Create exchange rate providers in finance and operations version 8.0
This article describes the steps that are required in order to set up an exchange rate provider in Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance version 8.0 (April 2018). For the purpose of illustration, the OANDA exchange rate service is used throughout this article.
By following the steps that are described in this article, you can create a functional exchange rate provider. The code is production code. You can find the source in the ExchangeRateProviderOanda class. You can reference that class as you read through this article.
To request an OANDA test account and receive information about the OANDA exchange rate service, go to https://developer.oanda.com/exchange-rates-api/.
Terminology
- Import currency exchange rates – The process that retrieves exchange rates from exchange rate providers and imports them. This process is a system operation that supports batch processing.
- Exchange rate provider – An X++ or C# class that is responsible for retrieving exchange rates from external sources.
- Exchange rate provider registration – The process of enabling an exchange rate provider so that it can be used. By default, exchange rate providers aren't registered when they are deployed.
- Exchange rate provider configuration – The configuration settings of an exchange rate provider that determine how it will be used.
- Exchange rate service – A free or paid subscription service that provides a list of exchange rates that have been published. Foreign Exchange Rates Powered by OANDA is an example of a service that provides exchange rates.
- The framework – The import currency exchange rates framework that coordinates the retrieval of exchange rates from providers and appropriate storage of those exchange rates.
Conceptual/class model
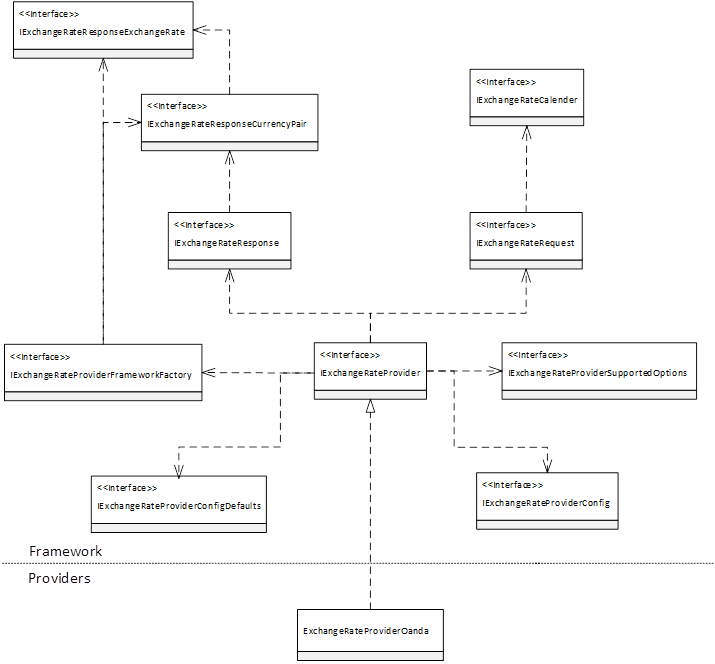
The following illustration shows the main interfaces and classes that make up the exchange rate provider framework, and the relationships among them. New exchange rate providers should be implemented from the IExchangeRateProvider interface. Exchange rate providers are written in X++ or C#. Because X++ is a .NET language, you can easily use the Microsoft .NET Framework. All providers that are written in C# must be wrapped by an X++ class to be recognized as C# providers. For example, the Central Bank of Europe exchange rate provider is a provider that Microsoft wrote in C#. It's wrapped by the ExchangeRateProviderCBOE X++ class.
Here are the interfaces and classes that are shown in the illustration:
- IExchangeRateProvider – By implementing this interface, you enable the exchange rate provider framework to recognize a class as an exchange rate provider.
- IExchangeRateProviderFrameworkFactory – This interface enables the exchange rate provider to construct various types of provider framework classes that represent some of the interfaces in the illustration.
- IExchangeRateProviderSupportedOptions – The exchange rate provider supports several options when rates are imported. The exchange rate provider uses this interface to inform the framework about the options that it supports.
- IExchangeRateProviderConfig – Each exchange rate provider can have a unique configuration. This interface enables the provider to retrieve this configuration.
- IExchangeRateProviderConfigDefaults – The exchange rate provider can create and provide default values for its configuration. Users can change these values on the Configure exchange rate providers page (General ledger > Currencies > Configure exchange rate providers).
- IExchangeRateRequest – This interface represents data that is specific to a request to import exchange rates. This data includes the date range, options, and the currency pairs to retrieve rates for.
- IExchangeRateCalendar – This interface represents an exchange rate calendar that is used to retrieve the next working day (Monday through Friday).
- IExchangeRateResponse – The exchange rate provider uses this interface to store the currency pairs and the exchange rates that are returned from the service.
- IExchangeRateResponseCurrencyPair – The exchange rate provider uses this interface to store the details for a specific currency pair that is returned from the service.
- IExchangeRateResponseExchangeRate – The exchange rate provider uses this interface to store a specific exchange rate for a specific currency pair.
- ExchangeRateProviderOanda – This example of an exchange rate provider that is implemented by Microsoft connects to the OANDA service to return exchange rates.
Write an exchange rate provider
Follow these steps to create an exchange rate provider. The code examples are taken from the ExchangeRateProviderOanda class.
Use extensions to add a new value to the ExchangeRateProvider extensible enum to represent your new exchange rate provider.
In your development model, create a class that implements the IExchangeRateProvider interface.
using Microsoft.Dynamics.ApplicationSuite.FinancialManagement.Currency.Framework; using Microsoft.Dynamics.Currency.Instrumentation; using System.Collections; using System.ComponentModel.Composition; /// <summary> /// The <c>ExchangeRateProviderOanda</c> class is an exchange rate provider for OANDA. /// </summary> [ExportMetadataAttribute(enumStr(ExchangeRateProvider), ExchangeRateProvider::OANDA), ExportAttribute('Microsoft.Dynamics.ApplicationSuite.FinancialManagement.Currency.Framework.IExchangeRateProvider')] class ExchangeRateProviderOanda implements IExchangeRateProvider { }Add the following constants and variable declarations to the class. Provide your own unique globally unique identifier (GUID) for ProviderId.
private const ExchangeRateProviderPropertyKey ServiceURL = 'https://www.oanda.com/rates/api/v1/rates/%1.xml?quote=%2&start=%3&end=%4&fields=%5&decimal_places=%6'; private const ExchangeRateProviderId ProviderId = '795500B1-4258-4343-868C-433CE390848C'; private const str OANDADateFormat = 'yyyy-MM-dd'; private const str HttpWebRequestMethod = 'GET'; private const str HttpWebRequestContentType = 'application/xml'; private const str HttpHeaderAuthorization = 'Authorization'; private const str KeyTokenPrefix = 'Bearer '; private const str XPathQuote = '//response/quotes/quote'; private const str XPathAverageBid = '//bid'; private const str XPathAverageAsk = '//ask'; private const str XPathLowBid = '//low_bid'; private const str XPathLowAsk = '//low_ask'; private const str XPathMidpoint = '//midpoint'; private const str XPathDate = '//quote/date'; private const str XPathHighBid = '//high_bid'; private const str XPathHighAsk = '//high_ask'; private const str QuoteParameterAverages = 'averages'; private const str QuoteParameterLows = 'lows'; private const str QuoteParameterMidPoint = 'midpoint'; private const str QuoteParameterHighs = 'highs'; IExchangeRateProviderFrameworkFactory factory;Implement the get_Name method. You should use a label to enable correct translation. When users set up the provider's configuration information, they can change the name that is provided here.
public ExchangeRateProviderName get_Name() { return "@CurrencyExchange:Currency_ConfigField_OandaName"; }Implement the get_Id method. This method returns a GUID that uniquely identifies this provider.
public ExchangeRateProviderId get_Id() { return ProviderId; }Implement the set_Factory method. The exchange rate provider framework will invoke this method to set an object that implements the IExchangeRateProviderFrameworkFactory interface on your provider. This factory can be used to instantiate new objects that represent some of the interfaces from the previous illustration.
public void set_Factory(IExchangeRateProviderFrameworkFactory _factory) { factory = _factory; }Implement the GetSupportedOptions method. This method indicates whether the exchange rate provider supports some framework features.
Set the doesSupportSpecificCurrencyPairs property to true only if the exchange rate service requires that a source currency and a destination currency be passed to get an exchange rate. Many exchange rate services return rates for a fixed currency or a given set of currency pairs. For these services, this property should be set to false. If the prices that a service charges are based on quotas on the number of rates, a value of true will cause the IExchangeRateRequest interface to contain only those currency pairs that are configured for an exchange rate type on the Exchange rate page (General ledger > Currencies > Exchange rates). The provider can then specifically request these rates from the service and therefore lower the cost.
Set the fixedBaseIsoCurrency property to the three-character International Organization for Standardization (ISO) currency code that represents the fixed base currency of the exchange rates that are returned from the exchange rate service. If the exchange rate service doesn't support a fixed base currency, return an empty string. For example, the euro is often used as a fixed base currency. When you create a new provider, be sure to research the exchange rate service so that you can select the correct value.
Set the singleRateForDateRange property to true if the service can return a single rate that represents the whole date range. For example, you can use this setting to return a single exchange rate that represents the average exchange rate for a month. If the service doesn't support this functionality, set this property to false.
public IExchangeRateProviderSupportedOptions GetSupportedOptions() { IExchangeRateProviderSupportedOptions options = factory.CreateExchangeRateProviderSupportedOptions(); options.set_doesSupportSpecificCurrencyPairs(true); options.set_doesSupportSpecificDates(false); options.set_fixedBaseIsoCurrency(''); options.set_singleRateForDateRange(true); options.set_doesSupportPreventImportOnNationalHoliday(false); return options;
Implement the GetConfigurationDefaults method. Configuration defaults are name-value pairs that represent the default configuration settings for the exchange rate provider. These settings are automatically loaded when the provider is registered, but users can change them. Take the necessary precautions when you convert these strings into usable values. The value field is stored as an encrypted field in SQL. Therefore, sensitive data such as an application programming interface (API) key will be more secure.
public IExchangeRateProviderConfigDefaults GetConfigurationDefaults() { IExchangeRateProviderConfigDefaults configurationDefaults = factory.CreateExchangeRateProviderConfigDefaults(); configurationDefaults.addNameValueConfigurationPair("@CurrencyExchange:Currency_ConfigField_ServiceTimeout", '5000'); configurationDefaults.addNameValueConfigurationPair("@CurrencyExchange:Currency_ConfigField_OandaAPIKey", ''); configurationDefaults.addNameValueConfigurationPair("@CurrencyExchange:Currency_ConfigField_DecimalPlaces", '5'); configurationDefaults.addNameValueConfigurationPair("("@CurrencyExchange:Currency_ConfigField_QuoteTypeLocked", '1'); return configurationDefaults; }Implement the ValidateConfigurationDetail method. This method enables the exchange rate provider to validate the configuration information that the user modifies on the Configure exchange rate providers page.
public boolean ValidateConfigurationDetail(ExchangeRateProviderPropertyKey _key, ExchangeRateProviderPropertyValue _value) { boolean result = true; switch (_key) { case "@CurrencyExchange:Currency_ConfigField_DecimalPlaces": int decimals = str2Int(_value); if ((decimals > 12) || (decimals < 1)) { CurrencyEventSource eventSource = CurrencyEventSource::Log; eventSource.ImportExchangeRateMark("@CurrencyExchange:Currency_ConfigMessage_DecimalPlacesInvalid"); error("@CurrencyExchange:Currency_ConfigMessage_DecimalPlacesInvalid"); result = false; } break; case "@CurrencyExchange:Currency_ConfigField_OandaAPIKey": if (_value == '') { CurrencyEventSource eventSource = CurrencyEventSource::Log; eventSource.ImportExchangeRateMark("@CurrencyExchange:Currency_ConfigMessage_OANDAKeyRequired"); warning("@CurrencyExchange:Currency_ConfigMessage_OANDAKeyRequired"); } break; } return result; }Implement the EnumNameForLookup method. This method enables the exchange rate provider to enable a lookup for a specific ExchangeRateProviderPropertyKey key. Just return the name of an existing enumerated type for the appropriate key. If this feature isn't required, return an empty string.
public str EnumNameForLookup(ExchangeRateProviderPropertyKey _key) { if (_key == "@CurrencyExchange:Currency_ConfigField_QuoteType") { return enumStr(ExchangeRateProviderOANDAQuoteType); } return ''; }Implement the GetExchangeRates method. This method uses the configuration information and the IExchangeRateRequest interface that is provided to call out to the exchange rate service and return the appropriate instance of the IExchangeRateResponse class. When you write this method, consider these important points:
Any configuration information that is required should be retrieved from the IExchangeRateProviderConfig interface. A call to the GetPropertyValue method on that interface will provide the string representation of the property value for the property key that is provided. Take the required precautions when you convert this string value to another type.
Do any required validation up front. For example, OANDA requires that an API key be supplied on every service call. If this API key isn't set, the service will fail. Verify that if the API key isn't set then, throw the appropriate error message to exit prior to importing rates.
Some providers require explicit currency pairs when exchange rates are requested. These providers are the same providers that set the IExchangeRateProviderSupportedOptions.doesSupportSpecificCurrencyPairs property to true. In this case, you must use the currency pairs that the IExchangeRateRequest interface provides to drive the retrieval process. The OANDA provider implementation that follows shows a good example of this type of provider. Typically, providers that don't support specific currency pairs return data for a fixed set of currency pairs. In this case, the currency pairs that the IExchangeRateRequest interface provides can be ignored. Providers should return all the rates that are available. The framework will then import the correct rates, based on the user's decision about whether to automatically create the required currency pairs. The CentralBankOfEuropeProvider provider is a good example of this type of provider.
The IExchangeRateRequest interface has a property that is named ImportDateType. This property indicates the dates that should be used to retrieve exchange rates from the service. The two values that are available are CurrentDate and DateRange.
- CurrentDate retrieves the most current exchange rate from the exchange rate service. When this value is passed to the provider, the framework also sets IExchangeRateRequest.FromDate and IExchangeRateRequest.ToDate to the system date of the Application Object Server (AOS) computer that is making the request. If exchange rate services support the retrieval of exchange rates for specific dates, the date that the framework provides should be passed. However, if the exchange rate service instead provides a call to get the most current exchange rate (regardless of the date), the date that is returned must be validated to make sure that it's less than or equal to the requested date.
- DateRange retrieves the exchange rates for a specific date range. Only exchange rates in the specified date range should be allowed. If an exchange rate service requires that specific dates be included in the request, this process is straightforward. However, if an exchange rate service instead returns a group of historical dates that might be outside the valid range of dates, the provider must filter out the dates that aren't relevant before it passes the dates back to the framework.
When exchange rates are returned, always use the date that the exchange rate service provides instead of the dates that the instance of the IExchangeRateRequest class supplies. In this way, you help guarantee that the exchange rate that is returned is associated with the correct date, because an exchange rate service might occasionally return rates for dates that weren't expected. For example, if an exchange rate is requested for a date in the future, some providers return the most recent exchange rate instead of throwing an error or returning nothing.
If you encounter errors when you try to retrieve exchange rates from the exchange rate service, don't throw custom error messages. The framework will alert the user that there is an issue by throwing generic error messages that state that the expected currency pairs could not be retrieved from the provider. If you must log additional errors, use CurrencyEventSource. For an example, see the catch statement and the if condition for the oandaKey variable in the following code.
public IExchangeRateResponse GetExchangeRates(IExchangeRateRequest _request, IExchangeRateProviderConfig _config) { System.Exception exception; // cache configuration and request properties locally for performance ExchangeRateProviderPropertyValue oandaKey = _config.GetPropertyValue(this.get_Id(), "@CurrencyExchange:Currency_ConfigField_OandaAPIKey"); if (oandaKey == '') { CurrencyEventSource eventSource = CurrencyEventSource::Log; eventSource.ImportRatesException("@CurrencyExchange:Currency_ConfigMessage_OANDAKeyRequired", ""); throw error("@CurrencyExchange:Currency_ConfigMessage_OANDAKeyRequired"); } int decimalPlaces = str2Int(_config.GetPropertyValue(this.get_Id(), "@CurrencyExchange:Currency_ConfigField_DecimalPlaces")); int serviceTimeout = str2int(_config.getPropertyValue(this.get_Id(), "@CurrencyExchange:Currency_ConfigField_ServiceTimeout")); boolean singleRateForDateRange = _request.get_SingleRateForDateRange(); ExchangeRateProviderOANDAQuoteType quoteType = str2Int(_config.getPropertyValue(this.get_Id(), "@CurrencyExchange:Currency_ConfigField_QuoteTypeLocked")); str quoteTypeParameterForOANDA = this.getQuoteTypeParameterForURL(quoteType); List rates = new List(Types::Real); List dates = new List(Types::Date); System.TimeZone localTimeZone = System.TimeZone::get_CurrentTimeZone(); System.DateTime toUTCDate = localTimeZone.ToUniversalTime(_request.get_ToDate()); str toDateForRequest = toUTCDate.ToString(OANDADateFormat); IExchangeRateResponse response = factory.CreateExchangeRateResponse(); // Iterate over the requested currency pairs. This is only required for providers // that support specific currency pairs. IEnumerator currencyPairsEnumerator = _request.GetEnumerator(); while(currencyPairsEnumerator.MoveNext()) { URL OandaUrl = ServiceURL; // This loop will either execute once if singleRateForDateRange is true; otherwise, it will // execute once for each day. If we make a single request for multiple dates // then OANDA will return an average rate for the date range. System.DateTime fromDate = _request.get_FromDate(); int compareResult = fromDate.CompareTo(_request.get_ToDate()); while (compareResult <= 0) { IExchangeRateRequestCurrencyPair currencyPairRequest = currencyPairsEnumerator.Current; IExchangeRateResponseCurrencyPair currencyPairResponse = factory.CreateExchangeRateResponseCurrencyPair(); currencyPairResponse.set_FromCurrency(currencyPairRequest.get_FromCurrency()); currencyPairResponse.set_ToCurrency(currencyPairRequest.get_ToCurrency()); // All rates are requested with a display factor of 1 for this provider. If the rates // internally are represented using a different exchange rate display factor, the // framework will make the necessary adjustments when saving the exchange rates. currencyPairResponse.set_ExchangeRateDisplayFactor(ExchangeRateDisplayFactor::One); // convert to UTC which is required by OANDA System.DateTime fromUTCDate = localTimeZone.ToUniversalTime(fromDate); str fromDateForRequest = fromUTCDate.ToString(OANDADateFormat); // Build the request URL. str oandaRequestString; if (singleRateForDateRange) { // getting an average rate for the date range so we invoke the service // only once per currency pair using the from and to date oandaRequestString = strFmt(OandaUrl, currencyPairRequest.get_FromCurrency(), currencyPairRequest.get_ToCurrency(), fromDateForRequest, toDateForRequest, quoteTypeParameterForOANDA, decimalPlaces); } else { // invoke the service once for each day. oandaRequestString = strFmt(OandaUrl, currencyPairRequest.get_FromCurrency(), currencyPairRequest.get_ToCurrency(), fromDateForRequest, fromDateForRequest, quoteTypeParameterForOANDA, decimalPlaces); } // Configure the request for OANDA. System.Net.HttpWebRequest httpWebRequest = System.Net.WebRequest::CreateHttp(oandaRequestString); httpWebRequest.set_Method(HttpWebRequestMethod); httpWebRequest.set_ContentType(HttpWebRequestContentType); httpWebRequest.set_Timeout(serviceTimeout); // Authentication System.Net.WebHeaderCollection webCollection = httpWebRequest.get_Headers(); webCollection.Add(HttpHeaderAuthorization, KeyTokenPrefix + oandaKey); try { // Invoke the service System.Net.WebResponse webResponse; webResponse = httpWebRequest.GetResponse(); // Retrieve the XML response. System.IO.Stream stream = webResponse.GetResponseStream(); System.IO.StreamReader streamReader = new System.IO.StreamReader(stream); str XMLOut = streamReader.ReadToEnd(); // Parse the XML to retrieve the rate and date. this.processResult(quoteType, singleRateForDateRange, _request.get_FromDate(), XMLOut, rates, dates); ListEnumerator rateEnumerator = rates.getEnumerator(); ListEnumerator dateEnumerator = dates.getEnumerator(); // Create the Exchange Rate Provider Response. rateEnumerator.moveNext(); dateEnumerator.moveNext(); CurrencyExchangeRate exchangeRate = rateEnumerator.current(); date currentDate = dateEnumerator.current(); if (currentDate != dateNull() && exchangeRate) { IExchangeRateResponseExchangeRate exchangeRateResponse = factory.CreateExchangeRateResponseExchangeRate(); exchangeRateResponse.set_ValidFrom(currentDate); exchangeRateResponse.set_ExchangeRate(exchangeRate); currencyPairResponse.addExchangeRate(exchangeRateResponse); } } catch(exception) { CurrencyEventSource eventSource = CurrencyEventSource::Log; eventSource.ImportRatesException(exception.Message, Exception.StackTrace); } response.addOrUpdateCurrencyPair(currencyPairResponse); rates = new List(Types::Real); dates = new List(Types::Date); fromDate = fromDate.AddDays(1); if (singleRateForDateRange) { // getting an average rate across the date range so we invoke the service // only once per currency pair compareResult = 1; } else { compareResult = fromDate.CompareTo(_request.get_ToDate()); } } } return response;Implement the following helper methods. These methods are specific to this example and aren't required for every provider.
private str getQuoteTypeParameterForURL(IExchangeRateProviderConfig _config) { ExchangeRateProviderOANDAQuoteType quoteType = str2Int(_config.getPropertyValue(this.get_Id(), "@CurrencyExchange:Currency_ConfigField_QuoteType")); str quoteTypeParameter; switch (quoteType) { case ExchangeRateProviderOANDAQuoteType::AverageAsk: case ExchangeRateProviderOANDAQuoteType::AverageBid: quoteTypeParameter = QuoteParameterAverages; break; case ExchangeRateProviderOANDAQuoteType::LowAsk: case ExchangeRateProviderOANDAQuoteType::LowBid: quoteTypeParameter = QuoteParameterLows; break; case ExchangeRateProviderOANDAQuoteType::MidPoint: quoteTypeParameter = QuoteParameterMidPoint; break; case ExchangeRateProviderOANDAQuoteType::HighAsk: case ExchangeRateProviderOANDAQuoteType::HighBid: quoteTypeParameter = QuoteParameterHighs; break; } return quoteTypeParameter; } private void readRate(IExchangeRateProviderConfig _config, System.Xml.XmlNode _xmlQuoteNode, List _rates) { System.Xml.XmlNode xmlRateNode; CurrencyExchangeRate exchangeRate; str value; ExchangeRateProviderOANDAQuoteType quoteType = str2Int(_config.getPropertyValue(this.get_Id(), "@CurrencyExchange:Currency_ConfigField_QuoteType")); // Find the exchange rate switch (quoteType) { case ExchangeRateProviderOANDAQuoteType::AverageBid: xmlRateNode = _xmlQuoteNode.SelectSingleNode(XPathAverageBid); break; case ExchangeRateProviderOANDAQuoteType::AverageAsk: xmlRateNode = _xmlQuoteNode.SelectSingleNode(XPathAverageAsk); break; case ExchangeRateProviderOANDAQuoteType::LowBid: xmlRateNode = _xmlQuoteNode.SelectSingleNode(XPathLowBid); break; case ExchangeRateProviderOANDAQuoteType::LowAsk: xmlRateNode = _xmlQuoteNode.SelectSingleNode(XPathLowAsk); break; case ExchangeRateProviderOANDAQuoteType::MidPoint: xmlRateNode = _xmlQuoteNode.SelectSingleNode(XPathMidpoint); break; case ExchangeRateProviderOANDAQuoteType::HighBid: xmlRateNode = _xmlQuoteNode.SelectSingleNode(XPathHighBid); break; case ExchangeRateProviderOANDAQuoteType::HighAsk: xmlRateNode = _xmlQuoteNode.SelectSingleNode(XPathHighAsk); break; } if (xmlRateNode) { value = xmlRateNode.get_InnerText(); exchangeRate = str2num(value); if (exchangeRate) { _rates.addEnd(exchangeRate); } } } private void processResult(IExchangeRateProviderConfig _config, boolean _singleRateForDateRange, System.DateTime _defaultDate, str _xmlString, List _rates, List _dates) { System.Xml.XmlDocument xmlDom = new System.Xml.XmlDocument(); System.Xml.XmlNode xmlQuoteNode, xmlDateNode; ValidFromDate exchangeDate; str value; xmlDom.LoadXml(_xmlString); // Find the Quote xmlQuoteNode = xmlDom.SelectSingleNode(XPathQuote); if (xmlQuoteNode) { this.readRate(_config, xmlQuoteNode, _rates); // Find the date of the exchange rate. xmlDateNode = xmlQuoteNode.SelectSingleNode(XPathDate); if (xmlDateNode || _singleRateForDateRange) { if (xmlDateNode) { value = xmlDateNode.get_InnerText(); } if (value) { // convert the date from UTC to local timezone. exchangeDate = System.DateTime::Parse(value, System.Globalization.CultureInfo::get_CurrentUICulture(), System.Globalization.DateTimeStyles::AssumeUniversal); if (exchangeDate) { _dates.addEnd(exchangeDate); } } else if (!value && _singleRateForDateRange) { exchangeDate = _defaultDate; _dates.addEnd(exchangeDate); } } } }Compile the ExchangeRateProviderOanda class. The provider will be run as part of a SysOperation. It's helpful to understand the following framework classes and methods when you debug issues:
- ExchangeRateProviderFactory.initialize() – This method creates instances of the exchange rate providers, and is called when exchange rates are registered or imported. If your provider isn't instantiated, start to debug here.
- ExchangeRateProviderRegistration.initialize() – This method searches for providers, so that they can be registered. If you can't see your provider on the registration page, start to debug here.
- ExchangeRateImportOperation.import() – This method drives the import process by calling the required provider and storing the exchange rates.
- ExchangeRateProviderConfig – This class provides access to configuration information for the providers.
Ideas to consider
Because there are no limits to the methods that exchange rate providers use to get exchange rates, the framework enables some interesting scenarios. Here are some ideas that you might want to explore:
- Providers that retrieve exchange rates from other exchange rate types – If you implement this scenario, it will enable synchronization of exchange rates among various exchange rate types. This functionality can be useful in situations where many exchange rate types exist, because it will help maintain isolation between different ledgers.
- Providers that use Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformations (XSLT) to transform any format for an exchange rate service into an instance of the ExchangeRateResponse class – If you implement this scenario, users can add the XSLT transform that is required for their exchange rate service, and the application will support the service. Provider-specific code isn't required.
- Some exchange rate provider services charge for every rate that is consumed – Consider combining the first idea in this list with a limit on the number of rates that you retrieve from the service. This functionality can be useful for scenarios where you're charged for each rate that is consumed from the service.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for