3.7 Example 7: Creating a Scheduled Report Job
This example demonstrates the use cases described in section 2.5.4.2.
The admin client creates a report job and configures it.
Prerequisites
The participating client and server computers are configured to belong to the same Active Directory domain.
The admin tool has acquired an RPC calling context that provides the FSRM server ([MS-FSRM] section 2.1).
Initial System State
None.
Final System State
The report job is created and configured.
The following sequence diagram shows the steps to create and configure a scheduled report job.
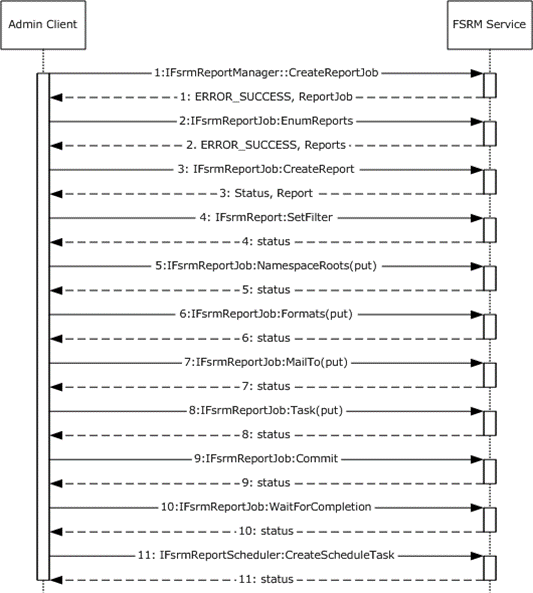
Figure 20: Sequence diagram for creating and configuring a scheduled report job
Sequence of Events
The admin client creates a report job instance by using the IFsrmReportManager::CreateReportJob method ([MS-FSRM] section 3.2.4.2.33.2). The FSRM Service returns a pointer to the created report job and a success code.
The admin client calls the IFsrmReportJob::EnumReports method to enumerate all the reports that are configured for the newly created job. The server returns S_OK upon successful completion ([MS-FSRM] section 3.2.4.2.34.14).
The admin client creates a report by calling the IFsrmReportJob::CreateReport method for each of the report types to add the report to the report job ([MS-FSRM] section 3.2.4.2.34.15). The FSRM Service returns a pointer to the created reports and a success code.
The admin client sets the filter of the created report objects by calling the IFsrmReport::SetFilter method for each report object to set the filter ([MS-FSRM] section 3.2.4.2.35.8). The FSRM Service returns a success code.
The admin client sets the NamespaceRoots of the newly created Report Job by calling the IFsrmReportJob::NamespaceRoots(put) method ([MS-FSRM] section 3.2.4.2.34.5). The FSRM Service returns a success code.
The admin client sets the list of report formats that the report job creates when the report job is generated by calling the IFsrmReportJob::Formats(put) method ([MS-FSRM] section 3.2.4.2.34.7). The FSRM Service returns a success code.
The admin client sets the email address recipient list to which the reports are emailed when the report job is successfully finished by calling the IFsrmReportJob::MailTo(put) method ([MS-FSRM] section 3.2.4.2.34.9). The FSRM Service returns a success code.
The Admin client calls the IFsrmReportJob::Task(put) method ([MS-FSRM] section 3.2.4.2.34.3), with the name of the scheduled task to be used in step 11. The FSRM Service returns a success code.
The admin client persists the report by calling the IFsrmReportJob::Commit method ([MS-FSRM] section 3.2.4.2.34.1). The FSRM Service returns a success code.
The admin client calls the IFsrmReportJob::WaitForCompletion method to wait until report task is finished ([MS-FSRM] section 3.2.4.2.34.17). The FSRM Service returns a success code.
The admin client calls the IFsrmReportScheduler::CreateScheduleTask method ([MS-FSRM] section 3.2.4.2.36.2) that passes in the name, namespaces as used in step 8, and serialized text for the task. The FSRM Service returns a success code.