Proactive Recommendations
You asked for personalized proactive support recommendations to empower you to achieve more. We delivered.
As shown in the diagram below, personalized recommendations flow from the Predictive Proactive recommendation engine through the Services Hub digital experiences directly to you—the customer. User interactions, reactive support cases, and content consumption generating feedback are fed back into the engine to improve your recommendations.
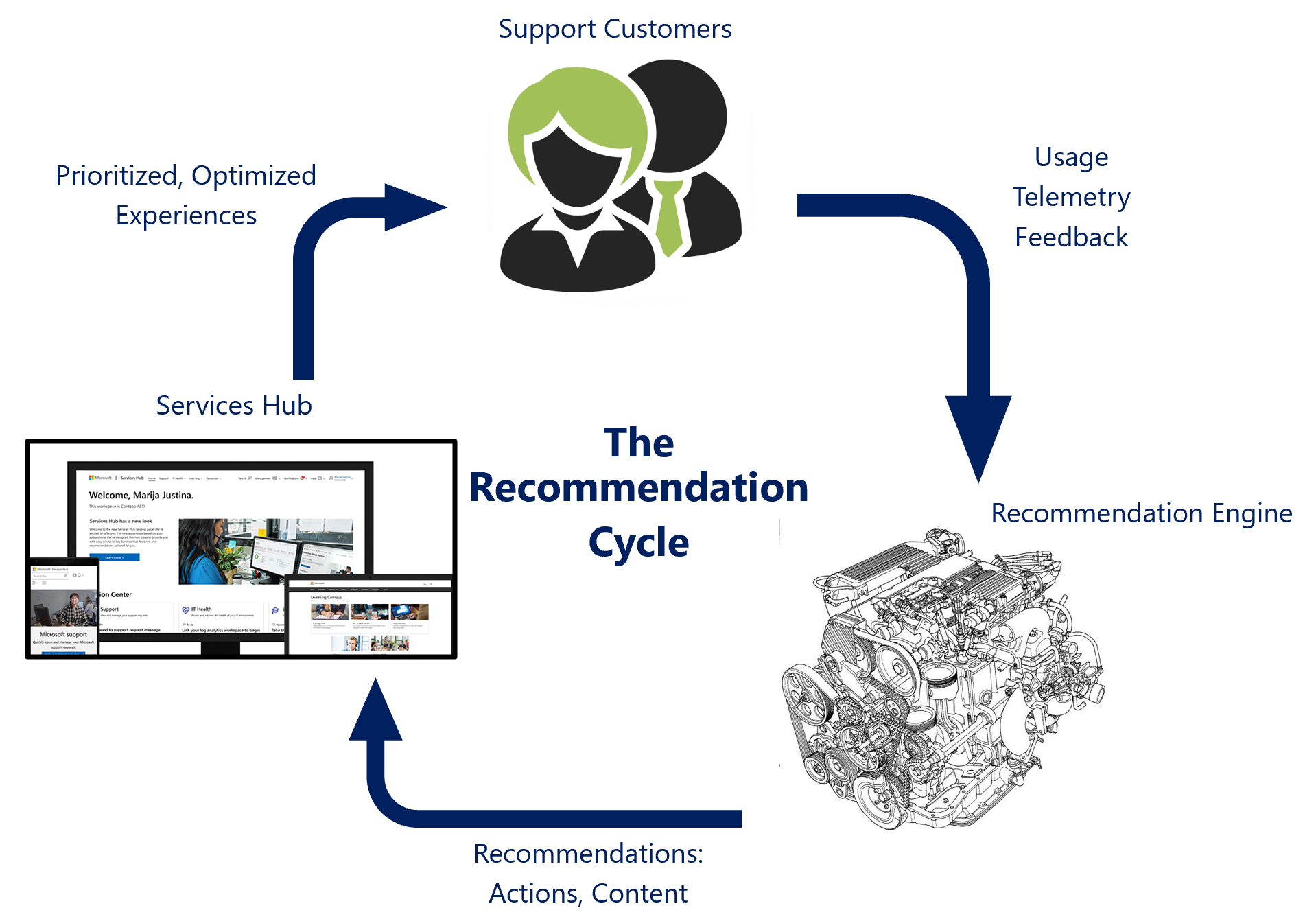
Our vision for proactive recommendations includes:
- Serve action and IP based recommendations specific to user and customer content (license footprint, reactive support cases, workshops, and assessments)
- Recommendations should be inclusive of the Services Catalog and MS Learn
- Deliver personalized and context relevant recommendations within Services Hub
- Recommendations are rendered in real-time with no performance impact on the overall digital experience
What services are recommended?
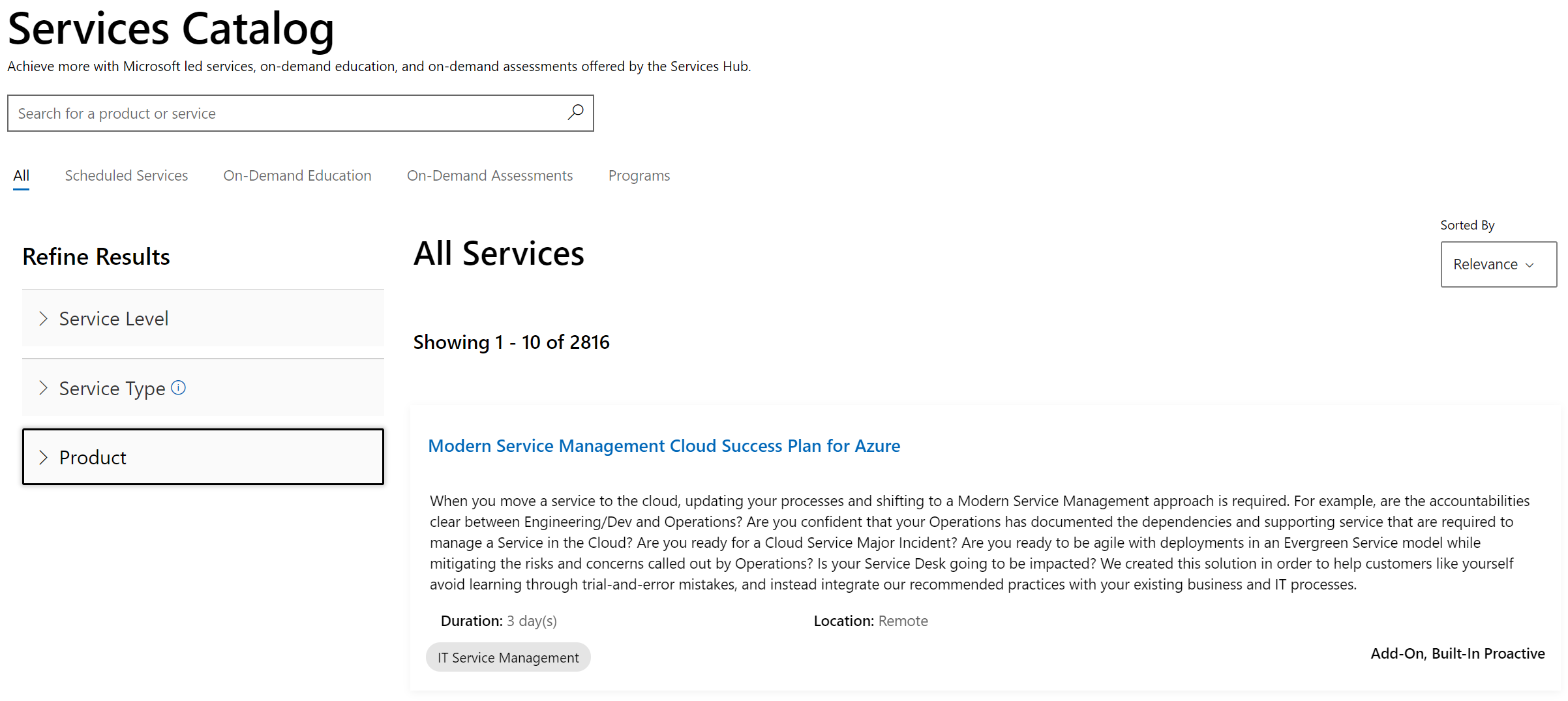
The predictive proactive recommendation engine serves up content from the Microsoft Services Catalog and MS Learn. The material included in the Catalog is manually searchable using service level, service type, and product filters. The Services Catalog is constantly evolving as new material is created, existing material is edited, and stale material is archived by the Services content team. Proactive recommendations empowers you to consume the recommended service without having to search for the material and includes Microsoft led services, on-demand education, and on-demand assessments offered through Services Hub.
Where do recommendations appear on the Services Hub?
Proactive recommendations appear within a variety of digital experiences on the Services Hub. The recommendations served within these experiences are tailored for the context of the specific digital experience and personalized for you.
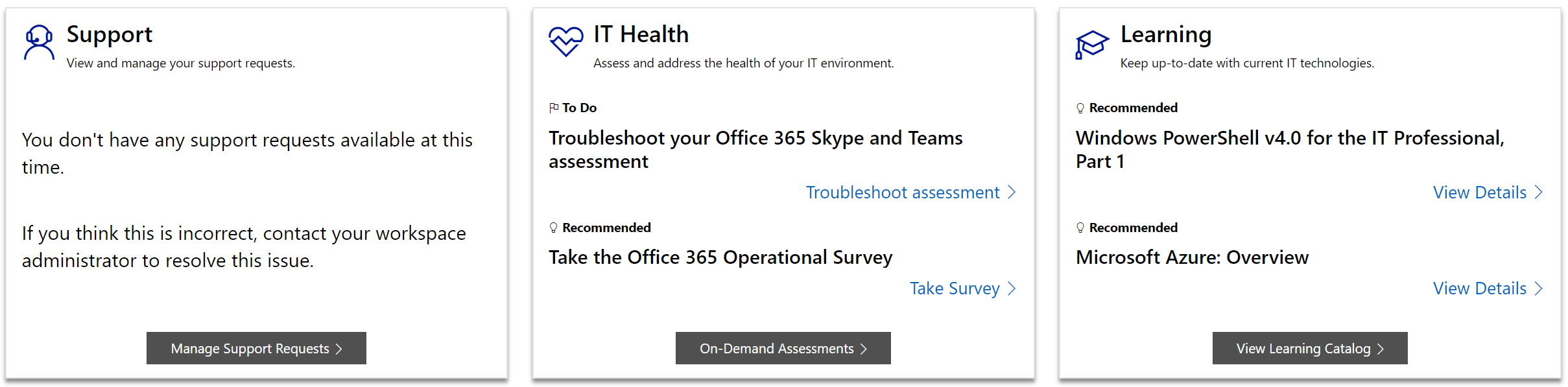
On the Services Hub home page, Services Hub On-Demand Assessment content recommendations tailored for you can be found in the IT Health tile while your learning-on-demand and workshop recommendations live in the Learning tile.
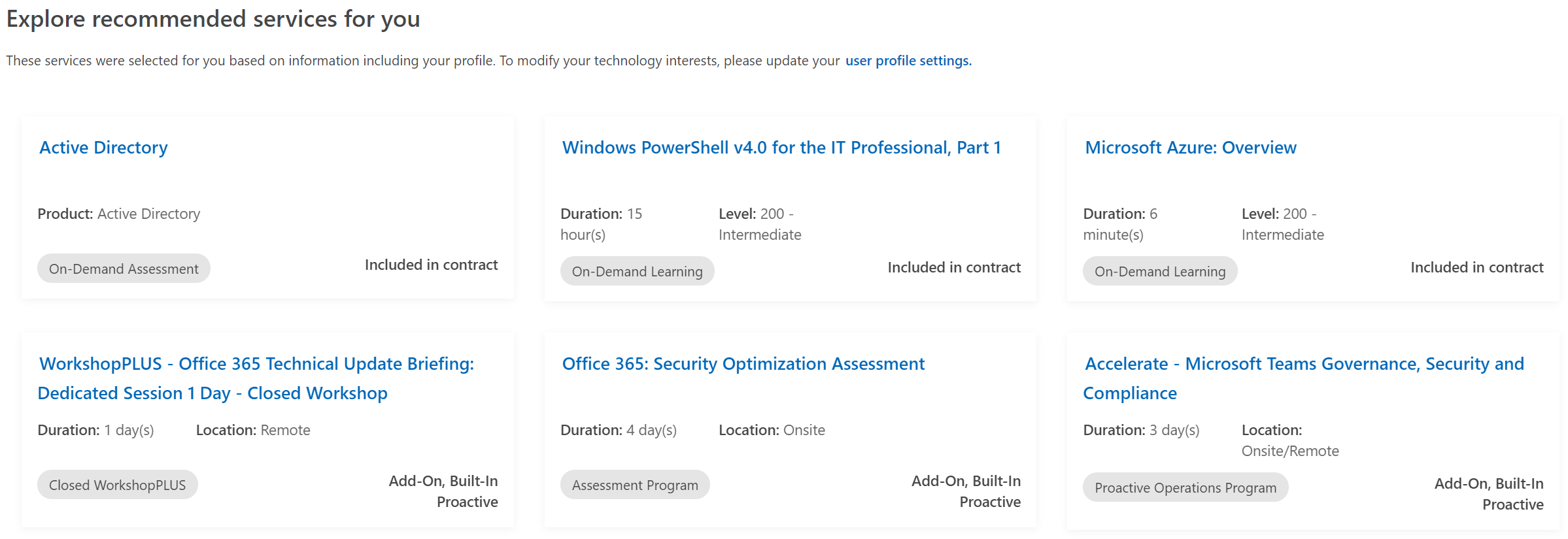
Predictive Proactive recommendations are included below the Services Hub Services Catalog search feature and are represented in the diagram below. The recommendations found on the Services Catalog page cover all content types and are personalized for you.
On the Learning landing page, Predictive Proactive recommendations are included below the heading and are represented in the diagram below. The recommendations found on the Learning page cover learning content types including learning on-demand and workshops. These recommendations are personalized for you.
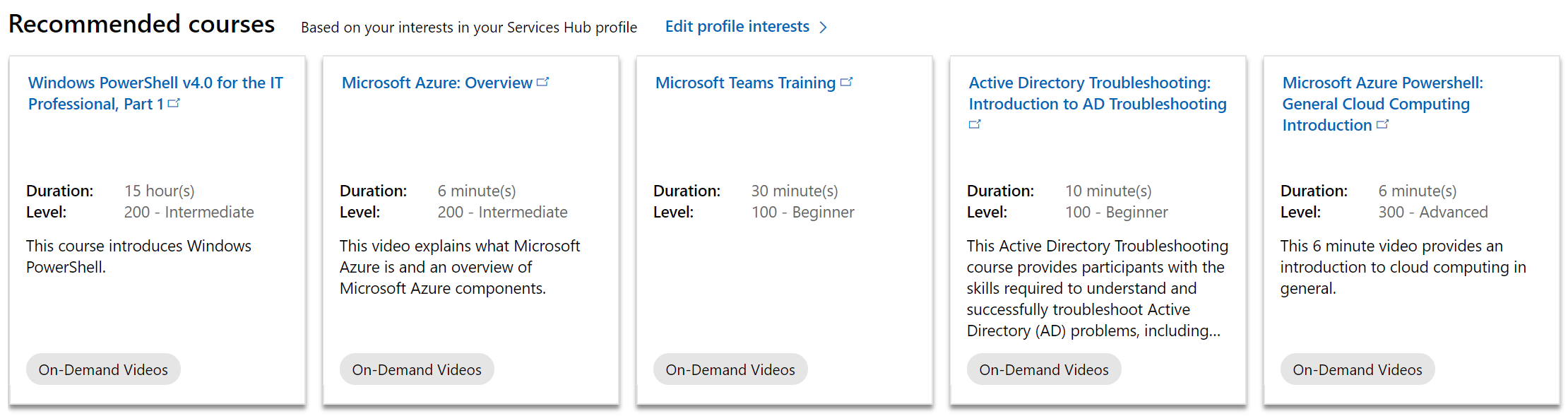
On the Assessments page, Predictive Proactive recommendations are included below the assessment summary and are represented in the diagram below. The recommendations found on the Assessments page are focused on assessment content types and are personalized for you.

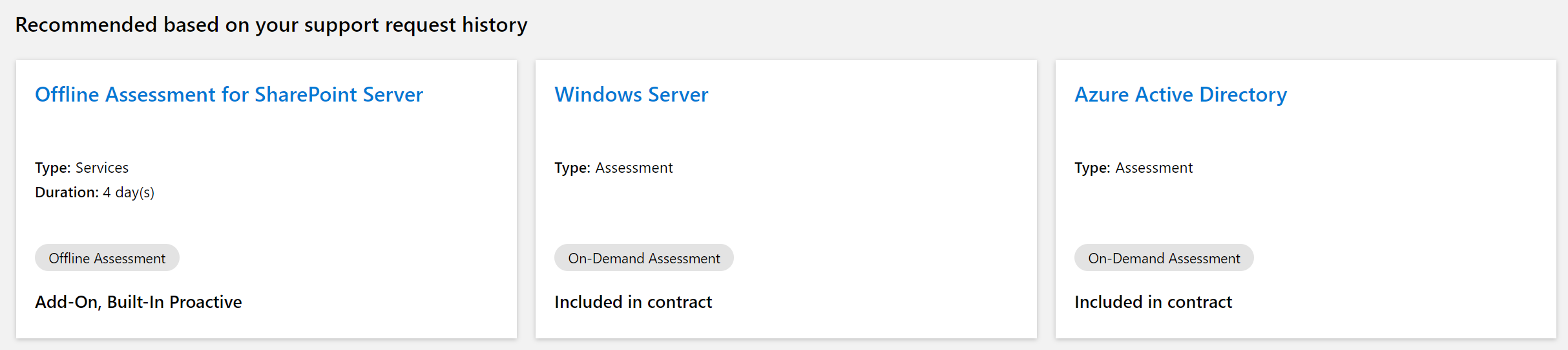
On the Support Landing Page, Predictive Proactive recommendations are found below the case trending visualization on the page. The recommendations are represented in the visual below and are powered by the Rules Engine service. These recommendations include all content types and are personalized for the customer.
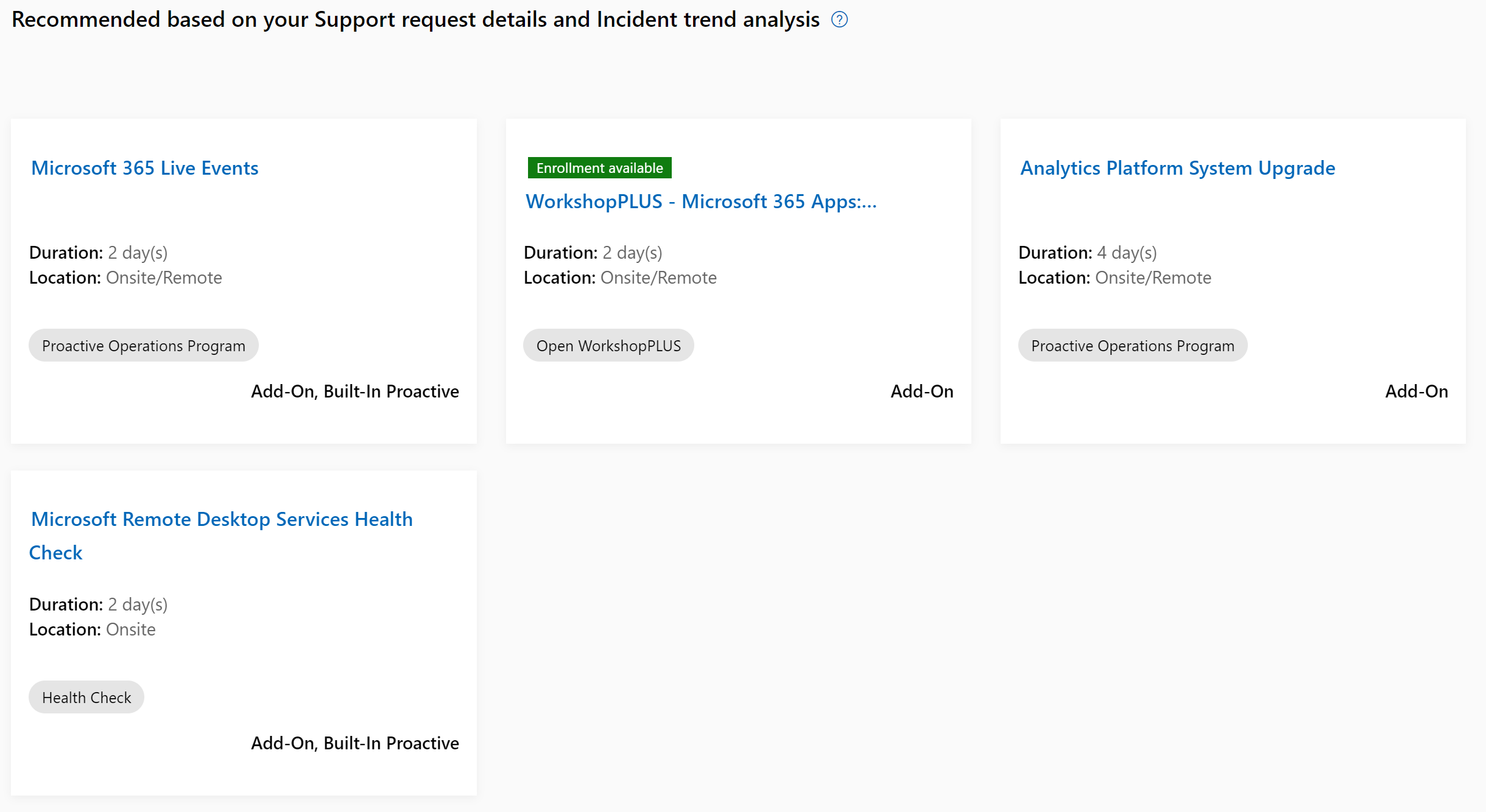
On the Support Detail Page, Predictive Proactive recommendations are found below the case details and case trending visual on the page. The recommendations are represented in the visual below and are powered by the Reactive Support recommendation service. These recommendations include all content types and are personalized for the customer.
How does the recommendation engine work?
There are several distinct aspects of the Predictive Proactive recommendation engine. Each aspect plays a different role within Services Hub.
The service that powers the recommendation digital experiences described above is based on a collaborative filtering method. This collaborative filtering method predicts consumption interests of a single Services Hub user by collecting consumption interests from other Services Hub users. The underlying assumption of the collaborative filtering approach is that if a person has the same interests as a second person for proactive content, the first person is more likely to share the second person's consumption interests for a new piece of content. Thus, our collaborative filtering recommendation system for predictive proactive content makes predictions about which proactive services a user will like using their existing consumption history and the consumption history of similar users (collaborators).
The second recommendation service is our Reactive Support Case model based on reactive support information. This service leverages the following information to generate recommended LOD, assessments, and services:
- Product family
- Case title
- Case description
- Case notes
This recommendation service pulls these features from text which are used for computing similarity to services within the Services Catalog. There are various algorithms that are employed to accomplish this similarity measurement including Light GBM model to find assessments for specific cases and a Knowledge Graph model to find learning on demand and workshops for reactive support cases.
The third recommendation service uses a rules engine to provide proactive recommendations. Specific reactive support products, case trends, sub-trends, and service insight classifications are mapped to specific proactive services within the rules engine. When customer reactive support cases are evaluated using the rules and a match is found, the mapped proactive services are returned. Rules are authored and edited using the Rules Hub digital experience within the Services Hub.
How do users influence which recommendations are presented?
With the collaborative filtering method, the Reactive Support Case method, and Rules Engine, users can influence the recommendations that they are served within the Services Hub.
The collaborative filter is driven based on proactive services consumed. This consumption indicates the user preferences. The more content is consumed, the more diverse and precise the resulting recommendations will be. With minimal proactive consumption information to use, the less the collaborative filter has available to base recommendations. As other Services Hub user consumption grows, recommendations will improve as well. Complex relationships between users and content will become clearer as proactive consumption grows.
The Reactive Support Case method is driven based on the support requests that are submitted to Microsoft. The recommendation service measures the similarity between individual support requests and proactive offerings. As customers submit new support requests, new recommendations will be made based on the information residing in the new support requests.
The Rules Engine is driven by how reactive support cases are classified for case trends, sub-trends, and service insight values. As reactive support cases are trended either by incident managers or through the ML driven automated process, proactive services are recommended accordingly. Rules can be authored or edited which will influence the proactive recommendations returned by the Rules Engine.
What recommendations are shown when users first engage with Services Hub?
As new users are onboarded into the Services Hub, proactive consumption will be at a minimum. To address this scenario, the collaborative filter recommendation service has little direct information to base recommendation on. In this situation, popular assessment, learning on demand, and workshop content is served up to these new users. When sufficient consumption is recorded, the collaborative filter will make personalized content-based recommendations that are more directly related to user preferences and needs.
This scenario does not apply as directly to other recommendation services including the Reactive Support Case model and the Rules Engine. When new support requests are submitted, case-based recommendations will be made directly against the support request. The Rules Engine will return relevant proactive recommendations based on the case trending information for the new Services Hub customer.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for