How to expand virtual hard disks attached to a Windows virtual machine
Applies to: ✔️ Windows VMs ✔️ Flexible scale sets
When you create a new virtual machine (VM) in a resource group by deploying an image from Azure Marketplace, the default operating system (OS) disk is usually 127 GiB (some images have smaller OS disk sizes by default). You can add data disks to your VM (the amount depends on the VM SKU you selected) and we recommend installing applications and CPU-intensive workloads on data disks. You may need to expand the OS disk if you're supporting a legacy application that installs components on the OS disk or if you're migrating a physical PC or VM from on-premises that has a larger OS disk. This article covers expanding either OS disks or data disks.
An OS disk has a maximum capacity of 4,095 GiB. However, many operating systems are partitioned with master boot record (MBR) by default. MBR limits the usable size to 2 TiB. If you need more than 2 TiB, create and attach data disks and use them for data storage. If you need to store data on the OS disk and require the additional space, convert it to GUID Partition Table (GPT). To learn about the differences between MBR and GPT on Windows deployments, see Windows and GPT FAQ.
Important
Unless you use Expand without downtime, expanding a data disk requires the VM to be deallocated.
Shrinking an existing disk isn’t supported and may result in data loss.
After expanding the disks, you need to Expand the volume in the operating system to take advantage of the larger disk.
You can't expand the size of striped volumes.
Expand without downtime
You can expand data disks without deallocating your VM. The host cache setting of your disk doesn't change whether or not you can expand a data disk without deallocating your VM.
This feature has the following limitations:
- Only supported for data disks.
- If a disk is 4 TiB or less, you should deallocate your VM and detach the disk before expanding it beyond 4 TiB. If a disk is already greater than 4 TiB, you can expand it without deallocating the VM and detaching the disk.
- Not supported for Ultra disks or Premium SSD v2 disks.
- Not supported for shared disks.
- Install and use either:
- The latest Azure CLI
- The latest Azure PowerShell module
- The Azure portal
- Or an Azure Resource Manager template with an API version that's
2021-04-01or newer.
- Not available on some classic VMs. Use this script to get a list of classic VM SKUs that support expanding without downtime.
Resize a managed disk in the Azure portal
Important
If your disk meets the requirements in Expand without downtime, you can skip step 1.
In the Azure portal, go to the virtual machine in which you want to expand the disk. Select Stop to deallocate the VM.
In the left menu under Settings, select Disks.
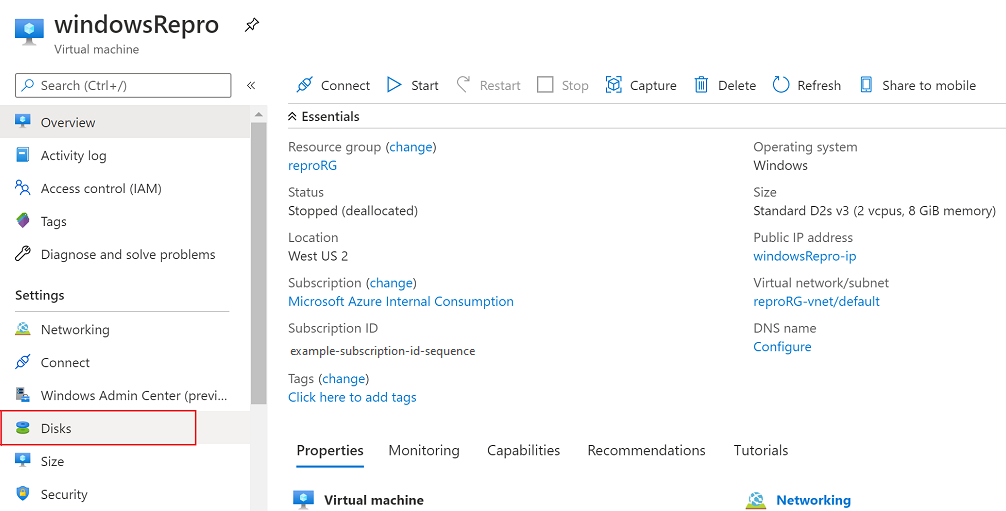
Under Disk name, select the disk you want to expand.
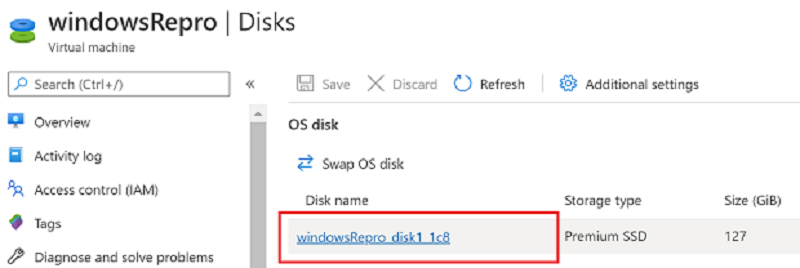
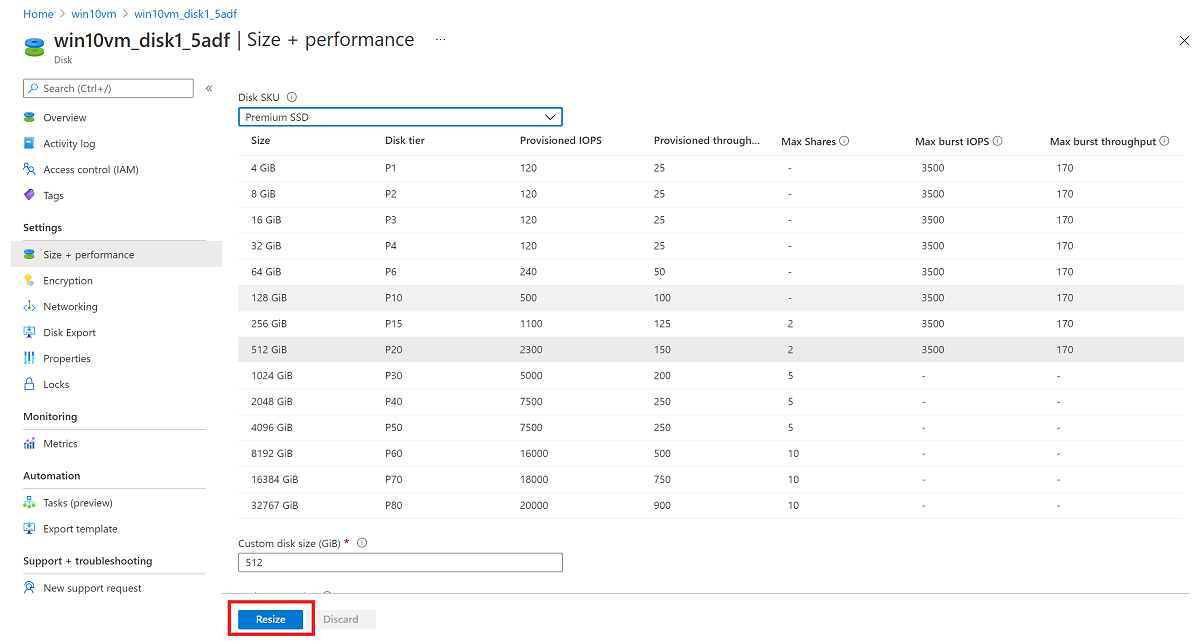
In the left menu under Settings, select Size + performance.
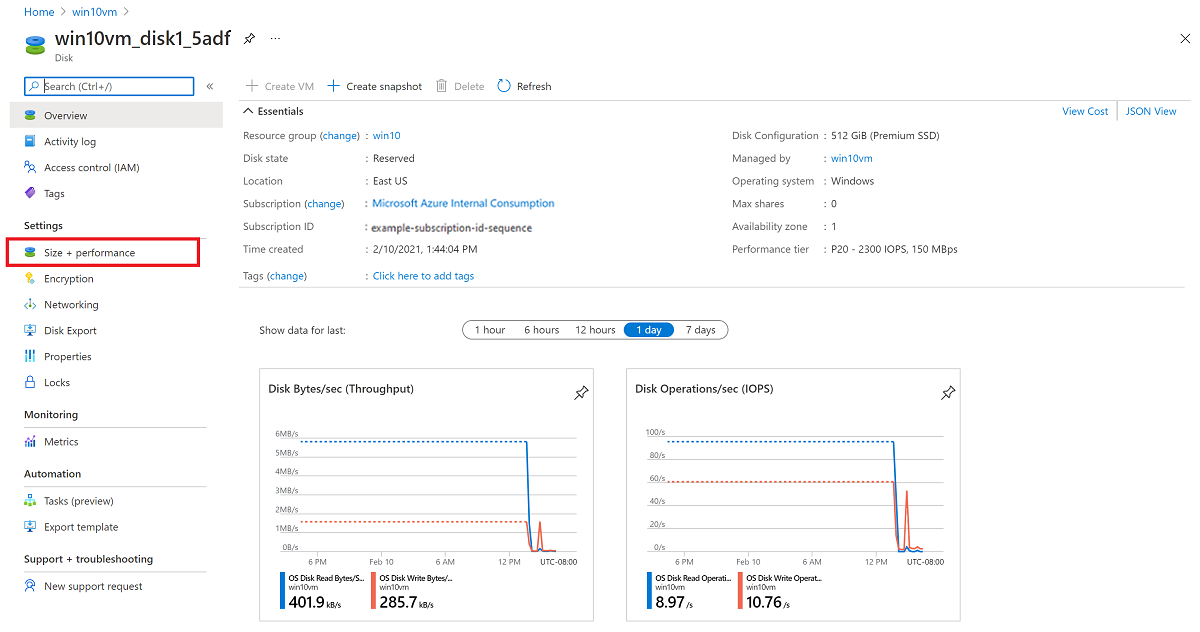
In Size + performance, select the disk size you want.
Warning
The new size should be greater than the existing disk size. The maximum allowed is 4,095 GB for OS disks. (It's possible to expand the VHD blob beyond that size, but the OS works only with the first 4,095 GB of space.)
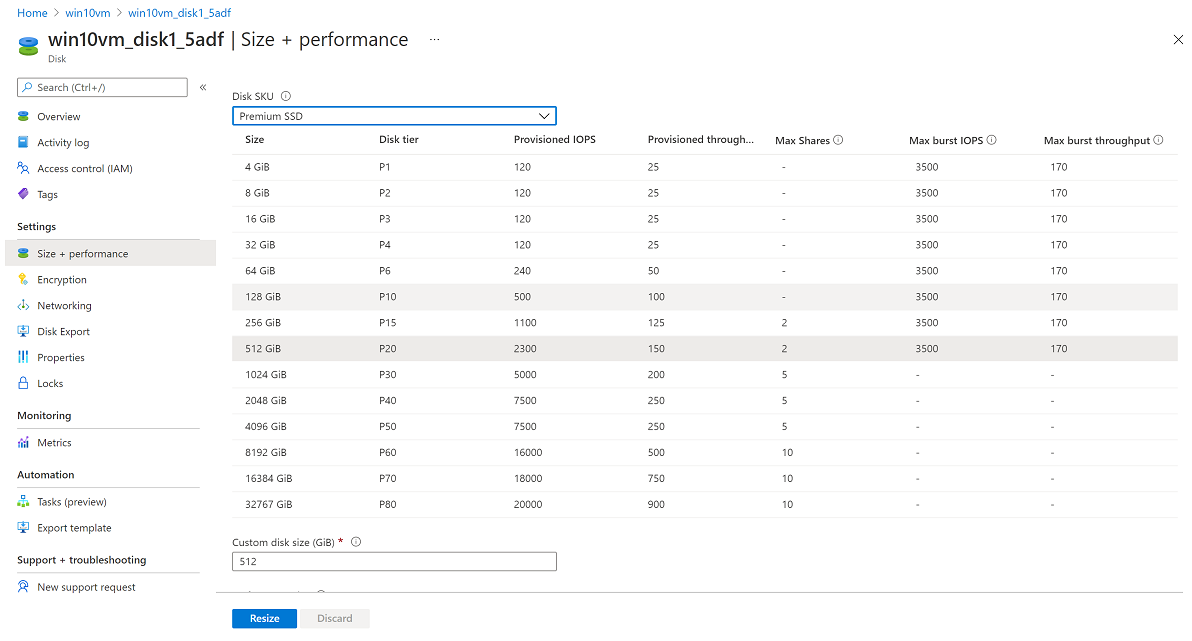
Select Resize at the bottom of the page.
Resize a managed disk by using PowerShell
Open your PowerShell ISE or PowerShell window in administrative mode and follow the steps below:
Sign in to your Microsoft Azure account in resource management mode and select your subscription:
Connect-AzAccount
Select-AzSubscription –SubscriptionName 'my-subscription-name'
Set your resource group name and VM name:
$rgName = 'my-resource-group-name'
$vmName = 'my-vm-name'
$diskName = 'my-disk-name'
Obtain a reference to your VM:
$vm = Get-AzVM -ResourceGroupName $rgName -Name $vmName
Important
If your disk meets the requirements in expand without downtime, you can skip step 4 and 6.
Stop the VM before resizing the disk:
Stop-AzVM -ResourceGroupName $rgName -Name $vmName
Obtain a reference to the managed OS disk. Set the size of the managed OS disk to the desired value and update the Disk:
$disk= Get-AzDisk -ResourceGroupName $rgName -DiskName $diskName
$disk.DiskSizeGB = 1023
Update-AzDisk -ResourceGroupName $rgName -Disk $disk -DiskName $disk.Name
Warning
The new size should be greater than the existing disk size. The maximum allowed is 4,095 GB for OS disks. (It is possible to expand the VHD blob beyond that size, but the OS works only with the first 4,095 GB of space.)
Updating the VM might take a few seconds. When the command finishes executing, restart the VM:
Start-AzVM -ResourceGroupName $rgName -Name $vmName
Remote into the VM, open Computer Management (or Disk Management) and expand the drive using the newly allocated space.
Expand the volume in the operating system
When you've expanded the disk for the VM, you need to go into the OS and expand the volume to encompass the new space. There are several methods for expanding a partition. This section covers connecting the VM using an RDP connection to expand the partition using Using Diskpart or Using Disk Manager.
Using DiskPart
When you've expanded the disk for the VM, you need to go into the OS and expand the volume to encompass the new space. There are several methods for expanding a partition. This section covers connecting the VM using an RDP connection to expand the partition using DiskPart.
Open an RDP connection to your VM.
Open a command prompt and type diskpart.
At the DISKPART prompt, type
list volume. Make note of the volume you want to extend.At the DISKPART prompt, type
select volume <volumenumber>. This selects the volume volumenumber that you want to extend into contiguous, empty space on the same disk.At the DISKPART prompt, type
extend [size=<size>]. This extends the selected volume by size in megabytes (MB).
Using Disk Manager
Start a remote desktop session with the VM.
Open Disk Management.
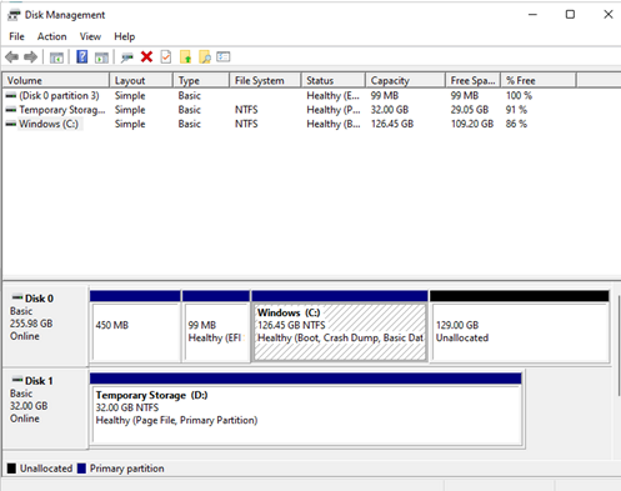
Right-click on existing C: drive partition -> Extend Volume.
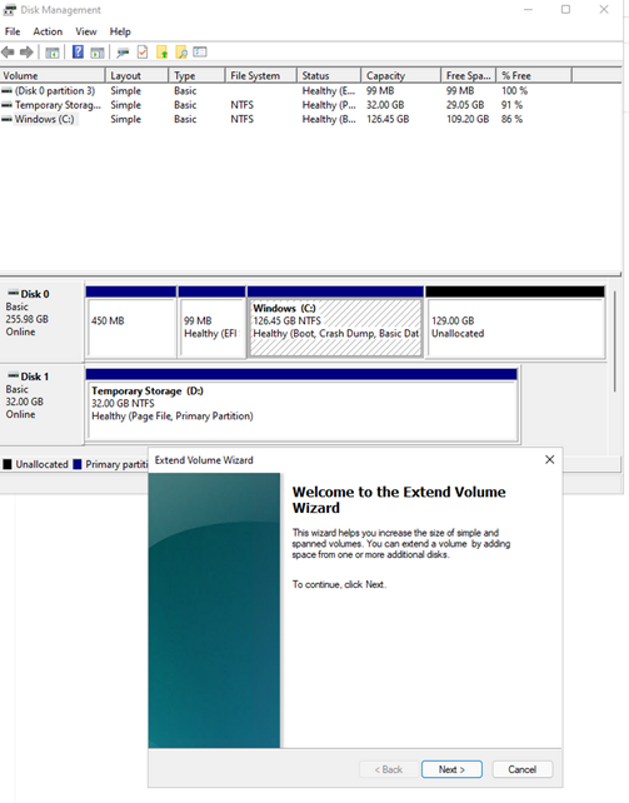
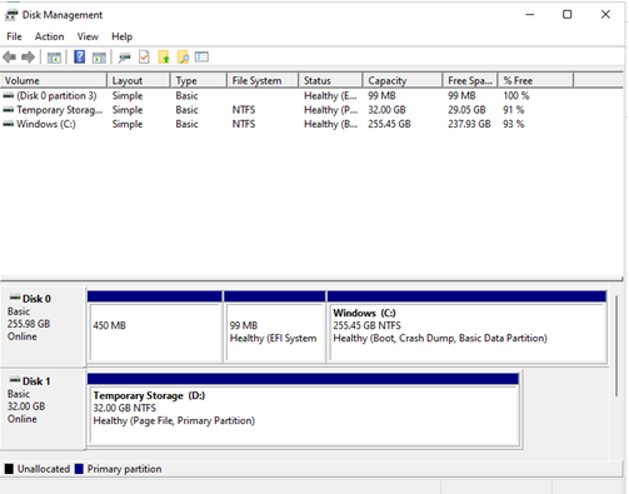
Follow the steps you should be able to see the disk with updated capacity:
Expanding without downtime classic VM SKU support
If you're using a classic VM SKU, it might not support expanding disks without downtime.
Use the following PowerShell script to determine which VM SKUs it's available with:
Connect-AzAccount
$subscriptionId="yourSubID"
$location="desiredRegion"
Set-AzContext -Subscription $subscriptionId
$vmSizes=Get-AzComputeResourceSku -Location $location | where{$_.ResourceType -eq 'virtualMachines'}
foreach($vmSize in $vmSizes){
foreach($capability in $vmSize.Capabilities)
{
if(($capability.Name -eq "EphemeralOSDiskSupported" -and $capability.Value -eq "True") -or ($capability.Name -eq "PremiumIO" -and $capability.Value -eq "True") -or ($capability.Name -eq "HyperVGenerations" -and $capability.Value -match "V2"))
{
$vmSize.Name
}
}
}
Next steps
You can also attach disks using the Azure portal.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for