VidPN Objects and Interfaces
The video present network (VidPN) manager uses a VidPN object to maintain information about associations between video present sources, video present targets, and display modes. For more information, see the Introduction to Video Present Networks topic.
VidPN object
A VidPN object contains the following sub-objects.
Topology
Source mode set
Target mode set
Monitor source mode set
Monitor frequency range set
Monitor descriptor set
Path
Source
Target
Source mode
Target mode
Monitor source mode
The following diagram illustrates a VidPN object and its sub-objects.
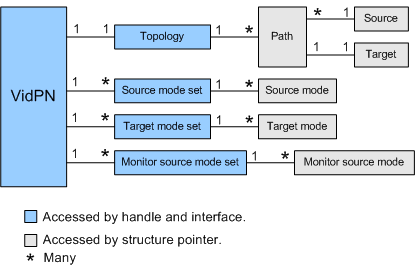
The preceding diagram illustrates whether a particular association is one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-one, or many-to-many. For example, the diagram shows that a source can belong to more than one path, but a target can belong to only one path.
The blue objects in the diagram are accessed through handles and interfaces, and the gray objects are accessed through structure pointers. An interface in this context is a structure that contains function pointers. For example, the DXGK_VIDPNTOPOLOGY_INTERFACE structure contains pointers to functions (implemented by the VidPN manager) that the display miniport driver calls to inspect and alter a topology object. When the display miniport driver calls any one of those functions, it must supply a handle to a topology object. The following table lists the handle, interface, and pointer data types used to access a VidPN object and its sub-objects.
| Object | Access method and data type |
|---|---|
| VidPN (VidPN Interface) | Accessed through handle and interface. D3DKMDT_HVIDPN, DXGK_VIDPN_INTERFACE |
| Topology (VidPN Topology Interface) | Accessed through handle and interface. D3DKMDT_HVIDPNTOPOLOGY, DXGK_VIDPNTOPOLOGY_INTERFACE |
| Source mode set (VidPN Source Mode Set Interface) | Accessed through handle and interface. D3DKMDT_HVIDPNSOURCEMODESET, DXGK_VIDPNSOURCEMODESET_INTERFACE |
| Target mode set (VidPN Target Mode Set Interface) | Accessed through handle and interface. D3DKMDT_HVIDPNTARGETMODESET, DXGK_VIDPNTARGETMODESET_INTERFACE |
| Monitor source mode set | Accessed through handle and interface. D3DKMDT_HMONITORSOURCEMODESET, DXGK_MONITORSOURCEMODESET_INTERFACE |
| Path | Accessed through structure pointer. D3DKMDT_VIDPN_PRESENT_PATH |
| Source | Accessed through structure pointer. D3DKMDT_VIDEO_PRESENT_SOURCE |
| Target | Accessed through structure pointer. D3DKMDT_VIDEO_PRESENT_TARGET |
| Source mode | Accessed through structure pointer. D3DKMDT_VIDPN_SOURCE_MODE |
| Target mode | Accessed through structure pointer. D3DKMDT_VIDPN_TARGET_MODE |
| Monitor source mode | Accessed through structure pointer. D3DKMDT_MONITOR_SOURCE_MODE |
| Monitor frequency range set | Accessed through structure pointer. [DXGK_MONITORFREQUENCYRANGESET_INTERFACE |
| Monitor descriptor set | Accessed through structure pointer. [DXGK_MONITORDESCRIPTORSET_INTERFACE |
VidPN Manager
The VidPN manager, which is one of the components of the DirectX graphics kernel subsystem, cooperates with the display miniport driver to build and maintain VidPNs. The following steps describe how the display miniport driver obtains a handle and an interface to a VidPN object.
During initialization, the DirectX graphics kernel subsystem calls the display miniport driver's DxgkDdiStartDevice function. That call provides the display miniport driver with a DXGKRNL_INTERFACE structure, which contains pointers to functions implemented by the DirectX graphics kernel subsystem. One of those functions is DxgkCbQueryVidPnInterface.
At some point, the VidPN manager needs help from the display miniport driver, so it provides the display miniport driver with a handle to a VidPN object by calling one of the following functions:
The display miniport driver passes the handle obtained in Step 2 to DxgkCbQueryVidPnInterface, which returns a pointer to a DXGK_VIDPN_INTERFACE structure.
After the display miniport driver has a handle and an interface to a VidPN object, it can get handles and interfaces (as needed) to the primary sub-objects: topology, source mode set, target mode set, and monitor source mode set. For example, the display miniport driver can call pfnGetTopology (one of the functions in the VidPN interface) to get a handle to a VidPN topology object and a pointer to a DXGK_VIDPNTOPOLOGY_INTERFACE structure.
The following functions (in the VidPN interface) provide handles and interfaces to the primary sub-objects of a VidPN object.
Note that two of the functions in the preceding list have corresponding functions that release VidPN sub-objects.
After the display miniport driver obtains a handle and an interface to one of a VidPNs primary sub-objects, it can call the interface functions to get descriptors of objects related to the sub-object. For example, given a handle and an interface to a topology object, the display miniport driver could perform the following steps to get descriptors of all the paths in topology.
-
Call the pfnAcquireFirstPathInfo function of the VidPN topology interface to obtain a pointer to a D3DKMDT_VIDPN_PRESENT_PATH structure that describes the first path in the topology.
-
Call the pfnAcquireNextPathInfo function repeatedly to obtain pointers to D3DKMDT_VIDPN_PRESENT_PATH structures that describe the remaining paths in the topology.
Similarly, the display miniport driver can get descriptors of the modes in a mode set by calling the pfnAcquireFirstModeInfo and pfnAcquireNextModeInfo functions of any of the following mode set interfaces.
Note that the DXGK_VIDPNSOURCEMODESET_INTERFACE interface has no function for removing a mode from a source mode set. When the display miniport driver needs to update a source mode set, it does not alter an existing mode set by adding and removing modes. Instead, it creates a new mode set that replaces the old mode set. An example of a function that must update mode sets is the display miniport driver's DxgkDdiEnumVidPnCofuncModality function. The steps involved in updating a source mode set are as follows:
Call the pfnCreateNewModeInfo of the DXGK_VIDPNSOURCEMODESET_INTERFACE interface to get a pointer to a D3DKMDT_VIDPN_SOURCE_MODE structure (allocated by the VidPN manager).
Call pfnAddMode repeatedly to add modes to the source mode set.
Call the pfnAssignSourceModeSet function of the DXGK_VIDPN_INTERFACE to assign the new mode set to a particular video present source. The new source mode set replaces the source mode set that is currently assigned to that source.
Updating a target mode set is similar to updating a source mode set. The DXGK_VIDPNTARGETMODESET_INTERFACE interface has the following functions:
VidPN Target Mode Set interface
A pfnCreateNewModeInfo function for creating a new target mode set and a pfnAddMode function for adding modes to the set.
There is no interface (set of functions) for obtaining the source and target that belong to a particular path. The display miniport driver can determine which source and target belong to a particular path by inspecting the VidPnSourceId and VidPnTargetId members of the D3DKMDT_VIDPN_PRESENT_PATH structure that represents the path.
See also
Determining Whether a VidPN is Supported on a Display Adapter
Enumerating Cofunctional VidPN Source and Target Modes
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for