Performance Tuning NFS File Servers
Services for NFS model
The following sections provide information about the Microsoft Services for Network File System (NFS) model for client-server communication. Since NFS v2 and NFS v3 are still the most widely deployed versions of the protocol, all of the registry keys except for MaxConcurrentConnectionsPerIp apply to NFS v2 and NFS v3 only.
No registry tuning is required for NFS v4.1 protocol.
Service for NFS model overview
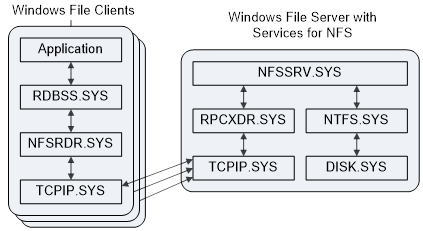
Microsoft Services for NFS provides a file-sharing solution for enterprises that have a mixed Windows and UNIX environment. This communication model consists of client computers and a server. Applications on the client request files that are located on the server through the redirector (Rdbss.sys) and NFS mini-redirector (Nfsrdr.sys). The mini-redirector uses the NFS protocol to send its request through TCP/IP. The server receives multiple requests from the clients through TCP/IP and routes the requests to the local file system (Ntfs.sys), which accesses the storage stack.
The following figure shows the communication model for NFS.
Tuning parameters for NFS file servers
The following REG_DWORD registry settings can affect the performance of NFS file servers:
OptimalReads
HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\NfsServer\Parameters\OptimalReadsThe default is 0. This parameter determines whether files are opened for FILE_RANDOM_ACCESS or for FILE_SEQUENTIAL_ONLY, depending on the workload I/O characteristics. Set this value to 1 to force files to be opened for FILE_RANDOM_ACCESS. FILE_RANDOM_ACCESS prevents the file system and cache manager from prefetching.
Note
This setting must be carefully evaluated because it may have potential impact on system file cache grow.
RdWrHandleLifeTime
HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\NfsServer\Parameters\RdWrHandleLifeTimeThe default is 5. This parameter controls the lifetime of an NFS cache entry in the file handle cache. The parameter refers to cache entries that have an associated open NTFS file handle. Actual lifetime is approximately equal to RdWrHandleLifeTime multiplied by RdWrThreadSleepTime. The minimum is 1 and the maximum is 60.
RdWrNfsHandleLifeTime
HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\NfsServer\Parameters\RdWrNfsHandleLifeTimeThe default is 5. This parameter controls the lifetime of an NFS cache entry in the file handle cache. The parameter refers to cache entries that do not have an associated open NTFS file handle. Services for NFS uses these cache entries to store file attributes for a file without keeping an open handle with the file system. Actual lifetime is approximately equal to RdWrNfsHandleLifeTime multiplied by RdWrThreadSleepTime. The minimum is 1 and the maximum is 60.
RdWrNfsReadHandlesLifeTime
HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\NfsServer\Parameters\RdWrNfsReadHandlesLifeTimeThe default is 5. This parameter controls the lifetime of an NFS read cache entry in the file handle cache. Actual lifetime is approximately equal to RdWrNfsReadHandlesLifeTime multiplied by RdWrThreadSleepTime. The minimum is 1 and the maximum is 60.
RdWrThreadSleepTime
HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\NfsServer\Parameters\RdWrThreadSleepTimeThe default is 5. This parameter controls the wait interval before running the cleanup thread on the file handle cache. The value is in ticks, and it is non-deterministic. A tick is equivalent to approximately 100 nanoseconds. The minimum is 1 and the maximum is 60.
FileHandleCacheSizeinMB
HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\NfsServer\Parameters\FileHandleCacheSizeinMBThe default is 4. This parameter specifies the maximum memory to be consumed by file handle cache entries. The minimum is 1 and the maximum is 1*1024*1024*1024 (1073741824).
LockFileHandleCacheInMemory
HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\NfsServer\Parameters\LockFileHandleCacheInMemoryThe default is 0. This parameter specifies whether the physical pages that are allocated for the cache size specified by FileHandleCacheSizeInMB are locked in memory. Setting this value to 1 enables this activity. Pages are locked in memory (not paged to disk), which improves the performance of resolving file handles, but reduces the memory that is available to applications.
MaxIcbNfsReadHandlesCacheSize
HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\NfsServer\Parameters\MaxIcbNfsReadHandlesCacheSizeThe default is 64. This parameter specifies the maximum number of handles per volume for the read data cache. Read cache entries are created only on systems that have more than 1 GB of memory. The minimum is 0 and the maximum is 0xFFFFFFFF.
HandleSigningEnabled
HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\NfsServer\Parameters\HandleSigningEnabledThe default is 1. This parameter controls whether handles that are given out by NFS File Server are signed cryptographically. Setting it to 0 disables handle signing.
RdWrNfsDeferredWritesFlushDelay
HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\NfsServer\Parameters\RdWrNfsDeferredWritesFlushDelayThe default is 60. This parameter is a soft timeout that controls the duration of NFS V3 UNSTABLE Write data caching. The minimum is 1, and the maximum is 600. Actual lifetime is approximately equal to RdWrNfsDeferredWritesFlushDelay multiplied by RdWrThreadSleepTime.
CacheAddFromCreateAndMkDir
HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\NfsServer\Parameters\CacheAddFromCreateAndMkDirThe default is 1 (enabled). This parameter controls whether handles that are opened during NFS V2 and V3 CREATE and MKDIR RPC procedure handlers are retained in the file handle cache. Set this value to 0 to disable adding entries to the cache in CREATE and MKDIR code paths.
AdditionalDelayedWorkerThreads
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SessionManager\Executive\AdditionalDelayedWorkerThreadsIncreases the number of delayed worker threads that are created for the specified work queue. Delayed worker threads process work items that are not considered time-critical and that can have their memory stack paged out while waiting for work items. An insufficient number of threads reduces the rate at which work items are serviced; a value that is too high consumes system resources unnecessarily.
NtfsDisable8dot3NameCreation
HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\FileSystem\NtfsDisable8dot3NameCreationThe default in Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2, and later versions of Windows Server is 2. In releases prior to Windows Server 2012, the default is 0. This parameter determines whether NTFS generates a short name in the 8dot3 (MSDOS) naming convention for long file names and for file names that contain characters from the extended character set. If the value of this entry is 0, files can have two names: the name that the user specifies and the short name that NTFS generates. If the user-specified name follows the 8dot3 naming convention, NTFS does not generate a short name. A value of 2 means that this parameter can be configured per volume.
Note
The system volume has 8dot3 enabled by default. All other volumes in Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2 have 8dot3 disabled by default. Changing this value does not change the contents of a file, but it avoids the short-name attribute creation for the file, which also changes how NTFS displays and manages the file. For most file servers, the recommended setting is 1 (disabled).
NtfsDisableLastAccessUpdate
HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\FileSystem\NtfsDisableLastAccessUpdateThe default is 1. This system-global switch reduces disk I/O load and latencies by disabling the updating of the date and time stamp for the last file or directory access.
MaxConcurrentConnectionsPerIp
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\Rpcxdr\Parameters\MaxConcurrentConnectionsPerIpThe default value of the MaxConcurrentConnectionsPerIp parameter is 16. You can increase this value up to a maximum of 8192 to increase the number of connections per IP address.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for