will contain the container logs for the dead container of the code package instance.
The request URI has the following form:
/Nodes/{nodeName}/$/GetApplications/{applicationId}/$/GetCodePackages/$/ContainerLogs?api-version=6.2&ServiceManifestName={ServiceManifestName}&CodePackageName={CodePackageName}&Previous={Previous}
Example request:
GET http://localhost:19080/Nodes/_Node_0/$/GetApplications/SimpleHttpServerApp/$/GetCodePackages/$/ContainerLogs?api-version=6.2&ServiceManifestName=SimpleHttpServerSvcPkg&CodePackageName=Code&Previous=true
200 Response body:
{ "Content": "Exception encountered: System.Net.Http.HttpRequestException: Response status code does not indicate success: 500 (Internal Server Error).\r\n\tat System.Net.Http.HttpResponseMessage.EnsureSuccessStatusCode()\r\n" }
Service Fabric (SFCTL)
Use the sfctl service get-container-logs command to fetch the logs for a crashed container. Specify the name of the node that the container was running on, application name, service manifest name, and the code package name. Specify the --previous flag. The response will contain the container logs for the dead container of the code package instance.
sfctl service get-container-logs --node-name _Node_0 --application-id SimpleHttpServerApp --service-manifest-name SimpleHttpServerSvcPkg --code-package-name Code –-previous
Response:
{ "content": "Exception encountered: System.Net.Http.HttpRequestException: Response status code does not indicate success: 500 (Internal Server Error).\r\n\tat System.Net.Http.HttpResponseMessage.EnsureSuccessStatusCode()\r\n" }
Next steps
- Work through the Create a Linux container application tutorial.
- Learn more about Service Fabric and containers
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for