Get JavaScript IntelliSense in Visual Studio
When you use Visual Studio 2019 and later to develop Office Add-ins, you can use JSDoc to enable IntelliSense for your JavaScript variables, objects, parameters, and return values. This article provides an overview of JSDoc and how you can use it to create IntellSense in Visual Studio. For more details, see JavaScript IntelliSense and JSDoc support in JavaScript.
Office.js type definitions
You need to provide the definitions of the types in Office.js to Visual Studio. To do this, you can:
Have a local copy of the Office.js files in a folder in your solution named
\Office\1\. The Office Add-in project templates in Visual Studio add this local copy when you create an add-in project.Use an online version of Office.js by adding a tsconfig.json file to the root of the web application project in the add-in solution. The file should include the following content.
{ "compilerOptions": { "allowJs": true, // These settings apply to JavaScript files also. "noEmit": true // Do not compile the JS (or TS) files in this project. }, "exclude": [ "node_modules", // Don't include any JavaScript found under "node_modules". "Scripts/Office/1" // Suppress loading all the JavaScript files from the Office NuGet package. ], "typeAcquisition": { "enable": true, // Enable automatic fetching of type definitions for detected JavaScript libraries. "include": [ "office-js" ] // Ensure that the "Office-js" type definition is fetched. } }
JSDoc syntax
The basic technique is to precede the variable (or parameter, and so on) with a comment that identifies its data type. This allows IntelliSense in Visual Studio to infer its members. The following are examples.
Variable
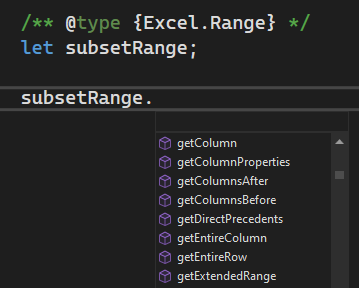
/** @type {Excel.Range} */
let subsetRange;
Parameter
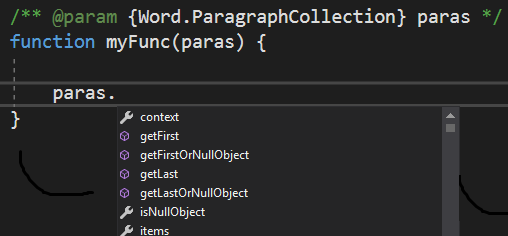
/** @param {Word.ParagraphCollection} paragraphs */
function myFunc(paragraphs){
}
Return value
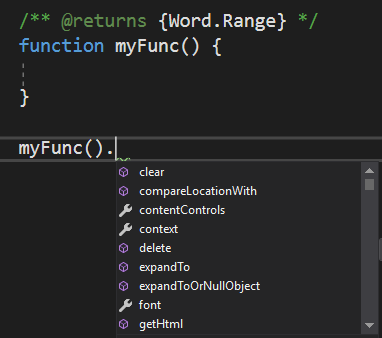
/** @returns {Word.Range} */
function myFunc() {
}
Complex types
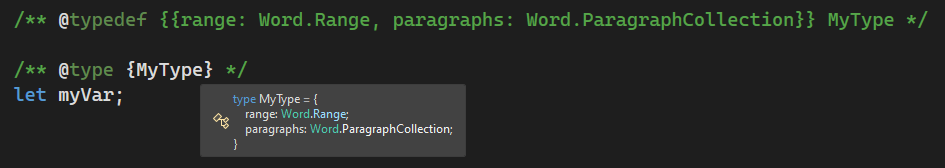
/** @typedef {{range: Word.Range, paragraphs: Word.ParagraphCollection}} MyType
/** @returns {MyType} */
function myFunc() {
}
See also
Office Add-ins
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for