Configuration requirements and troubleshooting tips for Xamarin Android with MSAL.NET
There are several configuration changes you're required to make in your code when using Xamarin Android with the Microsoft Authentication Library for .NET (MSAL.NET). The following sections describe the required modifications, followed by a Troubleshooting section to help you avoid some of the most common issues.
Set the parent activity
On Xamarin Android, set the parent activity so the token returns after the interaction:
var authResult = AcquireTokenInteractive(scopes)
.WithParentActivityOrWindow(parentActivity)
.ExecuteAsync();
In MSAL.NET 4.2 and later, you can also set this functionality at the level of PublicClientApplication. To do so, use a callback:
// Requires MSAL.NET 4.2 or later
var pca = PublicClientApplicationBuilder
.Create("<your-client-id-here>")
.WithParentActivityOrWindow(() => parentActivity)
.Build();
If you use CurrentActivityPlugin, then your PublicClientApplication builder code should look similar to this code snippet:
// Requires MSAL.NET 4.2 or later
var pca = PublicClientApplicationBuilder
.Create("<your-client-id-here>")
.WithParentActivityOrWindow(() => CrossCurrentActivity.Current)
.Build();
Ensure that control returns to MSAL
When the interactive portion of the authentication flow ends, return control to MSAL by overriding the Activity.OnActivityResult() method.
In your override, call MSAL.NET's AuthenticationContinuationHelper.SetAuthenticationContinuationEventArgs() method to return control to MSAL at the end of the interactive portion of the authentication flow.
protected override void OnActivityResult(int requestCode,
Result resultCode,
Intent data)
{
base.OnActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
// Return control to MSAL
AuthenticationContinuationHelper.SetAuthenticationContinuationEventArgs(requestCode,
resultCode,
data);
}
Update the Android manifest for System WebView support
To support System WebView, the AndroidManifest.xml file should contain the following values:
<activity android:name="microsoft.identity.client.BrowserTabActivity" android:configChanges="orientation|screenSize" android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data android:scheme="msal{Client Id}" android:host="auth" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
The android:scheme value is created from the redirect URI that's configured in the application portal. For example, if your redirect URI is msal00001111-aaaa-2222-bbbb-3333cccc4444://auth, the android:scheme entry in the manifest would look like this example:
<data android:scheme="msal00001111-aaaa-2222-bbbb-3333cccc4444" android:host="auth" />
Alternatively, create the activity in code rather than manually editing AndroidManifest.xml. To create the activity in code, first create a class that includes the Activity attribute and the IntentFilter attribute.
Here's an example of a class that represents the values of the XML file:
[Activity(Exported = true)]
[IntentFilter(new[] { Intent.ActionView },
Categories = new[] { Intent.CategoryBrowsable, Intent.CategoryDefault },
DataHost = "auth",
DataScheme = "msal{client_id}")]
public class MsalActivity : BrowserTabActivity
{
}
Use System WebView in brokered authentication
To use System WebView as a fallback for interactive authentication when you've configured your application to use brokered authentication and the device doesn't have a broker installed, enable MSAL to capture the authentication response by using the broker's redirect URI. MSAL will try to authenticate by using the default System WebView on the device when it detects that the broker is unavailable. Using this default, it will fail because the redirect URI is configured to use a broker, and System WebView doesn't know how to use it to return to MSAL. To resolve this, create an intent filter by using the broker redirect URI that you configured earlier. Add the intent filter by modifying your application's manifest like this example:
<!--Intent filter to capture System WebView or Authenticator calling back to our app after sign-in-->
<activity
android:name="microsoft.identity.client.BrowserTabActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data android:scheme="msauth"
android:host="Enter_the_Package_Name"
android:path="/Enter_the_Signature_Hash" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
Substitute the package name that you registered in the Azure portal for the android:host= value. Substitute the key hash that you registered in the Azure portal for the android:path= value. The signature hash should not be URL-encoded. Ensure that a leading forward slash (/) appears at the beginning of your signature hash.
Xamarin.Forms 4.3.x manifest
Xamarin.Forms 4.3.x generates code that sets the package attribute to com.companyname.{appName} in AndroidManifest.xml. If you use DataScheme as msal{client_id}, then you might want to change the value to match the value of the MainActivity.cs namespace.
Android 11 support
To use the system browser and brokered authentication in Android 11, you must first declare these packages, so they are visible to the app. Apps that target Android 10 (API 29) and earlier can query the OS for a list of packages that are available on the device at any given time. To support privacy and security, Android 11 reduces package visibility to a default list of OS packages and the packages that are specified in the app's AndroidManifest.xml file.
To enable the application to authenticate by using both the system browser and the broker, add the following section to AndroidManifest.xml:
<!-- Required for API Level 30 to make sure the app can detect browsers and other apps where communication is needed.-->
<!--https://developer.android.com/training/basics/intents/package-visibility-use-cases-->
<queries>
<package android:name="com.azure.authenticator" />
<package android:name="{Package Name}" />
<package android:name="com.microsoft.windowsintune.companyportal" />
<!-- Required for API Level 30 to make sure the app detect browsers
(that don't support custom tabs) -->
<intent>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
</intent>
<!-- Required for API Level 30 to make sure the app can detect browsers that support custom tabs -->
<!-- https://developers.google.com/web/updates/2020/07/custom-tabs-android-11#detecting_browsers_that_support_custom_tabs -->
<intent>
<action android:name="android.support.customtabs.action.CustomTabsService" />
</intent>
</queries>
Replace {Package Name} with the application package name.
Your updated manifest, which now includes support for the system browser and brokered authentication, should look similar to this example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0" package="com.companyname.XamarinDev">
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="21" android:targetSdkVersion="30" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<application android:theme="@android:style/Theme.NoTitleBar">
<activity android:name="microsoft.identity.client.BrowserTabActivity" android:configChanges="orientation|screenSize">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data android:scheme="msal00001111-aaaa-2222-bbbb-3333cccc4444" android:host="auth" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data android:scheme="msauth" android:host="com.companyname.XamarinDev" android:path="/Fc4l/5I4mMvLnF+l+XopDuQ2gEM=" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
<!-- Required for API Level 30 to make sure we can detect browsers and other apps we want to
be able to talk to.-->
<!--https://developer.android.com/training/basics/intents/package-visibility-use-cases-->
<queries>
<package android:name="com.azure.authenticator" />
<package android:name="com.companyname.xamarindev" />
<package android:name="com.microsoft.windowsintune.companyportal" />
<!-- Required for API Level 30 to make sure we can detect browsers
(that don't support custom tabs) -->
<intent>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
</intent>
<!-- Required for API Level 30 to make sure we can detect browsers that support custom tabs -->
<!-- https://developers.google.com/web/updates/2020/07/custom-tabs-android-11#detecting_browsers_that_support_custom_tabs -->
<intent>
<action android:name="android.support.customtabs.action.CustomTabsService" />
</intent>
</queries>
</manifest>
Use the embedded web view (optional)
By default, MSAL.NET uses the system web browser. This browser enables you to get single sign-on (SSO) by using web applications and other apps. In some rare cases, you might want your system to use an embedded web view.
This code example shows how to set up an embedded web view:
bool useEmbeddedWebView = !app.IsSystemWebViewAvailable;
var authResult = AcquireTokenInteractive(scopes)
.WithParentActivityOrWindow(parentActivity)
.WithEmbeddedWebView(useEmbeddedWebView)
.ExecuteAsync();
For more information, see Use web browsers for MSAL.NET and Xamarin Android system browser considerations.
Troubleshooting
General tips
- Update the existing MSAL.NET NuGet package to the latest version of MSAL.NET.
- Verify that Xamarin.Forms is on the latest version.
- Verify that Xamarin.Android.Support.v4 is on the latest version.
- Ensure all the Xamarin.Android.Support packages target the latest version.
- Clean or rebuild the application.
- In Visual Studio, try setting the maximum number of parallel project builds to 1. To do that, select Options > Projects and Solutions > Build and Run > Maximum number of parallel projects builds.
- If you're building from the command line and your command uses
/m, try removing this element from the command.
Error: The name AuthenticationContinuationHelper doesn't exist in the current context
If an error indicates that AuthenticationContinuationHelper doesn't exist in the current context, Visual Studio might have incorrectly updated the Android.csproj* file. Sometimes the file path in the <HintPath> element incorrectly contains netstandard13 instead of monoandroid90.
This example contains a correct file path:
<Reference Include="Microsoft.Identity.Client, Version=3.0.4.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=0a613f4dd989e8ae,
processorArchitecture=MSIL">
<HintPath>..\..\packages\Microsoft.Identity.Client.3.0.4-preview\lib\monoandroid90\Microsoft.Identity.Client.dll</HintPath>
</Reference>
Next steps
For more information, see the sample of a Xamarin mobile application that uses Microsoft identity platform. The following table summarizes the relevant information in the README file.
| Sample | Platform | Description |
|---|---|---|
| https://github.com/Azure-Samples/active-directory-xamarin-native-v2 | Xamarin.iOS, Android, UWP | A Xamarin mobile application that shows how to use MSAL.NET to authenticate work or school and Microsoft personal accounts with the Microsoft identity platform, and access the Microsoft Graph API with the resulting token. 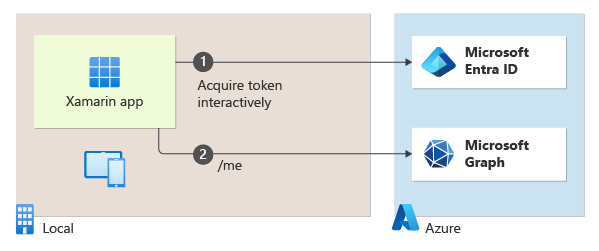 |
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for