你当前正在访问 Microsoft Azure Global Edition 技术文档网站。 如果需要访问由世纪互联运营的 Microsoft Azure 中国技术文档网站,请访问 https://docs.azure.cn。
使用语音 SDK 与客户端应用程序集成
重要
自定义命令将于 2026 年 4 月 30 日停用。 自 2023 年 10 月 30 日起,无法在 Speech Studio 中创建新的自定义命令应用程序。 与此更改相关的是,LUIS 将于 2025 年 10 月 1 日停用。 自 2023 年 4 月 1 日起,无法创建新的 LUIS 资源。
本文介绍如何从 UWP 应用程序中运行的语音 SDK 向已发布的自定义命令应用程序发出请求。 为了建立与自定义命令应用程序的连接,需要:
- 发布自定义命令应用程序,并获取应用程序标识符(应用 ID)
- 使用语音 SDK 创建一个通用 Windows 平台 (UWP) 客户端应用,以便你能够与自定义命令应用程序通信
先决条件
若要完成本文,需要自定义命令应用程序。 尝试根据快速入门来创建自定义命令应用程序:
还需要:
- Visual Studio 2019 或更高版本。 本指南基于 Visual Studio 2019。
- Azure AI 语音资源密钥和区域:在 Azure 门户上创建语音资源。 有关详细信息,请参阅创建多服务资源。
- 启用设备进行开发
步骤 1:发布自定义命令应用程序
打开你之前创建的自定义命令应用程序。
转到“设置”,选择“LUIS 资源”。
如果未分配“预测资源”,请选择一个查询预测密钥或创建一个新的查询预测密钥。
在发布应用程序之前,始终需要查询预测密钥。 有关 LUIS 资源的详细信息,请参阅创建 LUIS 资源
返回到编辑命令,选择“发布”。
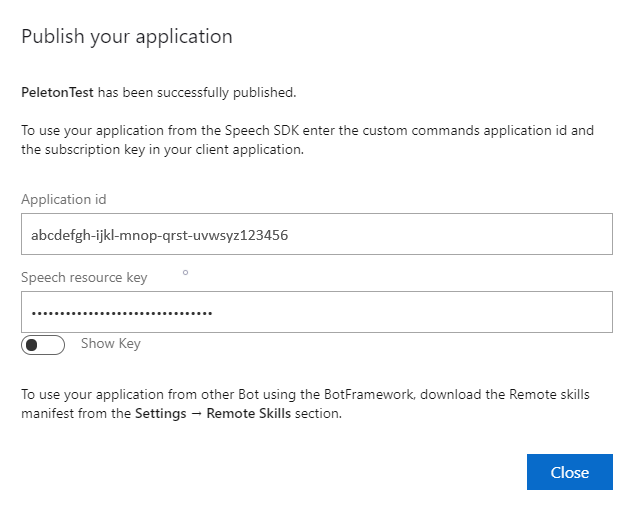
从“发布”通知中复制应用 ID 供以后使用。
复制语音资源密钥供以后使用。
步骤 2:创建 Visual Studio 项目
创建用于 UWP 开发的 Visual Studio 项目并安装语音 SDK。
步骤 3:添加示例代码
在此步骤中,添加定义应用程序用户界面的 XAML 代码,并添加 C# 代码隐藏实现。
XAML 代码
通过添加 XAML 代码创建应用程序的用户界面。
在“解决方案资源管理器”中打开
MainPage.xaml在设计器的 XAML 视图中,将整个内容替换为以下代码片段:
<Page x:Class="helloworld.MainPage" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" xmlns:local="using:helloworld" xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008" xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006" mc:Ignorable="d" Background="{ThemeResource ApplicationPageBackgroundThemeBrush}"> <Grid> <StackPanel Orientation="Vertical" HorizontalAlignment="Center" Margin="20,50,0,0" VerticalAlignment="Center" Width="800"> <Button x:Name="EnableMicrophoneButton" Content="Enable Microphone" Margin="0,10,10,0" Click="EnableMicrophone_ButtonClicked" Height="35"/> <Button x:Name="ListenButton" Content="Talk" Margin="0,10,10,0" Click="ListenButton_ButtonClicked" Height="35"/> <StackPanel x:Name="StatusPanel" Orientation="Vertical" RelativePanel.AlignBottomWithPanel="True" RelativePanel.AlignRightWithPanel="True" RelativePanel.AlignLeftWithPanel="True"> <TextBlock x:Name="StatusLabel" Margin="0,10,10,0" TextWrapping="Wrap" Text="Status:" FontSize="20"/> <Border x:Name="StatusBorder" Margin="0,0,0,0"> <ScrollViewer VerticalScrollMode="Auto" VerticalScrollBarVisibility="Auto" MaxHeight="200"> <!-- Use LiveSetting to enable screen readers to announce the status update. --> <TextBlock x:Name="StatusBlock" FontWeight="Bold" AutomationProperties.LiveSetting="Assertive" MaxWidth="{Binding ElementName=Splitter, Path=ActualWidth}" Margin="10,10,10,20" TextWrapping="Wrap" /> </ScrollViewer> </Border> </StackPanel> </StackPanel> <MediaElement x:Name="mediaElement"/> </Grid> </Page>
更新“设计”视图以显示应用程序的用户界面。
C# 代码隐藏源
添加代码隐藏源,以便应用程序按预期工作。 代码隐藏源包括:
Speech和Speech.Dialog命名空间的所需using语句。- 一个绑定到按钮处理程序的简单实现,用于确保麦克风访问。
- 基本的 UI 帮助程序,用于在应用程序中提供消息和错误。
- 初始化代码路径的登陆点。
- 用于播放文本转语音的帮助程序(没有流式处理支持)。
- 用于开始侦听的空按钮处理程序。
按如下所示添加代码隐藏源:
在“解决方案资源管理器”中,打开代码隐藏源文件
MainPage.xaml.cs(归入MainPage.xaml)将该文件的内容替换为以下代码:
using Microsoft.CognitiveServices.Speech; using Microsoft.CognitiveServices.Speech.Audio; using Microsoft.CognitiveServices.Speech.Dialog; using System; using System.IO; using System.Text; using Windows.UI.Xaml; using Windows.UI.Xaml.Controls; using Windows.UI.Xaml.Media; namespace helloworld { public sealed partial class MainPage : Page { private DialogServiceConnector connector; private enum NotifyType { StatusMessage, ErrorMessage }; public MainPage() { this.InitializeComponent(); } private async void EnableMicrophone_ButtonClicked( object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { bool isMicAvailable = true; try { var mediaCapture = new Windows.Media.Capture.MediaCapture(); var settings = new Windows.Media.Capture.MediaCaptureInitializationSettings(); settings.StreamingCaptureMode = Windows.Media.Capture.StreamingCaptureMode.Audio; await mediaCapture.InitializeAsync(settings); } catch (Exception) { isMicAvailable = false; } if (!isMicAvailable) { await Windows.System.Launcher.LaunchUriAsync( new Uri("ms-settings:privacy-microphone")); } else { NotifyUser("Microphone was enabled", NotifyType.StatusMessage); } } private void NotifyUser( string strMessage, NotifyType type = NotifyType.StatusMessage) { // If called from the UI thread, then update immediately. // Otherwise, schedule a task on the UI thread to perform the update. if (Dispatcher.HasThreadAccess) { UpdateStatus(strMessage, type); } else { var task = Dispatcher.RunAsync( Windows.UI.Core.CoreDispatcherPriority.Normal, () => UpdateStatus(strMessage, type)); } } private void UpdateStatus(string strMessage, NotifyType type) { switch (type) { case NotifyType.StatusMessage: StatusBorder.Background = new SolidColorBrush( Windows.UI.Colors.Green); break; case NotifyType.ErrorMessage: StatusBorder.Background = new SolidColorBrush( Windows.UI.Colors.Red); break; } StatusBlock.Text += string.IsNullOrEmpty(StatusBlock.Text) ? strMessage : "\n" + strMessage; if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(StatusBlock.Text)) { StatusBorder.Visibility = Visibility.Visible; StatusPanel.Visibility = Visibility.Visible; } else { StatusBorder.Visibility = Visibility.Collapsed; StatusPanel.Visibility = Visibility.Collapsed; } // Raise an event if necessary to enable a screen reader // to announce the status update. var peer = Windows.UI.Xaml.Automation.Peers.FrameworkElementAutomationPeer.FromElement(StatusBlock); if (peer != null) { peer.RaiseAutomationEvent( Windows.UI.Xaml.Automation.Peers.AutomationEvents.LiveRegionChanged); } } // Waits for and accumulates all audio associated with a given // PullAudioOutputStream and then plays it to the MediaElement. Long spoken // audio will create extra latency and a streaming playback solution // (that plays audio while it continues to be received) should be used -- // see the samples for examples of this. private void SynchronouslyPlayActivityAudio( PullAudioOutputStream activityAudio) { var playbackStreamWithHeader = new MemoryStream(); playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("RIFF"), 0, 4); // ChunkID playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(BitConverter.GetBytes(UInt32.MaxValue), 0, 4); // ChunkSize: max playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("WAVE"), 0, 4); // Format playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("fmt "), 0, 4); // Subchunk1ID playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(BitConverter.GetBytes(16), 0, 4); // Subchunk1Size: PCM playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(BitConverter.GetBytes(1), 0, 2); // AudioFormat: PCM playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(BitConverter.GetBytes(1), 0, 2); // NumChannels: mono playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(BitConverter.GetBytes(16000), 0, 4); // SampleRate: 16kHz playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(BitConverter.GetBytes(32000), 0, 4); // ByteRate playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(BitConverter.GetBytes(2), 0, 2); // BlockAlign playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(BitConverter.GetBytes(16), 0, 2); // BitsPerSample: 16-bit playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("data"), 0, 4); // Subchunk2ID playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(BitConverter.GetBytes(UInt32.MaxValue), 0, 4); // Subchunk2Size byte[] pullBuffer = new byte[2056]; uint lastRead = 0; do { lastRead = activityAudio.Read(pullBuffer); playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(pullBuffer, 0, (int)lastRead); } while (lastRead == pullBuffer.Length); var task = Dispatcher.RunAsync( Windows.UI.Core.CoreDispatcherPriority.Normal, () => { mediaElement.SetSource( playbackStreamWithHeader.AsRandomAccessStream(), "audio/wav"); mediaElement.Play(); }); } private void InitializeDialogServiceConnector() { // New code will go here } private async void ListenButton_ButtonClicked( object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { // New code will go here } } }注意
如果看到错误:“类型‘对象’在未被引用的程序集中定义”
- 右键单击解决方案。
- 选择“管理解决方案的 NuGet 包”,然后选择“更新”
- 如果在更新列表中看到 Microsoft.NETCore.UniversalWindowsPlatform,将 Microsoft.NETCore.UniversalWindowsPlatform 更新为最新版本
将以下代码添加到
InitializeDialogServiceConnector的方法主体// This code creates the `DialogServiceConnector` with your resource information. // create a DialogServiceConfig by providing a Custom Commands application id and Speech resource key // The RecoLanguage property is optional (default en-US); note that only en-US is supported in Preview const string speechCommandsApplicationId = "YourApplicationId"; // Your application id const string speechSubscriptionKey = "YourSpeechSubscriptionKey"; // Your Speech resource key const string region = "YourServiceRegion"; // The Speech resource region. var speechCommandsConfig = CustomCommandsConfig.FromSubscription(speechCommandsApplicationId, speechSubscriptionKey, region); speechCommandsConfig.SetProperty(PropertyId.SpeechServiceConnection_RecoLanguage, "en-us"); connector = new DialogServiceConnector(speechCommandsConfig);将字符串
YourApplicationId、YourSpeechSubscriptionKey和YourServiceRegion分别替换为自己的应用、语音密钥和区域值将以下代码片段追加到
InitializeDialogServiceConnector的方法主体的末尾// // This code sets up handlers for events relied on by `DialogServiceConnector` to communicate its activities, // speech recognition results, and other information. // // ActivityReceived is the main way your client will receive messages, audio, and events connector.ActivityReceived += (sender, activityReceivedEventArgs) => { NotifyUser( $"Activity received, hasAudio={activityReceivedEventArgs.HasAudio} activity={activityReceivedEventArgs.Activity}"); if (activityReceivedEventArgs.HasAudio) { SynchronouslyPlayActivityAudio(activityReceivedEventArgs.Audio); } }; // Canceled will be signaled when a turn is aborted or experiences an error condition connector.Canceled += (sender, canceledEventArgs) => { NotifyUser($"Canceled, reason={canceledEventArgs.Reason}"); if (canceledEventArgs.Reason == CancellationReason.Error) { NotifyUser( $"Error: code={canceledEventArgs.ErrorCode}, details={canceledEventArgs.ErrorDetails}"); } }; // Recognizing (not 'Recognized') will provide the intermediate recognized text // while an audio stream is being processed connector.Recognizing += (sender, recognitionEventArgs) => { NotifyUser($"Recognizing! in-progress text={recognitionEventArgs.Result.Text}"); }; // Recognized (not 'Recognizing') will provide the final recognized text // once audio capture is completed connector.Recognized += (sender, recognitionEventArgs) => { NotifyUser($"Final speech to text result: '{recognitionEventArgs.Result.Text}'"); }; // SessionStarted will notify when audio begins flowing to the service for a turn connector.SessionStarted += (sender, sessionEventArgs) => { NotifyUser($"Now Listening! Session started, id={sessionEventArgs.SessionId}"); }; // SessionStopped will notify when a turn is complete and // it's safe to begin listening again connector.SessionStopped += (sender, sessionEventArgs) => { NotifyUser($"Listening complete. Session ended, id={sessionEventArgs.SessionId}"); };将以下代码片段添加到
MainPage类中ListenButton_ButtonClicked方法的正文// This code sets up `DialogServiceConnector` to listen, since you already established the configuration and // registered the event handlers. if (connector == null) { InitializeDialogServiceConnector(); // Optional step to speed up first interaction: if not called, // connection happens automatically on first use var connectTask = connector.ConnectAsync(); } try { // Start sending audio await connector.ListenOnceAsync(); } catch (Exception ex) { NotifyUser($"Exception: {ex.ToString()}", NotifyType.ErrorMessage); }在菜单栏中,选择“文件”>“全部保存”以保存所做的更改
试试看
从菜单栏中,选择“构建”>“构建解决方案”以构建应用程序。 编译代码时应不会出错。
选择“调试”>“开始调试”(或按 F5)以启动应用程序。 此时将显示“helloworld”窗口。
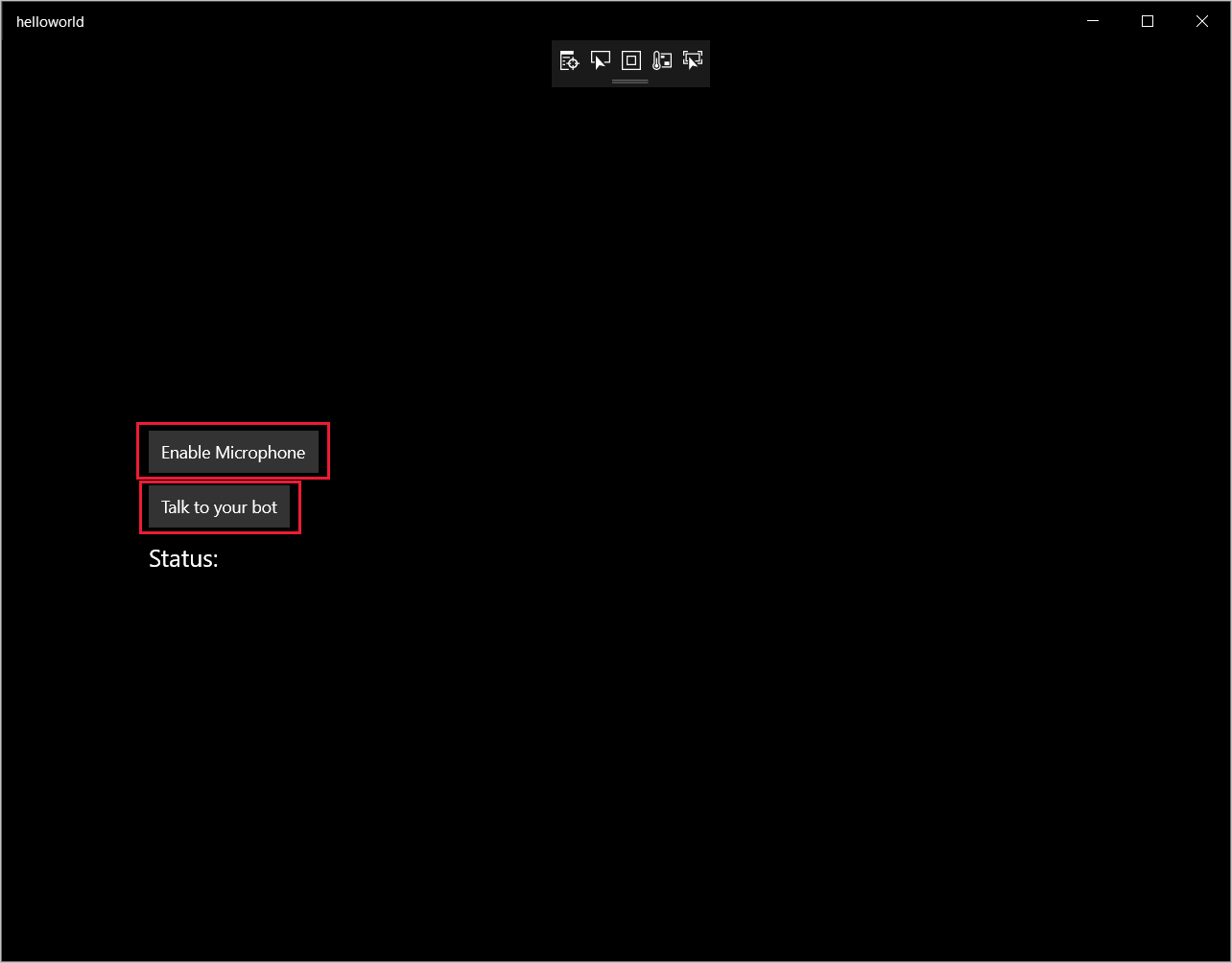
选择“启用麦克风”。 如果弹出访问权限请求,请选择“是”。

选择“讲话”,然后对着设备的麦克风讲出一个英文短语或句子。 你的语音将传输到 Direct Line 语音通道并转录为文本,该文本会显示在窗口中。