Tutorial: Create a .NET console application using Visual Studio
This tutorial shows how to create and run a .NET console application in Visual Studio 2022.
Prerequisites
Visual Studio 2022 with the .NET desktop development workload installed. The .NET 8 SDK is automatically installed when you select this workload.
For more information, see Install the .NET SDK with Visual Studio.
Create the app
Create a .NET console app project named "HelloWorld".
Start Visual Studio 2022.
On the start page, choose Create a new project.
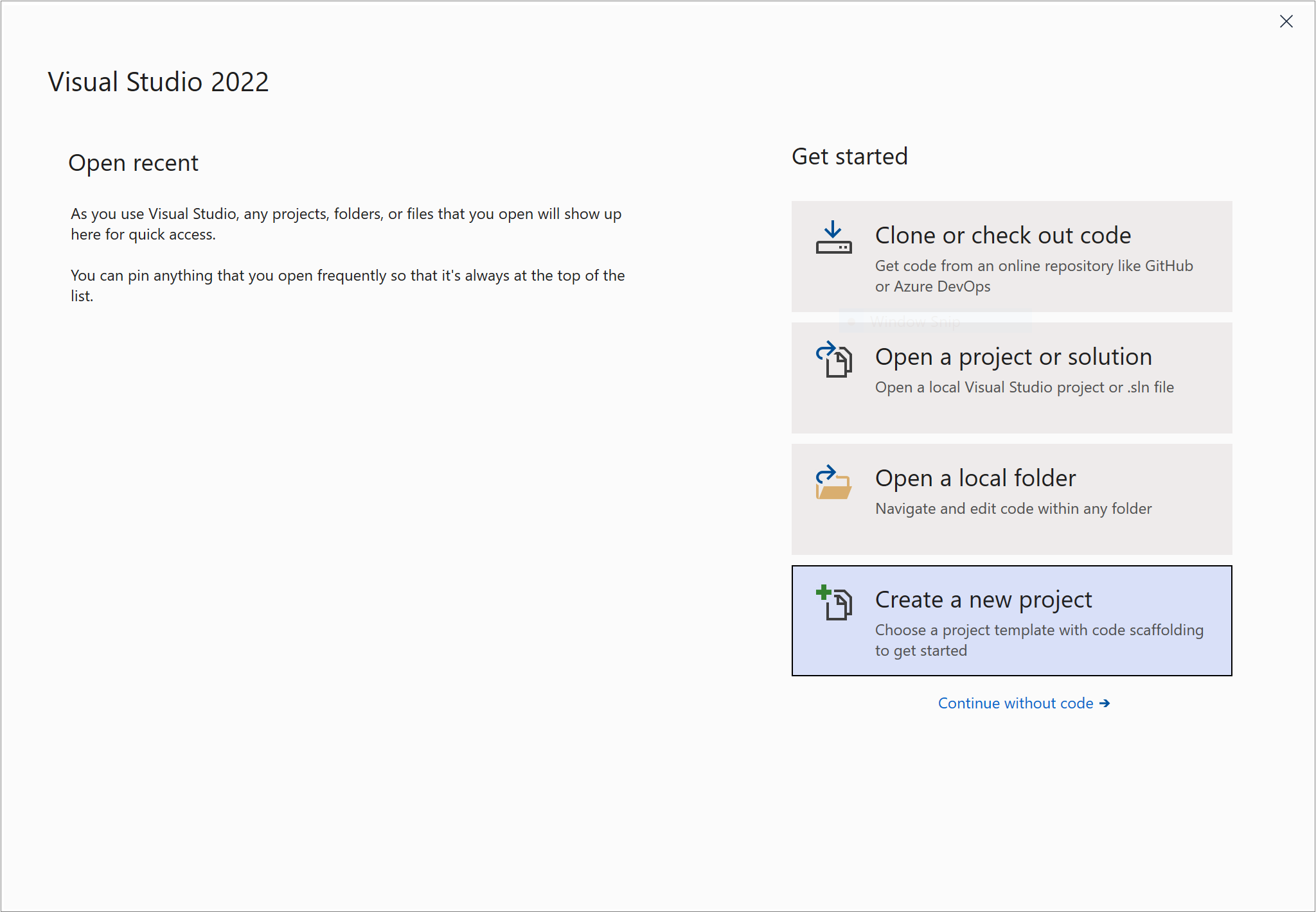
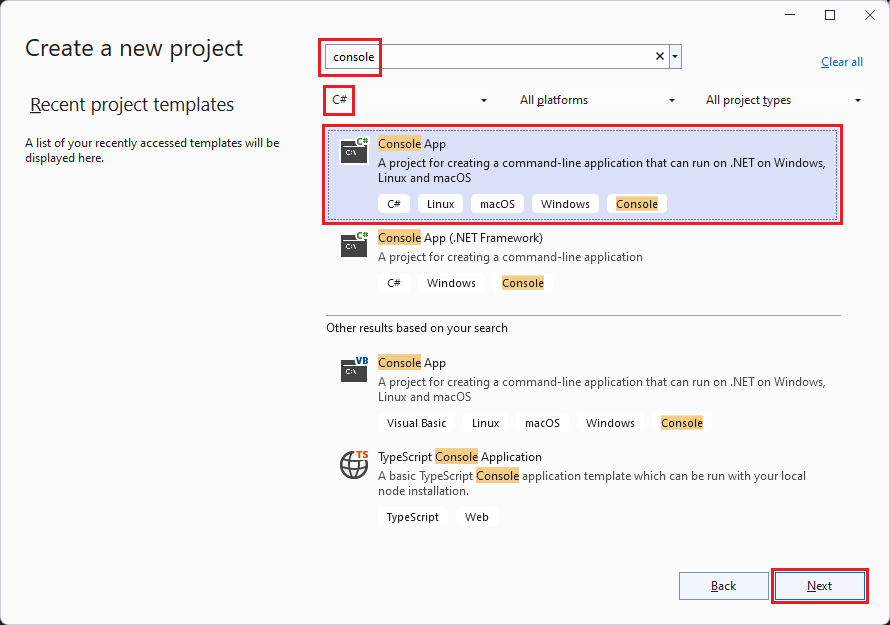
On the Create a new project page, enter console in the search box. Next, choose C# or Visual Basic from the language list, and then choose All platforms from the platform list. Choose the Console App template, and then choose Next.
Tip
If you don't see the .NET templates, you're probably missing the required workload. Under the Not finding what you're looking for? message, choose the Install more tools and features link. The Visual Studio Installer opens. Make sure you have the .NET desktop development workload installed.
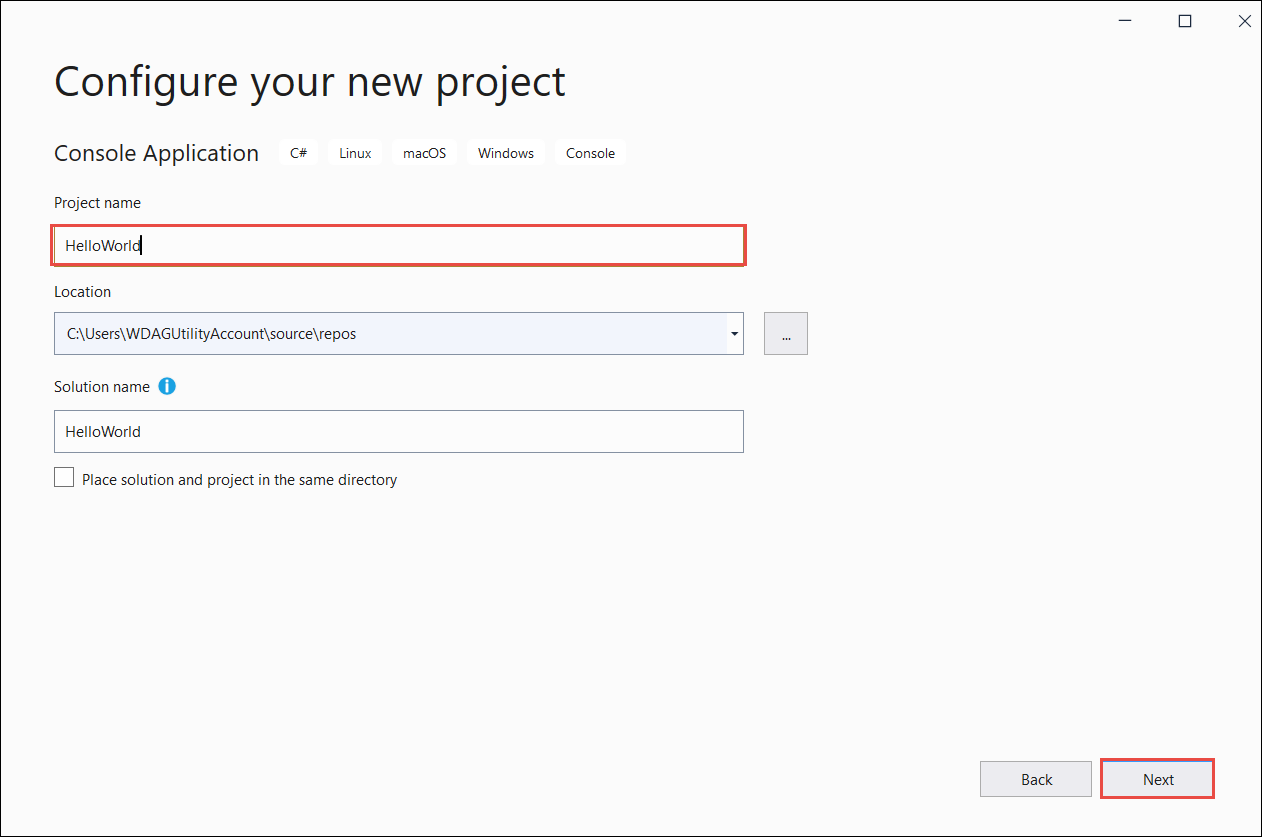
In the Configure your new project dialog, enter HelloWorld in the Project name box. Then choose Next.
In the Additional information dialog:
- Select .NET 8.
- Select Do not use top-level statements.
- Select Create.
The template creates a simple application that displays "Hello, World!" in the console window. The code is in the Program.cs or Program.vb file:
namespace HelloWorld; internal class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Hello, World!"); } }Imports System Module Program Sub Main(args As String()) Console.WriteLine("Hello World!") End Sub End ModuleIf the language you want to use is not shown, change the language selector at the top of the page.
The code defines a class,
Program, with a single method,Main, that takes a String array as an argument.Mainis the application entry point, the method that's called automatically by the runtime when it launches the application. Any command-line arguments supplied when the application is launched are available in the args array.C# has a feature named top-level statements that lets you omit the
Programclass and theMainmethod. This tutorial doesn't use this feature. Whether you use it in your programs is a matter of style preference.
Run the app
Press Ctrl+F5 to run the program without debugging.
A console window opens with the text "Hello, World!" printed on the screen. (Or "Hello World!" without a comma in the Visual Basic project template.)
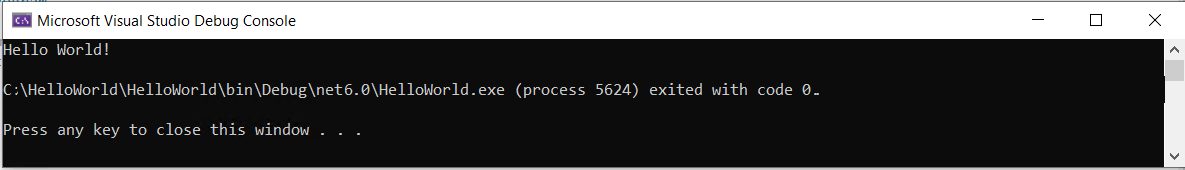
Press any key to close the console window.
Enhance the app
Enhance the application to prompt the user for their name and display it along with the date and time.
In Program.cs or Program.vb, replace the contents of the
Mainmethod, which is the line that callsConsole.WriteLine, with the following code:Console.WriteLine("What is your name?"); var name = Console.ReadLine(); var currentDate = DateTime.Now; Console.WriteLine($"{Environment.NewLine}Hello, {name}, on {currentDate:d} at {currentDate:t}!"); Console.Write($"{Environment.NewLine}Press any key to exit..."); Console.ReadKey(true);Console.WriteLine("What is your name?") Dim name = Console.ReadLine() Dim currentDate = DateTime.Now Console.WriteLine($"{Environment.NewLine}Hello, {name}, on {currentDate:d} at {currentDate:t}") Console.Write($"{Environment.NewLine}Press any key to exit...") Console.ReadKey(True)This code displays a prompt in the console window and waits until the user enters a string followed by the Enter key. It stores this string in a variable named
name. It also retrieves the value of the DateTime.Now property, which contains the current local time, and assigns it to a variable namedcurrentDate. And it displays these values in the console window. Finally, it displays a prompt in the console window and calls the Console.ReadKey(Boolean) method to wait for user input.Environment.NewLine is a platform-independent and language-independent way to represent a line break. Alternatives are
\nin C# andvbCrLfin Visual Basic.The dollar sign (
$) in front of a string lets you put expressions such as variable names in curly braces in the string. The expression value is inserted into the string in place of the expression. This syntax is referred to as interpolated strings.Press Ctrl+F5 to run the program without debugging.
Respond to the prompt by entering a name and pressing the Enter key.
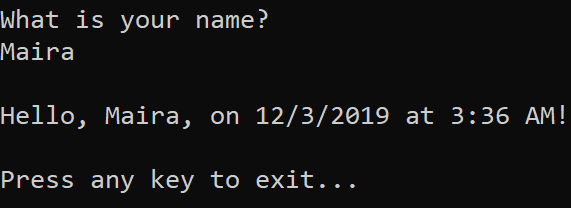
Press any key to close the console window.
Additional resources
Next steps
In this tutorial, you created a .NET console application. In the next tutorial, you debug the app.
This tutorial shows how to create and run a .NET console application in Visual Studio 2022.
Prerequisites
Visual Studio 2022 version 17.4 or later with the .NET desktop development workload installed. The .NET 7 SDK is automatically installed when you select this workload.
For more information, see Install the .NET SDK with Visual Studio.
Create the app
Create a .NET console app project named "HelloWorld".
Start Visual Studio 2022.
On the start page, choose Create a new project.

On the Create a new project page, enter console in the search box. Next, choose C# or Visual Basic from the language list, and then choose All platforms from the platform list. Choose the Console App template, and then choose Next.

Tip
If you don't see the .NET templates, you're probably missing the required workload. Under the Not finding what you're looking for? message, choose the Install more tools and features link. The Visual Studio Installer opens. Make sure you have the .NET desktop development workload installed.
In the Configure your new project dialog, enter HelloWorld in the Project name box. Then choose Next.

In the Additional information dialog:
- Select .NET 7 (Standard-term support).
- Select Do not use top-level statements.
- Select Create.
The template creates a simple application that displays "Hello, World!" in the console window. The code is in the Program.cs or Program.vb file:
namespace HelloWorld; internal class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Hello, World!"); } }Imports System Module Program Sub Main(args As String()) Console.WriteLine("Hello World!") End Sub End ModuleIf the language you want to use is not shown, change the language selector at the top of the page.
The code defines a class,
Program, with a single method,Main, that takes a String array as an argument.Mainis the application entry point, the method that's called automatically by the runtime when it launches the application. Any command-line arguments supplied when the application is launched are available in the args array.In the latest version of C#, a new feature named top-level statements lets you omit the
Programclass and theMainmethod. Most existing C# programs don't use top-level statements, so this tutorial doesn't use this new feature. But it's available in C# 10, and whether you use it in your programs is a matter of style preference.
Run the app
Press Ctrl+F5 to run the program without debugging.
A console window opens with the text "Hello, World!" printed on the screen. (Or "Hello World!" without a comma in the Visual Basic project template.)

Press any key to close the console window.
Enhance the app
Enhance the application to prompt the user for their name and display it along with the date and time.
In Program.cs or Program.vb, replace the contents of the
Mainmethod, which is the line that callsConsole.WriteLine, with the following code:Console.WriteLine("What is your name?"); var name = Console.ReadLine(); var currentDate = DateTime.Now; Console.WriteLine($"{Environment.NewLine}Hello, {name}, on {currentDate:d} at {currentDate:t}!"); Console.Write($"{Environment.NewLine}Press any key to exit..."); Console.ReadKey(true);Console.WriteLine("What is your name?") Dim name = Console.ReadLine() Dim currentDate = DateTime.Now Console.WriteLine($"{Environment.NewLine}Hello, {name}, on {currentDate:d} at {currentDate:t}") Console.Write($"{Environment.NewLine}Press any key to exit...") Console.ReadKey(True)This code displays a prompt in the console window and waits until the user enters a string followed by the Enter key. It stores this string in a variable named
name. It also retrieves the value of the DateTime.Now property, which contains the current local time, and assigns it to a variable namedcurrentDate. And it displays these values in the console window. Finally, it displays a prompt in the console window and calls the Console.ReadKey(Boolean) method to wait for user input.Environment.NewLine is a platform-independent and language-independent way to represent a line break. Alternatives are
\nin C# andvbCrLfin Visual Basic.The dollar sign (
$) in front of a string lets you put expressions such as variable names in curly braces in the string. The expression value is inserted into the string in place of the expression. This syntax is referred to as interpolated strings.Press Ctrl+F5 to run the program without debugging.
Respond to the prompt by entering a name and pressing the Enter key.

Press any key to close the console window.
Additional resources
Next steps
In this tutorial, you created a .NET console application. In the next tutorial, you debug the app.
This tutorial shows how to create and run a .NET console application in Visual Studio 2022.
Prerequisites
Visual Studio 2022 version 17.1 or later with the .NET desktop development workload installed. The .NET 6 SDK is automatically installed when you select this workload.
For more information, see Install the .NET SDK with Visual Studio.
Create the app
Create a .NET console app project named "HelloWorld".
Start Visual Studio 2022.
On the start page, choose Create a new project.

On the Create a new project page, enter console in the search box. Next, choose C# or Visual Basic from the language list, and then choose All platforms from the platform list. Choose the Console Application template, and then choose Next.

Tip
If you don't see the .NET templates, you're probably missing the required workload. Under the Not finding what you're looking for? message, choose the Install more tools and features link. The Visual Studio Installer opens. Make sure you have the .NET desktop development workload installed.
In the Configure your new project dialog, enter HelloWorld in the Project name box. Then choose Next.

In the Additional information dialog, select .NET 6 (Long-term support), and then select Create.
The template creates a simple application that displays "Hello World" in the console window. The code is in the Program.cs or Program.vb file:
Console.WriteLine("Hello, World!");Imports System Module Program Sub Main(args As String()) Console.WriteLine("Hello World!") End Sub End ModuleIf the language you want to use is not shown, change the language selector at the top of the page.
For C#, the code is just a line that calls the Console.WriteLine(String) method to display "Hello World!" in the console window. Replace the contents of Program.cs with the following code:
namespace HelloWorld { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Hello World!"); } } }' This step of the tutorial applies only to C#.The code defines a class,
Program, with a single method,Main, that takes a String array as an argument.Mainis the application entry point, the method that's called automatically by the runtime when it launches the application. Any command-line arguments supplied when the application is launched are available in the args array.In the latest version of C#, a new feature named top-level statements lets you omit the
Programclass and theMainmethod. Most existing C# programs don't use top-level statements, so this tutorial doesn't use this new feature. But it's available in C# 10, and whether you use it in your programs is a matter of style preference.
Run the app
Press Ctrl+F5 to run the program without debugging.
A console window opens with the text "Hello World!" printed on the screen.

Press any key to close the console window.
Enhance the app
Enhance the application to prompt the user for their name and display it along with the date and time.
In Program.cs or Program.vb, replace the contents of the
Mainmethod, which is the line that callsConsole.WriteLine, with the following code:Console.WriteLine("What is your name?"); var name = Console.ReadLine(); var currentDate = DateTime.Now; Console.WriteLine($"{Environment.NewLine}Hello, {name}, on {currentDate:d} at {currentDate:t}!"); Console.Write($"{Environment.NewLine}Press any key to exit..."); Console.ReadKey(true);Console.WriteLine("What is your name?") Dim name = Console.ReadLine() Dim currentDate = DateTime.Now Console.WriteLine($"{Environment.NewLine}Hello, {name}, on {currentDate:d} at {currentDate:t}") Console.Write($"{Environment.NewLine}Press any key to exit...") Console.ReadKey(True)This code displays a prompt in the console window and waits until the user enters a string followed by the Enter key. It stores this string in a variable named
name. It also retrieves the value of the DateTime.Now property, which contains the current local time, and assigns it to a variable namedcurrentDate. And it displays these values in the console window. Finally, it displays a prompt in the console window and calls the Console.ReadKey(Boolean) method to wait for user input.Environment.NewLine is a platform-independent and language-independent way to represent a line break. Alternatives are
\nin C# andvbCrLfin Visual Basic.The dollar sign (
$) in front of a string lets you put expressions such as variable names in curly braces in the string. The expression value is inserted into the string in place of the expression. This syntax is referred to as interpolated strings.Press Ctrl+F5 to run the program without debugging.
Respond to the prompt by entering a name and pressing the Enter key.

Press any key to close the console window.
Additional resources
Next steps
In this tutorial, you created a .NET console application. In the next tutorial, you debug the app.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for
