Highlight data points in Power BI Visuals
This article describes how to highlight data on Power BI visuals.
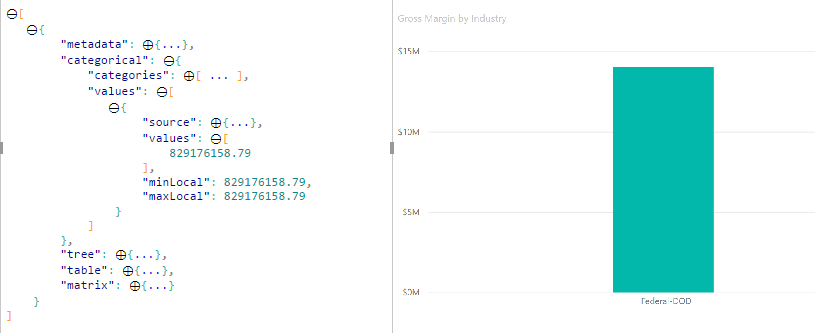
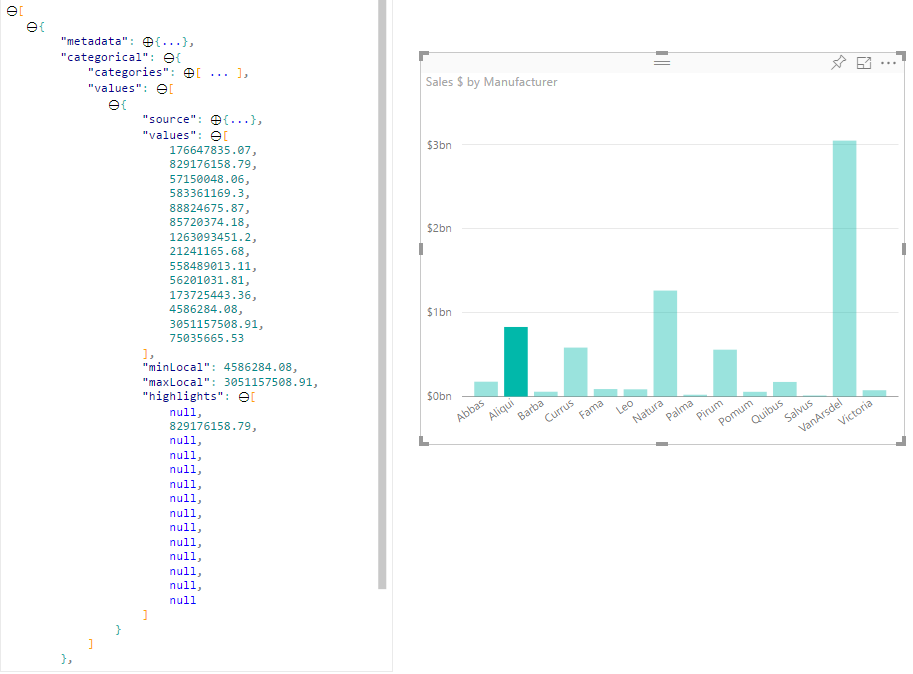
By default, when an element is selected, the values array in the dataView object is filtered to only show the selected values. When the values array is filtered, all other visuals on the page only show the selected data.
If you set the supportsHighlight property in your capabilities.json file to true, it results in the full unfiltered values array along with a highlights array. The highlights array is the same length as the values array, and any unselected values are set to null. With this property enabled, the appropriate data in the visual is highlighted by comparing the values array to the highlights array.
In the example, notice that:
- Without highlight support, the selection is the only value in the
valuesarray and the only bar presented in the data view. - With highlight support, all values are in the
valuesarray. Thehighlightsarray contains anullvalue for non-highlighted elements. All bars appear in the data view, and the highlighted bar is a different color.
There can also be multiple selections and partial highlights. The highlighted values are presented in the data view.
Note
Table data view mapping doesn't support the highlights feature.
Highlight data points with categorical data view mapping
For visuals with categorical data view mapping, add "supportsHighlight": true to the capabilities.json file. For example:
{
"dataRoles": [
{
"displayName": "Category",
"name": "category",
"kind": "Grouping"
},
{
"displayName": "Value",
"name": "value",
"kind": "Measure"
}
],
"dataViewMappings": [
{
"categorical": {
"categories": {
"for": {
"in": "category"
}
},
"values": {
"for": {
"in": "value"
}
}
}
}
],
"supportsHighlight": true
}
After you remove unnecessary code, the default visual source code looks like the following example:
"use strict";
// ... default imports list
import { FormattingSettingsService } from "powerbi-visuals-utils-formattingmodel";
import DataViewCategorical = powerbi.DataViewCategorical;
import DataViewCategoryColumn = powerbi.DataViewCategoryColumn;
import PrimitiveValue = powerbi.PrimitiveValue;
import DataViewValueColumn = powerbi.DataViewValueColumn;
import { VisualFormattingSettingsModel } from "./settings";
export class Visual implements IVisual {
private target: HTMLElement;
private formattingSettings: VisualFormattingSettingsModel;
private formattingSettingsService: FormattingSettingsService;
constructor(options: VisualConstructorOptions) {
console.log('Visual constructor', options);
this.formattingSettingsService = new FormattingSettingsService();
this.target = options.element;
this.host = options.host;
}
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
this.formattingSettings = this.formattingSettingsService.populateFormattingSettingsModel(VisualFormattingSettingsModel, options.dataViews);
console.log('Visual update', options);
}
// Returns properties pane formatting model content hierarchies, properties and latest formatting values, Then populate properties pane.
// This method is called once every time we open properties pane or when the user edit any format property.
public getFormattingModel(): powerbi.visuals.FormattingModel {
return this.formattingSettingsService.buildFormattingModel(this.formattingSettings);
}
}
Import required interfaces to process data from Power BI:
import DataViewCategorical = powerbi.DataViewCategorical;
import DataViewCategoryColumn = powerbi.DataViewCategoryColumn;
import PrimitiveValue = powerbi.PrimitiveValue;
import DataViewValueColumn = powerbi.DataViewValueColumn;
Create the root div element for category values:
export class Visual implements IVisual {
private target: HTMLElement;
private formattingSettings: VisualFormattingSettingsModel;
private formattingSettingsService: FormattingSettingsService;
private div: HTMLDivElement; // new property
constructor(options: VisualConstructorOptions) {
console.log('Visual constructor', options);
this.formattingSettingsService = new FormattingSettingsService();
this.target = options.element;
this.host = options.host;
// create div element
this.div = document.createElement("div");
this.div.classList.add("vertical");
this.target.appendChild(this.div);
}
// ...
}
Clear the contents of the div elements before rendering new data:
// ...
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
this.formattingSettings = this.formattingSettingsService.populateFormattingSettingsModel(VisualFormattingSettingsModel, options.dataViews);
console.log('Visual update', options);
while (this.div.firstChild) {
this.div.removeChild(this.div.firstChild);
}
// ...
}
Get the categories and measure values from the dataView object:
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
this.formattingSettings = this.formattingSettingsService.populateFormattingSettingsModel(VisualFormattingSettingsModel, options.dataViews);
console.log('Visual update', options);
while (this.div.firstChild) {
this.div.removeChild(this.div.firstChild);
}
const dataView: DataView = options.dataViews[0];
const categoricalDataView: DataViewCategorical = dataView.categorical;
const categories: DataViewCategoryColumn = categoricalDataView.categories[0];
const categoryValues = categories.values;
const measures: DataViewValueColumn = categoricalDataView.values[0];
const measureValues = measures.values;
const measureHighlights = measures.highlights;
// ...
}
Where categoryValues is an array of category values, measureValues is an array of measures, and measureHighlights is the highlighted parts of values.
Note
If values of the measureHighlights property are less than values of the categoryValues property, then the value was partially highlighted.
Enumerate the categoryValues array and get corresponding values and highlights:
// ...
const measureHighlights = measures.highlights;
categoryValues.forEach((category: PrimitiveValue, index: number) => {
const measureValue = measureValues[index];
const measureHighlight = measureHighlights && measureHighlights[index] ? measureHighlights[index] : null;
console.log(category, measureValue, measureHighlight);
});
Create div and p elements to display and visualize data view values in the visual DOM:
categoryValues.forEach((category: PrimitiveValue, index: number) => {
const measureValue = measureValues[index];
const measureHighlight = measureHighlights && measureHighlights[index] ? measureHighlights[index] : null;
console.log(category, measureValue, measureHighlight);
// div element. it contains elements to display values and visualize value as progress bar
let div = document.createElement("div");
div.classList.add("horizontal");
this.div.appendChild(div);
// div element to visualize value of measure
let barValue = document.createElement("div");
barValue.style.width = +measureValue * 10 + "px";
barValue.style.display = "flex";
barValue.classList.add("value");
// element to display category value
let bp = document.createElement("p");
bp.innerText = category.toString();
// div element to visualize highlight of measure
let barHighlight = document.createElement("div");
barHighlight.classList.add("highlight")
barHighlight.style.backgroundColor = "blue";
barHighlight.style.width = +measureHighlight * 10 + "px";
// element to display highlighted value of measure
let p = document.createElement("p");
p.innerText = `${measureHighlight}/${measureValue}`;
barHighlight.appendChild(bp);
div.appendChild(barValue);
barValue.appendChild(barHighlight);
div.appendChild(p);
});
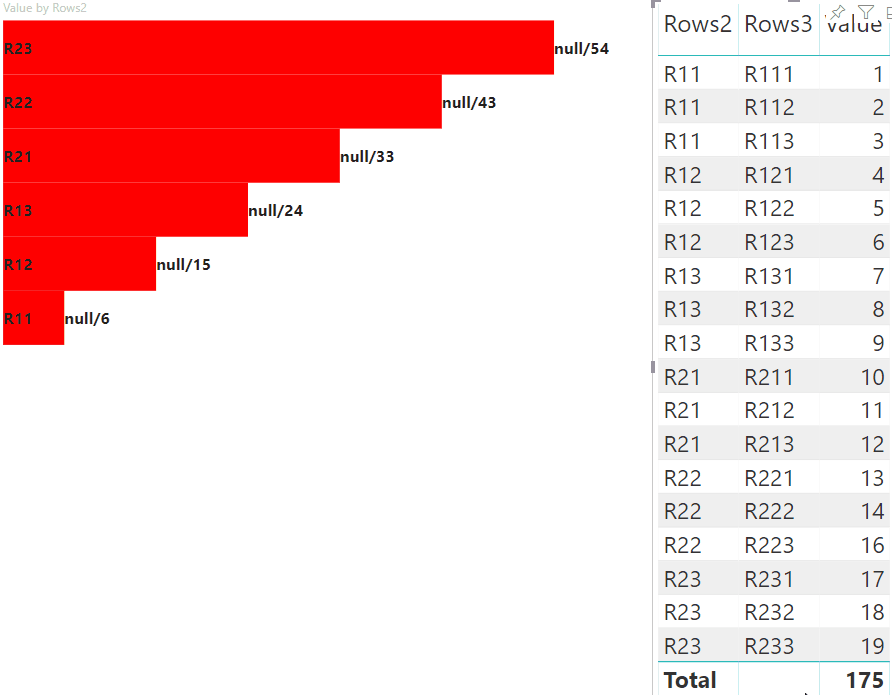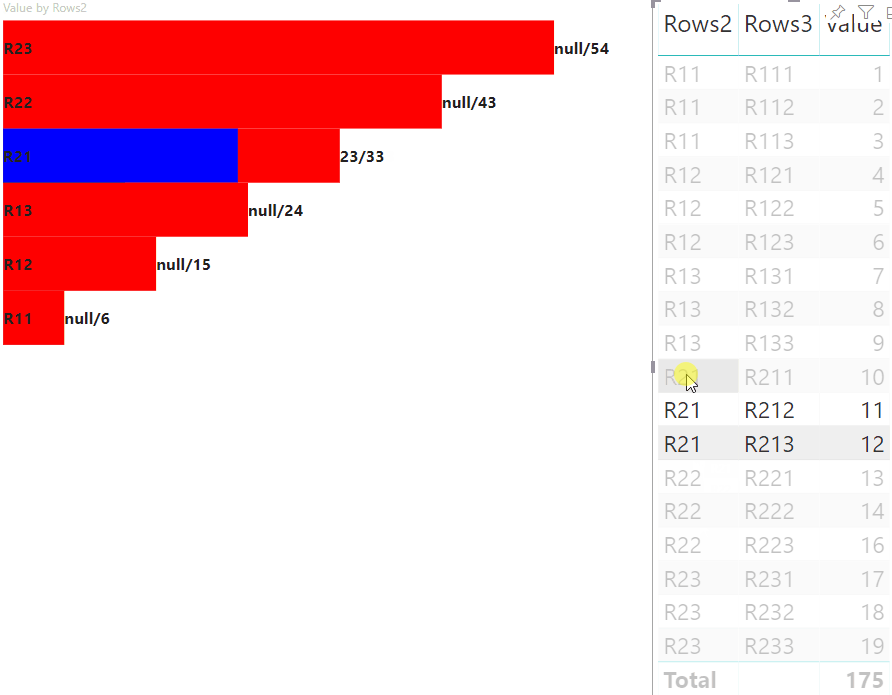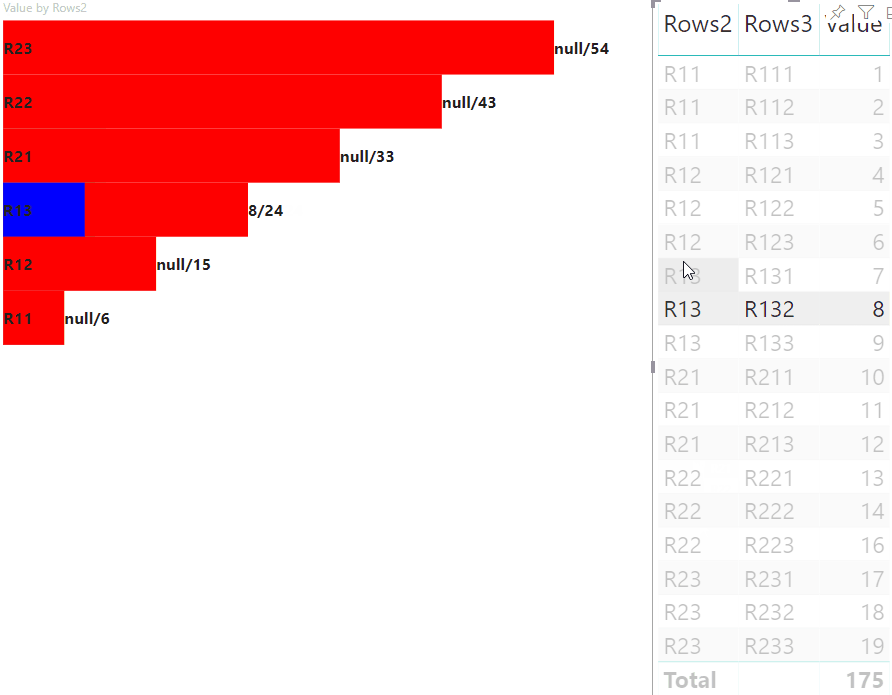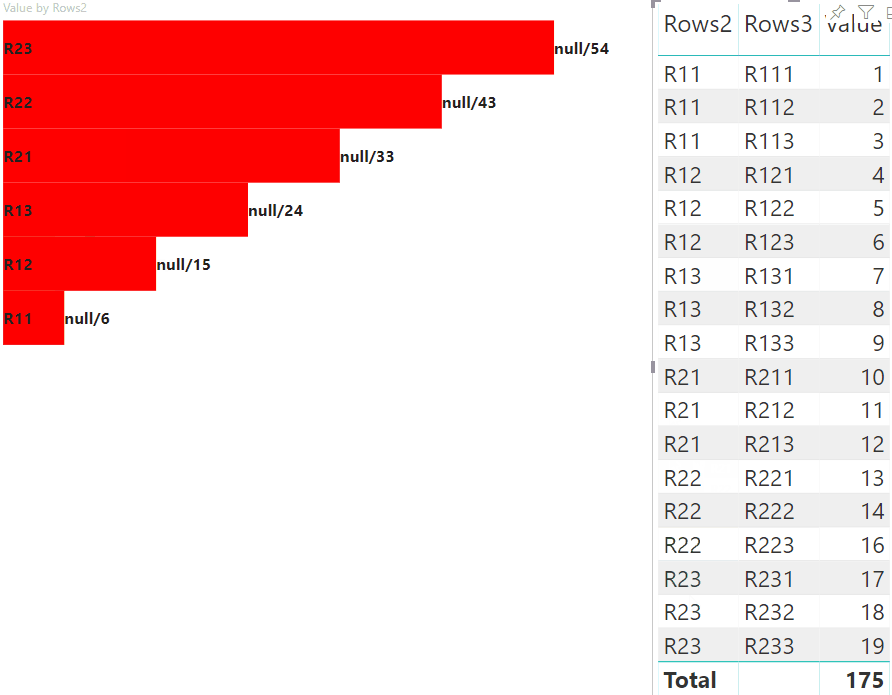
Apply the required styles for elements to use flexbox, and define colors for div elements:
div.vertical {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
div.horizontal {
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
}
div.highlight {
background-color: blue
}
div.value {
background-color: red;
display: flex;
}
The following view of the visual is the result:
Highlight data points with matrix data view mapping
For visuals with matrix data view mapping, add "supportsHighlight": true to the capabilities.json file. For example:
{
"dataRoles": [
{
"displayName": "Columns",
"name": "columns",
"kind": "Grouping"
},
{
"displayName": "Rows",
"name": "rows",
"kind": "Grouping"
},
{
"displayName": "Value",
"name": "value",
"kind": "Measure"
}
],
"dataViewMappings": [
{
"matrix": {
"columns": {
"for": {
"in": "columns"
}
},
"rows": {
"for": {
"in": "rows"
}
},
"values": {
"for": {
"in": "value"
}
}
}
}
],
"supportsHighlight": true
}
The sample data to create a hierarchy for matrix data view mapping:
| Row1 | Row2 | Row3 | Column1 | Column2 | Column3 | Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R11 | R111 | C1 | C11 | C111 | 1 |
| R1 | R11 | R112 | C1 | C11 | C112 | 2 |
| R1 | R11 | R113 | C1 | C11 | C113 | 3 |
| R1 | R12 | R121 | C1 | C12 | C121 | 4 |
| R1 | R12 | R122 | C1 | C12 | C122 | 5 |
| R1 | R12 | R123 | C1 | C12 | C123 | 6 |
| R1 | R13 | R131 | C1 | C13 | C131 | 7 |
| R1 | R13 | R132 | C1 | C13 | C132 | 8 |
| R1 | R13 | R133 | C1 | C13 | C133 | 9 |
| R2 | R21 | R211 | C2 | C21 | C211 | 10 |
| R2 | R21 | R212 | C2 | C21 | C212 | 11 |
| R2 | R21 | R213 | C2 | C21 | C213 | 12 |
| R2 | R22 | R221 | C2 | C22 | C221 | 13 |
| R2 | R22 | R222 | C2 | C22 | C222 | 14 |
| R2 | R22 | R223 | C2 | C22 | C223 | 16 |
| R2 | R23 | R231 | C2 | C23 | C231 | 17 |
| R2 | R23 | R232 | C2 | C23 | C232 | 18 |
| R2 | R23 | R233 | C2 | C23 | C233 | 19 |
Create the default visual project, and apply the sample of the capabilities.json file.
After you remove the unnecessary code, the default visual source code looks like the following example:
"use strict";
// ... default imports
import { FormattingSettingsService } from "powerbi-visuals-utils-formattingmodel";
import { VisualFormattingSettingsModel } from "./settings";
export class Visual implements IVisual {
private target: HTMLElement;
private formattingSettings: VisualFormattingSettingsModel;
private formattingSettingsService: FormattingSettingsService;
constructor(options: VisualConstructorOptions) {
console.log('Visual constructor', options);
this.formattingSettingsService = new FormattingSettingsService();
this.target = options.element;
this.host = options.host;
}
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
this.formattingSettings = this.formattingSettingsService.populateFormattingSettingsModel(VisualFormattingSettingsModel, options.dataViews);
console.log('Visual update', options);
}
/**
* Returns properties pane formatting model content hierarchies, properties and latest formatting values, Then populate properties pane.
* This method is called once every time we open properties pane or when the user edit any format property.
*/
public getFormattingModel(): powerbi.visuals.FormattingModel {
return this.formattingSettingsService.buildFormattingModel(this.formattingSettings);
}
}
Import the required interfaces to process data from Power BI:
import DataViewMatrix = powerbi.DataViewMatrix;
import DataViewMatrixNode = powerbi.DataViewMatrixNode;
import DataViewHierarchyLevel = powerbi.DataViewHierarchyLevel;
Create two div elements for the visual layout:
constructor(options: VisualConstructorOptions) {
// ...
this.rowsDiv = document.createElement("div");
this.target.appendChild(this.rowsDiv);
this.colsDiv = document.createElement("div");
this.target.appendChild(this.colsDiv);
this.target.style.overflowY = "auto";
}
Check the data in the update method to ensure that the visual gets data:
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
this.formattingSettings = this.formattingSettingsService.populateFormattingSettingsModel(VisualFormattingSettingsModel, options.dataViews);
console.log('Visual update', options);
const dataView: DataView = options.dataViews[0];
const matrixDataView: DataViewMatrix = dataView.matrix;
if (!matrixDataView ||
!matrixDataView.columns ||
!matrixDataView.rows ) {
return
}
// ...
}
Clear the contents of the div elements before rendering new data:
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
// ...
// remove old elements
// to better performance use D3js pattern:
// https://d3js.org/#enter-exit
while (this.rowsDiv.firstChild) {
this.rowsDiv.removeChild(this.rowsDiv.firstChild);
}
const prow = document.createElement("p");
prow.innerText = "Rows";
this.rowsDiv.appendChild(prow);
while (this.colsDiv.firstChild) {
this.colsDiv.removeChild(this.colsDiv.firstChild);
}
const pcol = document.createElement("p");
pcol.innerText = "Columns";
this.colsDiv.appendChild(pcol);
// ...
}
Create the treeWalker function to traverse the matrix data structure:
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
// ...
const treeWalker = (matrixNode: DataViewMatrixNode, index: number, levels: DataViewHierarchyLevel[], div: HTMLDivElement) => {
}
// ...
}
Where matrixNode is the current node, levels is metadata columns of this hierarchy level, div - parent element for child HTML elements.
The treeWalker is the recursive function, need to create div element and p for text as header, and call the function for child elements of node:
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
// ...
const treeWalker = (matrixNode: DataViewMatrixNode, index: number, levels: DataViewHierarchyLevel[], div: HTMLDivElement) => {
// ...
if (matrixNode.children) {
const childDiv = document.createElement("div");
childDiv.classList.add("vertical");
div.appendChild(childDiv);
const p = document.createElement("p");
const level = levels[matrixNode.level]; // get current level column metadata from current node
p.innerText = level.sources[level.sources.length - 1].displayName; // get column name from metadata
childDiv.appendChild(p); // add paragraph element to div element
matrixNode.children.forEach((node, index) => treeWalker(node, levels, childDiv, ++levelIndex));
}
}
// ...
}
Call the function for root elements of the column and row of the matrix data view structure:
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
// ...
const treeWalker = (matrixNode: DataViewMatrixNode, index: number, levels: DataViewHierarchyLevel[], div: HTMLDivElement) => {
// ...
}
// ...
// remove old elements
// ...
// ...
const rowRoot: DataViewMatrixNode = matrixDataView.rows.root;
rowRoot.children.forEach((node) => treeWalker(node, matrixDataView.rows.levels, this.rowsDiv));
const colRoot = matrixDataView.columns.root;
colRoot.children.forEach((node) => treeWalker(node, matrixDataView.columns.levels, this.colsDiv));
}
Generate selectionID for nodes and Create buttons to display nodes:
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
// ...
const treeWalker = (matrixNode: DataViewMatrixNode, index: number, levels: DataViewHierarchyLevel[], div: HTMLDivElement) => {
const selectionID: ISelectionID = this.host.createSelectionIdBuilder()
.withMatrixNode(matrixNode, levels)
.createSelectionId();
let nodeBlock = document.createElement("button");
nodeBlock.innerText = matrixNode.value.toString();
nodeBlock.addEventListener("click", (event) => {
// call select method in the selection manager
this.selectionManager.select(selectionID);
});
nodeBlock.addEventListener("contextmenu", (event) => {
// call showContextMenu method to display context menu on the visual
this.selectionManager.showContextMenu(selectionID, {
x: event.clientX,
y: event.clientY
});
event.preventDefault();
});
// ...
}
// ...
}
The main step of highlighting is to create another array of values.
The object of terminal node has two properties for the values array, value and highlight:
JSON.stringify(options.dataViews[0].matrix.rows.root.children[0].children[0].children[0], null, " ");
{
"level": 2,
"levelValues": [
{
"value": "R233",
"levelSourceIndex": 0
}
],
"value": "R233",
"identity": {
"identityIndex": 2
},
"values": {
"0": {
"value": null,
"highlight": null
},
"1": {
"value": 19,
"highlight": 19
}
}
}
Where value represents the value of the node without applying a selection from the other visual, highlight indicates which part of the data was highlighted.
Note
If the value of highlight is less than the value of value,
then value was partially highlighted.
Add code to process the values array of the node if it's presented:
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
// ...
const treeWalker = (matrixNode: DataViewMatrixNode, index: number, levels: DataViewHierarchyLevel[], div: HTMLDivElement) => {
// ...
if (matrixNode.values) {
const sumOfValues = Object.keys(matrixNode.values) // get key property of object (value are 0 to N)
.map(key => +matrixNode.values[key].value) // convert key property to number
.reduce((prev, curr) => prev + curr) // sum of values
let sumOfHighlights = sumOfValues;
sumOfHighlights = Object.keys(matrixNode.values) // get key property of object (value are 0 to N)
.map(key => matrixNode.values[key].highlight ? +matrixNode.values[key].highlight : null ) // convert key property to number if it exists
.reduce((prev, curr) => curr ? prev + curr : null) // convert key property to number
// create div container for value and highlighted value
const vals = document.createElement("div");
vals.classList.add("vertical")
vals.classList.replace("vertical", "horizontal");
// create paragraph element for label
const highlighted = document.createElement("p");
// Display complete value and highlighted value
highlighted.innerText = `${sumOfHighlights}/${sumOfValues}`;
// create div container for value
const valueDiv = document.createElement("div");
valueDiv.style.width = sumOfValues * 10 + "px";
valueDiv.classList.add("value");
// create div container for highlighted values
const highlightsDiv = document.createElement("div");
highlightsDiv.style.width = sumOfHighlights * 10 + "px";
highlightsDiv.classList.add("highlight");
valueDiv.appendChild(highlightsDiv);
// append button and paragraph to div containers to parent div
vals.appendChild(nodeBlock);
vals.appendChild(valueDiv);
vals.appendChild(highlighted);
div.appendChild(vals);
} else {
div.appendChild(nodeBlock);
}
if (matrixNode.children) {
// ...
}
}
// ...
}
The result is a visual with buttons and values, like highlighted value/default value.
Related content
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for