Tutoriel : Créer une application iOS qui lance le Lecteur immersif avec le contenu d'une photo (Swift)
Le lecteur immersif est un outil conçu de façon inclusive qui implémente des techniques éprouvées pour améliorer la compréhension de la lecture.
L'API Azure AI Vision Read détecte le contenu textuel d'une image à l'aide des derniers modèles de reconnaissance de Microsoft et convertit le texte identifié en un flux de caractères lisible par machine.
Dans ce tutoriel, vous générez une application iOS à partir de zéro et intégrer l’API Read ainsi que le lecteur immersif à l’aide du kit SDK Immersive Reader. Un exemple complet et fonctionnel de ce tutoriel est disponible sur GitHub.
Prérequis
- Un abonnement Azure. Vous pouvez en créer un gratuitement.
- MacOS et Xcode.
- Ressource Immersive Reader configurée pour l’authentification Microsoft Entra. Suivez ces instructions pour la configurer.
- Un abonnement au service Azure AI Vision. Créez une ressource Azure AI Vision dans le portail Azure.
Créer un projet Xcode
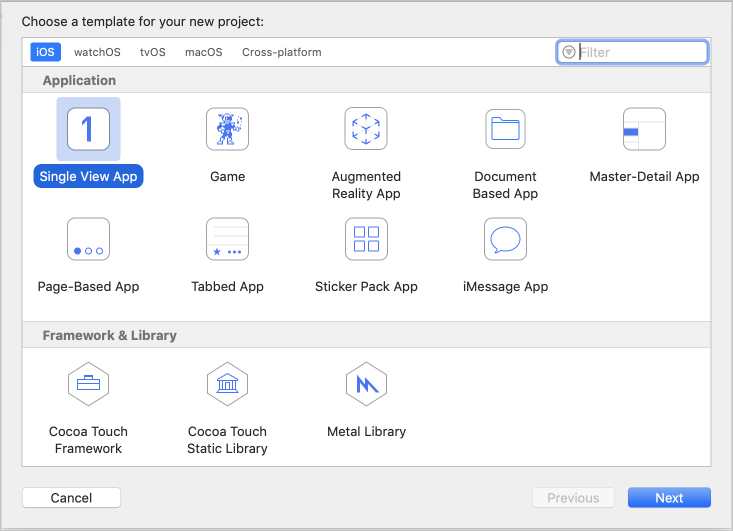
Créez un projet dans Xcode.

Choisissez Application avec affichage unique.
Obtenir l’outil CocoaPod pour le SDK
Le moyen le plus simple d’utiliser le kit SDK Lecteur immersif est via CocoaPods. Pour procéder à l’installation via Cocoapods :
Suivez le guide pour installer Cocoapods.
Créez un Podfile en exécutant
pod initdans le répertoire racine de votre projet XCode.Ajoutez le CocoaPod à votre Podfile en ajoutant
pod 'immersive-reader-sdk', :path => 'https://github.com/microsoft/immersive-reader-sdk/tree/master/iOS/immersive-reader-sdk'. Votre Podfile doit ressembler à ce qui suit, avec le nom de votre cible qui remplace picture-to-immersive-reader-swift :platform :ios, '9.0' target 'picture-to-immersive-reader-swift' do use_frameworks! # Pods for picture-to-immersive-reader-swift pod 'immersive-reader-sdk', :git => 'https://github.com/microsoft/immersive-reader-sdk.git' endDans le terminal, dans le répertoire de votre projet Xcode, exécutez la commande
pod installpour installer le pod du kit SDK Lecteur immersif.Ajoutez
import immersive_reader_sdkà tous les fichiers qui doivent référencer le kit SDK.Veillez à ouvrir le projet en ouvrant le fichier
.xcworkspace, et non le fichier.xcodeproj.
Acquérir un jeton d’authentification Microsoft Entra
Vous avez besoin de certaines valeurs de l’étape de configuration de l’authentification Microsoft Entra dans la section des prérequis. Reportez-vous au fichier texte que vous avez enregistré à partir de cette session.
TenantId => Azure subscription TenantId
ClientId => Microsoft Entra ApplicationId
ClientSecret => Microsoft Entra Application Service Principal password
Subdomain => Immersive Reader resource subdomain (resource 'Name' if the resource was created in the Azure portal, or 'CustomSubDomain' option if the resource was created with Azure CLI PowerShell. Check the Azure portal for the subdomain on the Endpoint in the resource Overview page, for example, 'https://[SUBDOMAIN].cognitiveservices.azure.com/')
Dans le dossier de projet principal, qui contient le fichier ViewController.swift, créez un fichier de classe Swift appelé Constants.swift. Remplacez la classe par le code suivant, en y ajoutant vos valeurs le cas échéant. Conservez ce fichier en tant que fichier local qui existe uniquement sur votre ordinateur et veillez à ne pas valider ce fichier dans le contrôle de code source, car il contient des secrets qui ne doivent pas être rendus publics. Nous vous recommandons de ne pas conserver de secrets dans votre application. Au lieu de cela, utilisez un service back-end pour obtenir le jeton, où les secrets peuvent être conservés en dehors de l’application et de l’appareil. Le point de terminaison d’API back-end doit être sécurisé avec une certaine forme d’authentification (par exemple, OAuth) pour empêcher les utilisateurs non autorisés d’obtenir des jetons à utiliser auprès de vos services Facturation et Lecteur immersif ; ce travail dépasse le cadre de ce tutoriel.
Configurer l’application pour qu’elle s’exécute sans plan conceptuel
Ouvrez AppDelegate.swift et remplacez le fichier par le code suivant.
import UIKit
@UIApplicationMain
class AppDelegate: UIResponder, UIApplicationDelegate {
var window: UIWindow?
var navigationController: UINavigationController?
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
// Override point for customization after application launch.
window = UIWindow(frame: UIScreen.main.bounds)
// Allow the app run without a storyboard
if let window = window {
let mainViewController = PictureLaunchViewController()
navigationController = UINavigationController(rootViewController: mainViewController)
window.rootViewController = navigationController
window.makeKeyAndVisible()
}
return true
}
func applicationWillResignActive(_ application: UIApplication) {
// Sent when the application is about to move from active to inactive state. This can occur for certain types of temporary interruptions (such as an incoming phone call or SMS message) or when the user quits the application and it begins the transition to the background state.
// Use this method to pause ongoing tasks, disable timers, and invalidate graphics rendering callbacks. Games should use this method to pause the game.
}
func applicationDidEnterBackground(_ application: UIApplication) {
// Use this method to release shared resources, save user data, invalidate timers, and store enough application state information to restore your application to its current state in case it is terminated later.
// If your application supports background execution, this method is called instead of applicationWillTerminate: when the user quits.
}
func applicationWillEnterForeground(_ application: UIApplication) {
// Called as part of the transition from the background to the active state; here you can undo many of the changes made on entering the background.
}
func applicationDidBecomeActive(_ application: UIApplication) {
// Restart any tasks that were paused (or not yet started) while the application was inactive. If the application was previously in the background, optionally refresh the user interface.
}
func applicationWillTerminate(_ application: UIApplication) {
// Called when the application is about to terminate. Save data if appropriate. See also applicationDidEnterBackground:.
}
}
Ajouter des fonctionnalités pour la prise et le chargement de photos
Renommez ViewController.swift en PictureLaunchViewController.swift et remplacez le fichier par le code suivant.
import UIKit
import immersive_reader_sdk
class PictureLaunchViewController: UIViewController, UINavigationControllerDelegate, UIImagePickerControllerDelegate {
private var photoButton: UIButton!
private var cameraButton: UIButton!
private var titleText: UILabel!
private var bodyText: UILabel!
private var sampleContent: Content!
private var sampleChunk: Chunk!
private var sampleOptions: Options!
private var imagePicker: UIImagePickerController!
private var spinner: UIActivityIndicatorView!
private var activityIndicatorBackground: UIView!
private var textURL = "vision/v2.0/read/core/asyncBatchAnalyze";
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
view.backgroundColor = .white
titleText = UILabel()
titleText.text = "Picture to Immersive Reader with OCR"
titleText.font = UIFont.boldSystemFont(ofSize: 32)
titleText.textAlignment = .center
titleText.lineBreakMode = .byWordWrapping
titleText.numberOfLines = 0
view.addSubview(titleText)
bodyText = UILabel()
bodyText.text = "Capture or upload a photo of handprinted text on a piece of paper, handwriting, typed text, text on a computer screen, writing on a white board and many more, and watch it be presented to you in the Immersive Reader!"
bodyText.font = UIFont.systemFont(ofSize: 18)
bodyText.lineBreakMode = .byWordWrapping
bodyText.numberOfLines = 0
let screenSize = self.view.frame.height
if screenSize <= 667 {
// Font size for smaller iPhones.
bodyText.font = bodyText.font.withSize(16)
} else if screenSize <= 812.0 {
// Font size for medium iPhones.
bodyText.font = bodyText.font.withSize(18)
} else if screenSize <= 896 {
// Font size for larger iPhones.
bodyText.font = bodyText.font.withSize(20)
} else {
// Font size for iPads.
bodyText.font = bodyText.font.withSize(26)
}
view.addSubview(bodyText)
photoButton = UIButton()
photoButton.backgroundColor = .darkGray
photoButton.contentEdgeInsets = UIEdgeInsets(top: 10, left: 5, bottom: 10, right: 5)
photoButton.layer.cornerRadius = 5
photoButton.setTitleColor(.white, for: .normal)
photoButton.setTitle("Choose Photo from Library", for: .normal)
photoButton.titleLabel?.font = UIFont.systemFont(ofSize: 18, weight: .bold)
photoButton.addTarget(self, action: #selector(selectPhotoButton(sender:)), for: .touchUpInside)
view.addSubview(photoButton)
cameraButton = UIButton()
cameraButton.backgroundColor = .darkGray
cameraButton.contentEdgeInsets = UIEdgeInsets(top: 10, left: 5, bottom: 10, right: 5)
cameraButton.layer.cornerRadius = 5
cameraButton.setTitleColor(.white, for: .normal)
cameraButton.setTitle("Take Photo", for: .normal)
cameraButton.titleLabel?.font = UIFont.systemFont(ofSize: 18, weight: .bold)
cameraButton.addTarget(self, action: #selector(takePhotoButton(sender:)), for: .touchUpInside)
view.addSubview(cameraButton)
activityIndicatorBackground = UIView()
activityIndicatorBackground.backgroundColor = UIColor.black
activityIndicatorBackground.alpha = 0
view.addSubview(activityIndicatorBackground)
view.bringSubviewToFront(_: activityIndicatorBackground)
spinner = UIActivityIndicatorView(style: .whiteLarge)
view.addSubview(spinner)
let layoutGuide = view.safeAreaLayoutGuide
titleText.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
titleText.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.topAnchor, constant: 25).isActive = true
titleText.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.leadingAnchor, constant: 20).isActive = true
titleText.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.trailingAnchor, constant: -20).isActive = true
bodyText.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
bodyText.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: titleText.bottomAnchor, constant: 35).isActive = true
bodyText.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.leadingAnchor, constant: 20).isActive = true
bodyText.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.trailingAnchor, constant: -20).isActive = true
cameraButton.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
if screenSize > 896 {
// Constraints for iPads.
cameraButton.heightAnchor.constraint(equalToConstant: 150).isActive = true
cameraButton.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.leadingAnchor, constant: 60).isActive = true
cameraButton.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.trailingAnchor, constant: -60).isActive = true
cameraButton.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: bodyText.bottomAnchor, constant: 150).isActive = true
} else {
// Constraints for iPhones.
cameraButton.heightAnchor.constraint(equalToConstant: 100).isActive = true
cameraButton.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.leadingAnchor, constant: 30).isActive = true
cameraButton.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.trailingAnchor, constant: -30).isActive = true
cameraButton.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: bodyText.bottomAnchor, constant: 100).isActive = true
}
cameraButton.bottomAnchor.constraint(equalTo: photoButton.topAnchor, constant: -40).isActive = true
photoButton.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
if screenSize > 896 {
// Constraints for iPads.
photoButton.heightAnchor.constraint(equalToConstant: 150).isActive = true
photoButton.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.leadingAnchor, constant: 60).isActive = true
photoButton.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.trailingAnchor, constant: -60).isActive = true
} else {
// Constraints for iPhones.
photoButton.heightAnchor.constraint(equalToConstant: 100).isActive = true
photoButton.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.leadingAnchor, constant: 30).isActive = true
photoButton.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.trailingAnchor, constant: -30).isActive = true
}
spinner.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
spinner.centerXAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.centerXAnchor).isActive = true
spinner.centerYAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.centerYAnchor).isActive = true
activityIndicatorBackground.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
activityIndicatorBackground.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.topAnchor).isActive = true
activityIndicatorBackground.bottomAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.bottomAnchor).isActive = true
activityIndicatorBackground.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.leadingAnchor).isActive = true
activityIndicatorBackground.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: layoutGuide.trailingAnchor).isActive = true
// Create content and options.
sampleChunk = Chunk(content: bodyText.text!, lang: nil, mimeType: nil)
sampleContent = Content(title: titleText.text!, chunks: [sampleChunk])
sampleOptions = Options(uiLang: nil, timeout: nil, uiZIndex: nil)
}
@IBAction func selectPhotoButton(sender: AnyObject) {
// Launch the photo picker.
imagePicker = UIImagePickerController()
imagePicker.delegate = self
self.imagePicker.sourceType = .photoLibrary
self.imagePicker.allowsEditing = true
self.present(self.imagePicker, animated: true, completion: nil)
self.photoButton.isEnabled = true
}
@IBAction func takePhotoButton(sender: AnyObject) {
if !UIImagePickerController.isSourceTypeAvailable(.camera) {
// If there is no camera on the device, disable the button
self.cameraButton.backgroundColor = .gray
self.cameraButton.isEnabled = true
} else {
// Launch the camera.
imagePicker = UIImagePickerController()
imagePicker.delegate = self
self.imagePicker.sourceType = .camera
self.present(self.imagePicker, animated: true, completion: nil)
self.cameraButton.isEnabled = true
}
}
func imagePickerController(_ picker: UIImagePickerController, didFinishPickingMediaWithInfo info: [UIImagePickerController.InfoKey : Any]) {
imagePicker.dismiss(animated: true, completion: nil)
photoButton.isEnabled = false
cameraButton.isEnabled = false
self.spinner.startAnimating()
activityIndicatorBackground.alpha = 0.6
// Retrieve the image.
let image = (info[.originalImage] as? UIImage)!
// Retrieve the byte array from image.
let imageByteArray = image.jpegData(compressionQuality: 1.0)
// Call the getTextFromImage function passing in the image the user takes or chooses.
getTextFromImage(subscriptionKey: Constants.computerVisionSubscriptionKey, getTextUrl: Constants.computerVisionEndPoint + textURL, pngImage: imageByteArray!, onSuccess: { cognitiveText in
print("cognitive text is: \(cognitiveText)")
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.photoButton.isEnabled = true
self.cameraButton.isEnabled = true
}
// Create content and options with the text from the image.
let sampleImageChunk = Chunk(content: cognitiveText, lang: nil, mimeType: nil)
let sampleImageContent = Content(title: "Text from image", chunks: [sampleImageChunk])
let sampleImageOptions = Options(uiLang: nil, timeout: nil, uiZIndex: nil)
// Callback to get token for Immersive Reader.
self.getToken(onSuccess: {cognitiveToken in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
launchImmersiveReader(navController: self.navigationController!, token: cognitiveToken, subdomain: Constants.subdomain, content: sampleImageContent, options: sampleImageOptions, onSuccess: {
self.spinner.stopAnimating()
self.activityIndicatorBackground.alpha = 0
self.photoButton.isEnabled = true
self.cameraButton.isEnabled = true
}, onFailure: { error in
print("An error occurred launching the Immersive Reader: \(error)")
self.spinner.stopAnimating()
self.activityIndicatorBackground.alpha = 0
self.photoButton.isEnabled = true
self.cameraButton.isEnabled = true
})
}
}, onFailure: { error in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.photoButton.isEnabled = true
self.cameraButton.isEnabled = true
}
print("An error occurred retrieving the token: \(error)")
})
}, onFailure: { error in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.photoButton.isEnabled = true
self.cameraButton.isEnabled = true
}
})
}
/// Retrieves the token for the Immersive Reader using Microsoft Entra authentication
///
/// - Parameters:
/// -onSuccess: A closure that gets called when the token is successfully received using Microsoft Entra authentication.
/// -theToken: The token for the Immersive Reader received using Microsoft Entra authentication.
/// -onFailure: A closure that gets called when the token fails to be obtained from the Microsoft Entra authentication.
/// -theError: The error that occurred when the token fails to be obtained from the Microsoft Entra authentication.
func getToken(onSuccess: @escaping (_ theToken: String) -> Void, onFailure: @escaping ( _ theError: String) -> Void) {
let tokenForm = "grant_type=client_credentials&resource=https://cognitiveservices.azure.com/&client_id=" + Constants.clientId + "&client_secret=" + Constants.clientSecret
let tokenUrl = "https://login.windows.net/" + Constants.tenantId + "/oauth2/token"
var responseTokenString: String = "0"
let url = URL(string: tokenUrl)!
var request = URLRequest(url: url)
request.httpBody = tokenForm.data(using: .utf8)
request.httpMethod = "POST"
let task = URLSession.shared.dataTask(with: request) { data, response, error in
guard let data = data,
let response = response as? HTTPURLResponse,
// Check for networking errors.
error == nil else {
print("error", error ?? "Unknown error")
onFailure("Error")
return
}
// Check for http errors.
guard (200 ... 299) ~= response.statusCode else {
print("statusCode should be 2xx, but is \(response.statusCode)")
print("response = \(response)")
onFailure(String(response.statusCode))
return
}
let responseString = String(data: data, encoding: .utf8)
print("responseString = \(String(describing: responseString!))")
let jsonResponse = try? JSONSerialization.jsonObject(with: data, options: [])
guard let jsonDictonary = jsonResponse as? [String: Any] else {
onFailure("Error parsing JSON response.")
return
}
guard let responseToken = jsonDictonary["access_token"] as? String else {
onFailure("Error retrieving token from JSON response.")
return
}
responseTokenString = responseToken
onSuccess(responseTokenString)
}
task.resume()
}
/// Returns the text string after it has been extracted from an Image input.
///
/// - Parameters:
/// -subscriptionKey: The Azure subscription key.
/// -pngImage: Image data in PNG format.
/// - Returns: a string of text representing the
func getTextFromImage(subscriptionKey: String, getTextUrl: String, pngImage: Data, onSuccess: @escaping (_ theToken: String) -> Void, onFailure: @escaping ( _ theError: String) -> Void) {
let url = URL(string: getTextUrl)!
var request = URLRequest(url: url)
request.setValue(subscriptionKey, forHTTPHeaderField: "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key")
request.setValue("application/octet-stream", forHTTPHeaderField: "Content-Type")
// Two REST API calls are required to extract text. The first call is to submit the image for processing, and the next call is to retrieve the text found in the image.
// Set the body to the image in byte array format.
request.httpBody = pngImage
request.httpMethod = "POST"
let task = URLSession.shared.dataTask(with: request) { data, response, error in
guard let data = data,
let response = response as? HTTPURLResponse,
// Check for networking errors.
error == nil else {
print("error", error ?? "Unknown error")
onFailure("Error")
return
}
// Check for http errors.
guard (200 ... 299) ~= response.statusCode else {
print("statusCode should be 2xx, but is \(response.statusCode)")
print("response = \(response)")
onFailure(String(response.statusCode))
return
}
let responseString = String(data: data, encoding: .utf8)
print("responseString = \(String(describing: responseString!))")
// Send the second call to the API. The first API call returns operationLocation which stores the URI for the second REST API call.
let operationLocation = response.allHeaderFields["Operation-Location"] as? String
if (operationLocation == nil) {
print("Error retrieving operation location")
return
}
// Wait 10 seconds for text recognition to be available as suggested by the Text API documentation.
print("Text submitted. Waiting 10 seconds to retrieve the recognized text.")
sleep(10)
// HTTP GET request with the operationLocation url to retrieve the text.
let getTextUrl = URL(string: operationLocation!)!
var getTextRequest = URLRequest(url: getTextUrl)
getTextRequest.setValue(subscriptionKey, forHTTPHeaderField: "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key")
getTextRequest.httpMethod = "GET"
// Send the GET request to retrieve the text.
let taskGetText = URLSession.shared.dataTask(with: getTextRequest) { data, response, error in
guard let data = data,
let response = response as? HTTPURLResponse,
// Check for networking errors.
error == nil else {
print("error", error ?? "Unknown error")
onFailure("Error")
return
}
// Check for http errors.
guard (200 ... 299) ~= response.statusCode else {
print("statusCode should be 2xx, but is \(response.statusCode)")
print("response = \(response)")
onFailure(String(response.statusCode))
return
}
// Decode the JSON data into an object.
let customDecoding = try! JSONDecoder().decode(TextApiResponse.self, from: data)
// Loop through the lines to get all lines of text and concatenate them together.
var textFromImage = ""
for textLine in customDecoding.recognitionResults[0].lines {
textFromImage = textFromImage + textLine.text + " "
}
onSuccess(textFromImage)
}
taskGetText.resume()
}
task.resume()
}
// Structs used for decoding the Text API JSON response.
struct TextApiResponse: Codable {
let status: String
let recognitionResults: [RecognitionResult]
}
struct RecognitionResult: Codable {
let page: Int
let clockwiseOrientation: Double
let width, height: Int
let unit: String
let lines: [Line]
}
struct Line: Codable {
let boundingBox: [Int]
let text: String
let words: [Word]
}
struct Word: Codable {
let boundingBox: [Int]
let text: String
let confidence: String?
}
}
Générer et exécuter l’application
Définissez le modèle d’archive dans Xcode en sélectionnant un simulateur ou une cible d’appareil.


Dans Xcode, appuyez sur Ctrl+R ou cliquez sur le bouton de lecture pour exécuter le projet. L’application doit être lancée sur le simulateur ou l’appareil spécifié.
Dans votre application, vous devriez voir :

Prenez ou chargez une photo de texte en appuyant sur le bouton Prendre une photo ou Choisir une photo à partir de la bibliothèque. L'Immersive Reader se lance alors et affiche le texte de la photo.
