Troubleshooting the Web connector
What's the difference between Web.Contents, Web.BrowserContents, and Web.Page?
Web.Contentsis used for retrieving web content that doesn't need to be accessed through a browser, such as CSV files, JSON API results, and so on.- It supports the widest variety of authentication options.
- It can be used in cloud environments, such as Power Query Online, without a gateway.
Web.Pageis a legacy function for retrieving web content that needs to be accessed through a browser, such as HTML pages.- It's built on Internet Explorer. Because of this requirement, it's being replaced in the UI with
Web.BrowserContents. However,Web.Pagewill continue to be available at the engine level for backward compatibility. - A gateway is required to use it in cloud environments, such as Power Query Online.
Web.BrowserContentsis an updated function for retrieving web content that needs to be accessed through a browser, such as HTML pages.- In the UI,
Web.BrowserContentsis replacingWeb.Page, becauseWeb.Pageis based on Internet Explorer. Web.BrowserContentswas initially built on Chromium, but it now uses Microsoft Edge's WebView2 control.- A gateway is required to use it in cloud environments, such as Power Query Online.
The following table summarizes the differences.
| Web.Contents | Web.Page | Web.BrowserContents | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-browser content (.txt/.csv files, JSON, and so on) | x | ||
| Browser content (HTML) | x | x | |
| Authentication Types Supported | Anonymous Windows Basic Web API Organizational Account |
Anonymous Windows (current user's credentials only) Web API |
Anonymous Windows Basic Web API |
| Requires a gateway in cloud hosts | N | Y | Y |
| Currently generated by | All hosts | Excel and Power Query Online | Power BI Desktop |
| Built on | .NET | Internet Explorer | Microsoft Edge's WebView2 control |
Note
POST requests can only be made anonymously when using Web.Contents.
"This browser is no longer supported" warnings in the Web View
When importing a web page, you can view a preview of the page using the Web View tab in Power Query's navigator dialog. This preview may sometimes display a warning such as "This browser is no longer supported". When this happens, it's usually because the Web View currently renders the Web View preview using Internet Explorer, which is no longer supported by some websites. However, this only affects the Web View and doesn't affect the web connector itself. As long as you're using the connectors based on Web.Contents or Web.BrowserContents (and not Web.Page), you can safely ignore such warnings. Refer to What's the difference between Web.Contents, Web.BrowserContents, and Web.Page? for more information on the different web connectors and their underlying technologies.
Handling dynamic web pages
Web pages that load their content dynamically might require special handling. If you notice sporadic errors in your web queries, it's possible that you're trying to access a dynamic web page. One common example of this type of error is:
- You refresh a query that connects to the site.
- You see an error (for example, "the column 'Foo' of the table wasn't found").
- You refresh the query again.
- No error occurs.
These kinds of issues are usually due to timing. Pages that load their content dynamically can sometimes be inconsistent since the content can change after the browser considers loading complete. Sometimes the web connector downloads the HTML after all the dynamic content has loaded. Other times the changes are still in progress when it downloads the HTML, leading to sporadic errors.
The solution is to use the WaitFor option of Web.BrowserContents, which indicates either a selector or a length of time that should be waited for before downloading the HTML.
How can you tell if a page is dynamic? Usually it's pretty simple. Open the page in a browser and watch it load. If the content shows up right away, it's a regular HTML page. If it appears dynamically or changes over time, it's a dynamic page.
Using a gateway with the Web connector
Both Web.BrowserContents and Web.Page require the use of an on-premises data gateway when published to a cloud service, such as Power BI semantic models or dataflows, or Power Apps dataflows. (Currently, Dynamics 365 Customer Insights doesn't support the use of a gateway.)
If you're using Web.Page and receive a Please specify how to connect error, ensure that you have Internet Explorer 10 or later installed on the machine that hosts your on-premises data gateway.
If you're using Web.BrowserContents and receive a We were unable to find the WebView2 runtime error, ensure that you have the WebView2 runtime installed on the machine that hosts your on-premises data gateway. The error message should provide a link to the WebView2 runtime installer. If you've installed the runtime but are still seeing the error, ensure that the gateway service account (usually PBIEgwService) has access to the install location of the WebView2 runtime (for example, C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft\EdgeWebView).
"We encountered an error when initializing the web browser" errors when using Web.BrowserContents
This error can occur if the process calling Web.BrowserContents is running in elevated mode, since WebView2 currently doesn't support running with administrator privileges.
Using Web.Page instead of Web.BrowserContents
In cases where you need to use Web.Page instead of Web.BrowserContents, you can still manually use Web.Page.
In Power BI Desktop, you can use the older Web.Page function by clearing the Enable web table inference option:
Under the File tab, select Options and settings > Options.
In the Global section, select Power Query Editor.
Clear the Enable web table inference option, and then select OK.
Restart Power BI Desktop.
Note
Currently, you can't turn off the use of
Web.BrowserContentsin Power BI Desktop optimized for Power BI Report Server.
You can also get a copy of a Web.Page query from Excel. To copy the code from Excel:
- Select From Web from the Data tab.
- Enter the address in the From Web dialog box, and then select OK.
- In Navigator, choose the data you want to load, and then select Transform Data.
- In the Home tab of Power Query, select Advanced Editor.
- In the Advanced Editor, copy the M formula.
- In the app that uses
Web.BrowserContents, select the Blank Query connector. - If you're copying to Power BI Desktop:
- In the Home tab, select Advanced Editor.
- Paste the copied
Web.Pagequery in the editor, and then select Done.
- If you're copying to Power Query Online:
- In the Blank Query, paste the copied
Web.Pagequery in the blank query. - Select an on-premises data gateway to use.
- Select Next.
- In the Blank Query, paste the copied
You can also manually enter the following code into a blank query. Ensure that you enter the address of the web page you want to load.
let
Source = Web.Page(Web.Contents("<your address here>")),
Navigation = Source{0}[Data]
in
Navigation
Capturing web requests and certificate revocation
We've strengthened the security of web connections to protect your data. However, this means that certain scenarios, like capturing web requests with Fiddler, will no longer work by default. To enable those scenarios:
Open Power BI Desktop.
Under the File tab, select Options and settings > Options.
In Options, under Global > Security, uncheck Enable certificate revocation check.
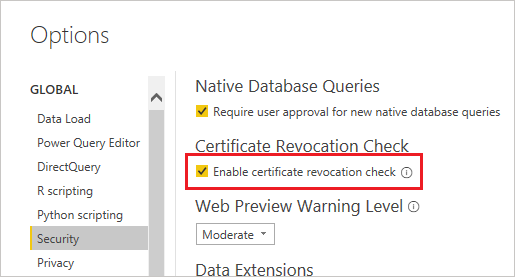
Select OK.
Restart Power BI Desktop.
Important
Be aware that unchecking Enable certificate revocation check will make web connections less secure.
To set this scenario in Group Policy, use the "DisableCertificateRevocationCheck" key under the registry path "Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Microsoft Power BI Desktop". Setting "DisableCertificateRevocationCheck" to 0 will always enable the check (stopping Fiddler and similar software from working) and setting "DisableCertificateRevocationCheck" to 1 will always disable the check (enabling Fiddler and similar software).
Changing the authentication method
In some cases, you may need to change the authentication method you use to access a particular site. If this change is necessary, go to Change the authentication method.
Authenticating to arbitrary services
Some services support the ability for the Web connector to authenticate with OAuth/Microsoft Entra ID authentication out of the box. However, this won't work in most cases.
When attempting to authenticate, if you see the following error:
We were unable to connect because this credential type isn’t supported for this resource. Please choose another credential type.
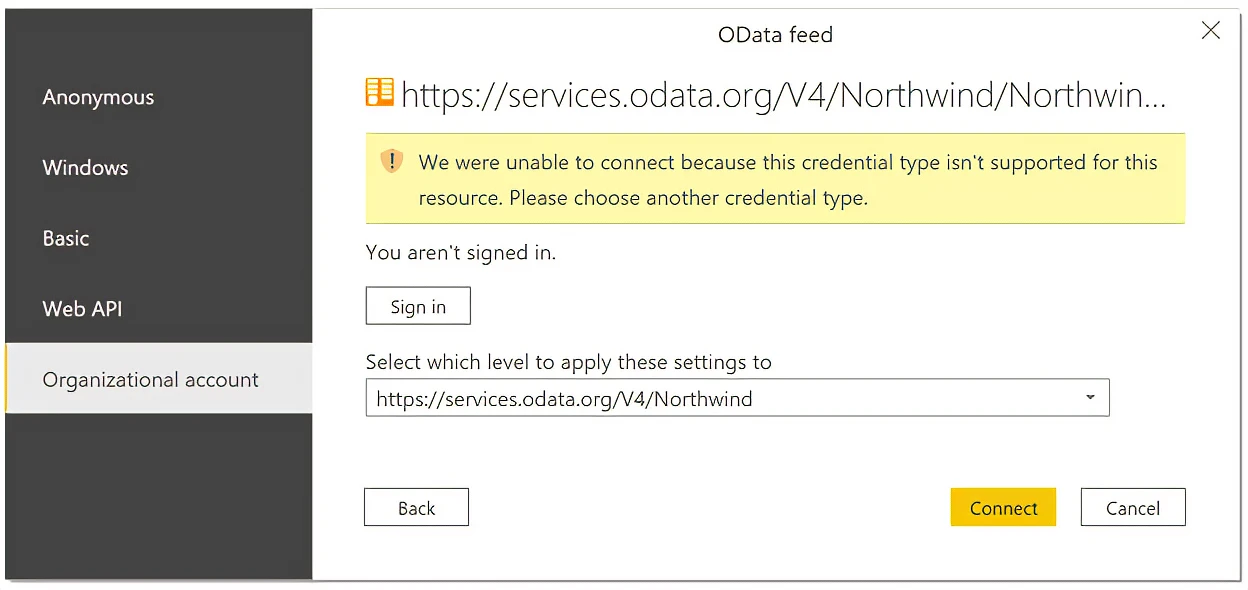
Contact the service owner. They either need to change the authentication configuration or build a custom connector.
Web connector uses HTTP 1.1 to communicate
The Power Query Web connector communicates with a data source using HTTP 1.1. If your data source is expecting to communicate using HTTP 1.0, you might receive an error, such as 500 Internal Server Error.
It's not possible to switch Power Query to use HTTP 1.0. Power Query always sends an Expect:100-continue when there's a body to avoid passing a possibly large payload when the initial call itself might fail (for example, due to a lack of permissions). Currently, this behavior can't be changed.
Connecting to Microsoft Graph
Power Query currently doesn't support connecting to Microsoft Graph REST APIs. More information: Lack of Support for Microsoft Graph in Power Query
See also
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for