SkiaSharp 线性渐变
SKPaint 类定义一个 Color 属性,用于以纯色划线或填充区域。 也可以使用渐变来划线或填充区域,渐变是颜色的逐渐混合:

最基本的渐变类型是线性渐变。 颜色混合发生在从一点到另一点的一条直线(称为渐变线)上。 垂直于渐变线的线具有相同的颜色。 可以使用两个静态 SKShader.CreateLinearGradient 方法之一创建线性渐变。 两个重载之间的差别在于,一个重载包含矩阵变换,另一个则不包含。
这些方法返回一个类型为 SKShader 的对象,其设置为 SKPaint 的 Shader 属性。 如果 Shader 属性不为 null,它将重写 Color 属性。 使用此 SKPaint 对象绘制的任何线条或填充的任何区域都基于渐变而不是纯色。
注意
在 DrawBitmap 调用中包含 SKPaint 对象时,Shader 属性将被忽略。 可以使用 SKPaint 的 Color 属性设置显示位图的透明度(如显示 SkiaSharp 位图一文中所述),但不能使用 Shader 属性显示具有渐变透明度的位图。 其他技术可用于显示具有渐变透明度的位图:这些技术在文章 SkiaSharp 圆形渐变以及 SkiaSharp 合成和混合模式中做了介绍。
角到角渐变
通常,线性渐变从矩形的一个角延伸到另一个角。 如果起点是矩形的左上角,则渐变可以延伸:
- 垂直渐变到左下角
- 水平渐变到右上角
- 呈对角线渐变到右下角
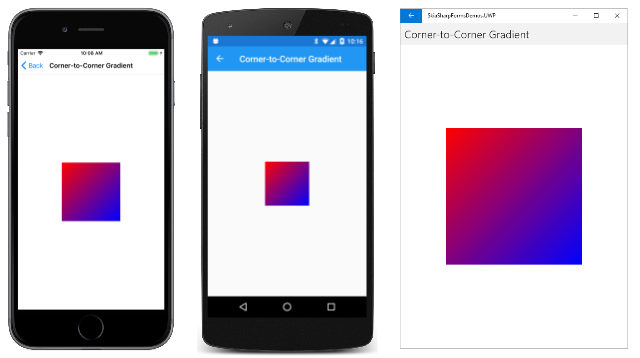
对角线线性渐变在 SkiaSharpFormsDemos 示例的“SkiaSharp 着色器和其他效果”部分中的第一页进行了演示。 “角到角渐变”页在其构造函数中创建一个 SKCanvasView。 PaintSurface 处理程序在 using 语句中创建一个 SKPaint 对象,然后定义一个位于画布中心的 300 像素正方形:
public class CornerToCornerGradientPage : ContentPage
{
···
public CornerToCornerGradientPage ()
{
Title = "Corner-to-Corner Gradient";
SKCanvasView canvasView = new SKCanvasView();
canvasView.PaintSurface += OnCanvasViewPaintSurface;
Content = canvasView;
···
}
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
SKImageInfo info = args.Info;
SKSurface surface = args.Surface;
SKCanvas canvas = surface.Canvas;
canvas.Clear();
using (SKPaint paint = new SKPaint())
{
// Create 300-pixel square centered rectangle
float x = (info.Width - 300) / 2;
float y = (info.Height - 300) / 2;
SKRect rect = new SKRect(x, y, x + 300, y + 300);
// Create linear gradient from upper-left to lower-right
paint.Shader = SKShader.CreateLinearGradient(
new SKPoint(rect.Left, rect.Top),
new SKPoint(rect.Right, rect.Bottom),
new SKColor[] { SKColors.Red, SKColors.Blue },
new float[] { 0, 1 },
SKShaderTileMode.Repeat);
// Draw the gradient on the rectangle
canvas.DrawRect(rect, paint);
···
}
}
}
为 SKPaint 的 Shader 属性分配静态 SKShader.CreateLinearGradient 方法的 SKShader 返回值。 五个参数如下:
- 渐变的起点,此处设置为矩形的左上角
- 渐变的终点,此处设置为矩形的右下角
- 有助于渐变的两种或多种颜色的数组
float值的数组,指示颜色在渐变线中的相对位置SKShaderTileMode枚举的成员,指示渐变在渐变线末端之外的行为方式
创建渐变对象后,DrawRect 方法使用包含着色器的 SKPaint 对象绘制 300 像素正方形。 此处,它在 iOS、Android 和通用 Windows 平台 (UWP) 上运行:
渐变线由指定为前两个参数的两个点定义。 请注意,这些点相对于画布,而不是与使用渐变显示的图形对象。 沿着渐变线,颜色逐渐从左上角的红色过渡到右下角的蓝色。 任何垂直于渐变线的线都具有恒定的颜色。
指定为第四个参数的 float 值数组与颜色数组具有一一对应的关系。 这些值指示这些颜色沿渐变线出现的相对位置。 此处,0 表示 Red 出现在渐变线的起点,1 表示 Blue 出现在渐变线的终点。 数字必须按升序排列,并且应在 0 到 1 的范围内。 如果它们不在该范围内,系统会将其调整到该范围内。
数组中的两个值可以设置为 0 和 1 以外的值。 试运行以下代码:
new float[] { 0.25f, 0.75f }
现在,整个渐变线的首四分之一是纯红色,最后四分之一是纯蓝色。 红色和蓝色的混合仅限于渐变线的中半部分。
通常,需要将这些位置值均匀地间隔在 0 到 1 之间。 如果是这种情况,只需提供 null 作为 CreateLinearGradient 的第四个参数即可。
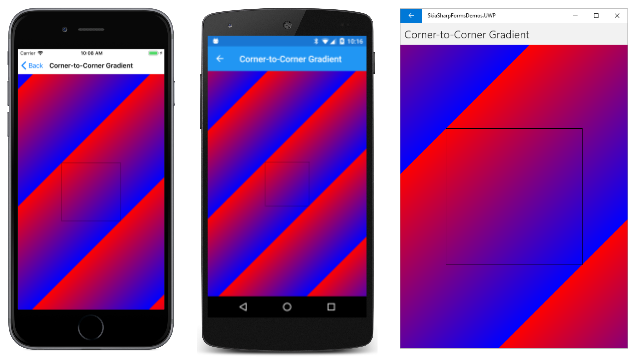
尽管此渐变是在 300 像素正方形的两个角之间定义的,但它并不限于填充该矩形。 “角到角渐变”页包含一些响应页上的点击或鼠标单击的额外代码。 每次点击,drawBackground 字段都会在 true 和 false 之间切换。 如果值为 true,则 PaintSurface 处理程序将使用相同的 SKPaint 对象来填充整个画布,然后绘制一个黑色矩形来指示较小的矩形:
public class CornerToCornerGradientPage : ContentPage
{
bool drawBackground;
public CornerToCornerGradientPage ()
{
···
TapGestureRecognizer tap = new TapGestureRecognizer();
tap.Tapped += (sender, args) =>
{
drawBackground ^= true;
canvasView.InvalidateSurface();
};
canvasView.GestureRecognizers.Add(tap);
}
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
···
using (SKPaint paint = new SKPaint())
{
···
if (drawBackground)
{
// Draw the gradient on the whole canvas
canvas.DrawRect(info.Rect, paint);
// Outline the smaller rectangle
paint.Shader = null;
paint.Style = SKPaintStyle.Stroke;
paint.Color = SKColors.Black;
canvas.DrawRect(rect, paint);
}
}
}
}
点击屏幕后会看到以下内容:
请注意,除了定义渐变线的点之外,渐变以相同的模式重复自身。 出现这种重复是因为 CreateLinearGradient 的最后一个参数是 SKShaderTileMode.Repeat。 (很快就会看到其他选项。)
另请注意,用于指定渐变线的点不是唯一的。 垂直于渐变线的线具有相同的颜色,因此可以指定无数条渐变线来获得相同的效果。 例如,使用水平渐变填充矩形时,可以指定左上角和右上角、左下角和右下角,或与这些线齐平且平行的任意两个点。
交互试验
可以通过“交互式线性渐变”页以交互方式试验线性渐变。 此页使用绘制圆弧的三种方法一文中介绍的 InteractivePage 类。InteractivePage 处理 TouchEffect 事件以维护可以用手指或鼠标移动的 TouchPoint 对象的集合。
XAML 文件将 TouchEffect 附加到 SKCanvasView 的父级,并且还包含一个 Picker,以允许选择 SKShaderTileMode 枚举的三个成员之一:
<local:InteractivePage xmlns="http://xamarin.com/schemas/2014/forms"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:SkiaSharpFormsDemos"
xmlns:skia="clr-namespace:SkiaSharp;assembly=SkiaSharp"
xmlns:skiaforms="clr-namespace:SkiaSharp.Views.Forms;assembly=SkiaSharp.Views.Forms"
xmlns:tt="clr-namespace:TouchTracking"
x:Class="SkiaSharpFormsDemos.Effects.InteractiveLinearGradientPage"
Title="Interactive Linear Gradient">
<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="*" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid BackgroundColor="White"
Grid.Row="0">
<skiaforms:SKCanvasView x:Name="canvasView"
PaintSurface="OnCanvasViewPaintSurface" />
<Grid.Effects>
<tt:TouchEffect Capture="True"
TouchAction="OnTouchEffectAction" />
</Grid.Effects>
</Grid>
<Picker x:Name="tileModePicker"
Grid.Row="1"
Title="Shader Tile Mode"
Margin="10"
SelectedIndexChanged="OnPickerSelectedIndexChanged">
<Picker.ItemsSource>
<x:Array Type="{x:Type skia:SKShaderTileMode}">
<x:Static Member="skia:SKShaderTileMode.Clamp" />
<x:Static Member="skia:SKShaderTileMode.Repeat" />
<x:Static Member="skia:SKShaderTileMode.Mirror" />
</x:Array>
</Picker.ItemsSource>
<Picker.SelectedIndex>
0
</Picker.SelectedIndex>
</Picker>
</Grid>
</local:InteractivePage>
代码隐藏文件中的构造函数为线性渐变的起点和终点创建两个 TouchPoint 对象。 PaintSurface 处理程序定义一个包含三种颜色的数组(从红到绿再到蓝的渐变),并从 Picker 获取当前的 SKShaderTileMode:
public partial class InteractiveLinearGradientPage : InteractivePage
{
public InteractiveLinearGradientPage ()
{
InitializeComponent ();
touchPoints = new TouchPoint[2];
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
touchPoints[i] = new TouchPoint
{
Center = new SKPoint(100 + i * 200, 100 + i * 200)
};
}
InitializeComponent();
baseCanvasView = canvasView;
}
void OnPickerSelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs args)
{
canvasView.InvalidateSurface();
}
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
SKImageInfo info = args.Info;
SKSurface surface = args.Surface;
SKCanvas canvas = surface.Canvas;
canvas.Clear();
SKColor[] colors = { SKColors.Red, SKColors.Green, SKColors.Blue };
SKShaderTileMode tileMode =
(SKShaderTileMode)(tileModePicker.SelectedIndex == -1 ?
0 : tileModePicker.SelectedItem);
using (SKPaint paint = new SKPaint())
{
paint.Shader = SKShader.CreateLinearGradient(touchPoints[0].Center,
touchPoints[1].Center,
colors,
null,
tileMode);
canvas.DrawRect(info.Rect, paint);
}
···
}
}
PaintSurface 处理程序根据所有这些信息创建 SKShader 对象,并使用它为整个画布着色。 float 值的数组设置为 null。 否则,要使三种颜色的间距相等,需要将该参数设置为值 0、0.5 和 1 的数组。
PaintSurface 处理程序主要用于显示多个对象:作为轮廓圆的触摸点、渐变线以及与触摸点处的与渐变线垂直的线:
public partial class InteractiveLinearGradientPage : InteractivePage
{
···
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
···
// Display the touch points here rather than by TouchPoint
using (SKPaint paint = new SKPaint())
{
paint.Style = SKPaintStyle.Stroke;
paint.Color = SKColors.Black;
paint.StrokeWidth = 3;
foreach (TouchPoint touchPoint in touchPoints)
{
canvas.DrawCircle(touchPoint.Center, touchPoint.Radius, paint);
}
// Draw gradient line connecting touchpoints
canvas.DrawLine(touchPoints[0].Center, touchPoints[1].Center, paint);
// Draw lines perpendicular to the gradient line
SKPoint vector = touchPoints[1].Center - touchPoints[0].Center;
float length = (float)Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow(vector.X, 2) +
Math.Pow(vector.Y, 2));
vector.X /= length;
vector.Y /= length;
SKPoint rotate90 = new SKPoint(-vector.Y, vector.X);
rotate90.X *= 200;
rotate90.Y *= 200;
canvas.DrawLine(touchPoints[0].Center,
touchPoints[0].Center + rotate90,
paint);
canvas.DrawLine(touchPoints[0].Center,
touchPoints[0].Center - rotate90,
paint);
canvas.DrawLine(touchPoints[1].Center,
touchPoints[1].Center + rotate90,
paint);
canvas.DrawLine(touchPoints[1].Center,
touchPoints[1].Center - rotate90,
paint);
}
}
}
连接两个接触点的渐变线很容易绘制,但绘制垂直线要麻烦一点。 渐变线将转换为矢量,标准化为一个单位的长度,然后旋转 90 度。 然后为该矢量指定 200 像素长度。 它用于绘制从触摸点延伸并垂直于渐变线的四条线。
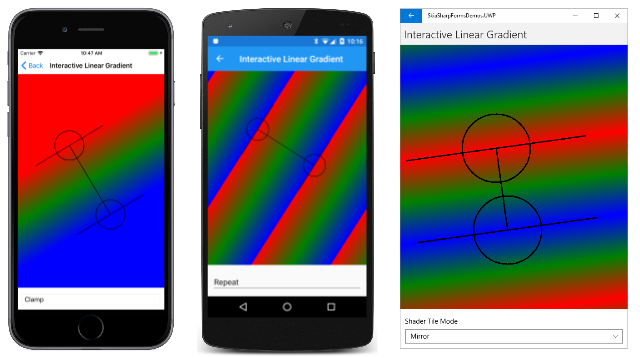
垂直线与渐变的起点和终点重合。 在这些线之外会发生什么情况取决于 SKShaderTileMode 枚举的设置:
这三个屏幕截图显示了 SKShaderTileMode 的三个不同值的结果。 iOS 屏幕截图显示了 SKShaderTileMode.Clamp,它只是扩展了渐变边框上的颜色。 Android 屏幕截图中的 SKShaderTileMode.Repeat 选项显示了渐变模式的重复方式。 UWP 屏幕截图中的 SKShaderTileMode.Mirror 选项也重复该模式,但每次都会反转该模式,从而避免导致颜色不连续。
渐变上的渐变
除 Dispose 之外,SKShader 类不会定义任何公共属性或方法。 因此,通过其静态方法创建的 SKShader 对象是不可变的。 即使对两个不同的对象使用相同的渐变,也可能需要稍微改变渐变。 为此,需要创建新的 SKShader 对象。
“渐变文本”页显示文本和背景,它们的颜色具有相似的渐变:
渐变的唯一差别在于起点和终点。 用于显示文本的渐变基于文本边框角上的两个点。 对于背景,这两个点基于整个画布。 下面是 代码:
public class GradientTextPage : ContentPage
{
const string TEXT = "GRADIENT";
public GradientTextPage ()
{
Title = "Gradient Text";
SKCanvasView canvasView = new SKCanvasView();
canvasView.PaintSurface += OnCanvasViewPaintSurface;
Content = canvasView;
}
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
SKImageInfo info = args.Info;
SKSurface surface = args.Surface;
SKCanvas canvas = surface.Canvas;
canvas.Clear();
using (SKPaint paint = new SKPaint())
{
// Create gradient for background
paint.Shader = SKShader.CreateLinearGradient(
new SKPoint(0, 0),
new SKPoint(info.Width, info.Height),
new SKColor[] { new SKColor(0x40, 0x40, 0x40),
new SKColor(0xC0, 0xC0, 0xC0) },
null,
SKShaderTileMode.Clamp);
// Draw background
canvas.DrawRect(info.Rect, paint);
// Set TextSize to fill 90% of width
paint.TextSize = 100;
float width = paint.MeasureText(TEXT);
float scale = 0.9f * info.Width / width;
paint.TextSize *= scale;
// Get text bounds
SKRect textBounds = new SKRect();
paint.MeasureText(TEXT, ref textBounds);
// Calculate offsets to center the text on the screen
float xText = info.Width / 2 - textBounds.MidX;
float yText = info.Height / 2 - textBounds.MidY;
// Shift textBounds by that amount
textBounds.Offset(xText, yText);
// Create gradient for text
paint.Shader = SKShader.CreateLinearGradient(
new SKPoint(textBounds.Left, textBounds.Top),
new SKPoint(textBounds.Right, textBounds.Bottom),
new SKColor[] { new SKColor(0x40, 0x40, 0x40),
new SKColor(0xC0, 0xC0, 0xC0) },
null,
SKShaderTileMode.Clamp);
// Draw text
canvas.DrawText(TEXT, xText, yText, paint);
}
}
}
首先设置 SKPaint 对象的 Shader 属性以显示覆盖背景的渐变。 渐变点设置为画布的左上角和右下角。
该代码设置 SKPaint 对象的 TextSize 属性,使文本显示在画布宽度的 90% 处。 文本边界用于计算 xText 和 yText 值,这些值将传递给 DrawText 方法来使文本居中。
但是,第二个 CreateLinearGradient 调用的渐变点必须引用相对于所显示画布的文本的左上角和右下角。 这是通过将 textBounds 矩形移动相同的 xText 和 yText 值来实现的:
textBounds.Offset(xText, yText);
现在可以使用矩形的左上角和右下角来设置渐变的起点和终点。
对渐变进行动画处理
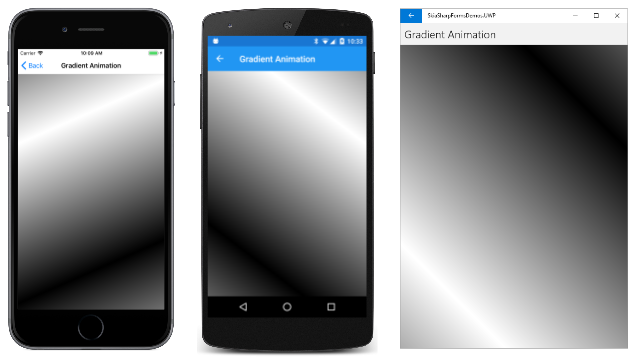
可通过多种方法对渐变进行动画处理。 一种方法是对起点和终点进行动画处理。 “渐变动画”页在画布上居中的圆中移动两个点。 该圆的半径是画布宽度或高度的一半,以较小者为准。 此圆上的起点和终点彼此相对,渐变采用 Mirror 平铺模式从白色渐变到黑色:
构造函数创建 SKCanvasView。 OnAppearing 和 OnDisappearing 方法处理动画逻辑:
public class GradientAnimationPage : ContentPage
{
SKCanvasView canvasView;
bool isAnimating;
double angle;
Stopwatch stopwatch = new Stopwatch();
public GradientAnimationPage()
{
Title = "Gradient Animation";
canvasView = new SKCanvasView();
canvasView.PaintSurface += OnCanvasViewPaintSurface;
Content = canvasView;
}
protected override void OnAppearing()
{
base.OnAppearing();
isAnimating = true;
stopwatch.Start();
Device.StartTimer(TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(16), OnTimerTick);
}
protected override void OnDisappearing()
{
base.OnDisappearing();
stopwatch.Stop();
isAnimating = false;
}
bool OnTimerTick()
{
const int duration = 3000;
angle = 2 * Math.PI * (stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds % duration) / duration;
canvasView.InvalidateSurface();
return isAnimating;
}
···
}
OnTimerTick 方法计算每 3 秒从 0 到 2π 进行动画处理的 angle 值。
这是计算两个渐变点的一种方法。 计算一个名为 vector 的 SKPoint 值,该值从画布中心延伸到圆半径上的某个点。 此矢量的方向基于角的正弦值和余弦值。 然后计算两个相对的渐变点:一个点是通过从中心点减去该矢量计算得出的,另一个点是通过将矢量与中心点相加计算得出的:
public class GradientAnimationPage : ContentPage
{
···
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
SKImageInfo info = args.Info;
SKSurface surface = args.Surface;
SKCanvas canvas = surface.Canvas;
canvas.Clear();
using (SKPaint paint = new SKPaint())
{
SKPoint center = new SKPoint(info.Rect.MidX, info.Rect.MidY);
int radius = Math.Min(info.Width, info.Height) / 2;
SKPoint vector = new SKPoint((float)(radius * Math.Cos(angle)),
(float)(radius * Math.Sin(angle)));
paint.Shader = SKShader.CreateLinearGradient(
center - vector,
center + vector,
new SKColor[] { SKColors.White, SKColors.Black },
null,
SKShaderTileMode.Mirror);
canvas.DrawRect(info.Rect, paint);
}
}
}
另一种稍微不同的方法所需的代码更少。 此方法利用 SKShader.CreateLinearGradient 重载方法,并将矩阵变换作为最后一个参数。 此方法是 SkiaSharpFormsDemos 示例中的版本:
public class GradientAnimationPage : ContentPage
{
···
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
SKImageInfo info = args.Info;
SKSurface surface = args.Surface;
SKCanvas canvas = surface.Canvas;
canvas.Clear();
using (SKPaint paint = new SKPaint())
{
paint.Shader = SKShader.CreateLinearGradient(
new SKPoint(0, 0),
info.Width < info.Height ? new SKPoint(info.Width, 0) :
new SKPoint(0, info.Height),
new SKColor[] { SKColors.White, SKColors.Black },
new float[] { 0, 1 },
SKShaderTileMode.Mirror,
SKMatrix.MakeRotation((float)angle, info.Rect.MidX, info.Rect.MidY));
canvas.DrawRect(info.Rect, paint);
}
}
}
如果画布的宽度小于高度,则两个渐变点设置为 (0, 0) 和 (info.Width, 0)。 作为最后一个参数传递给 CreateLinearGradient 的旋转变换有效地围绕屏幕中心旋转这两个点。
请注意,如果角度为 0,则不旋转,两个渐变点是画布的左上角和右上角。 这些点与之前的 CreateLinearGradient 调用中所示计算出的渐变点不同。 但这些点平行于平分画布中心的水平渐变线,并且它们会产生相同的渐变。
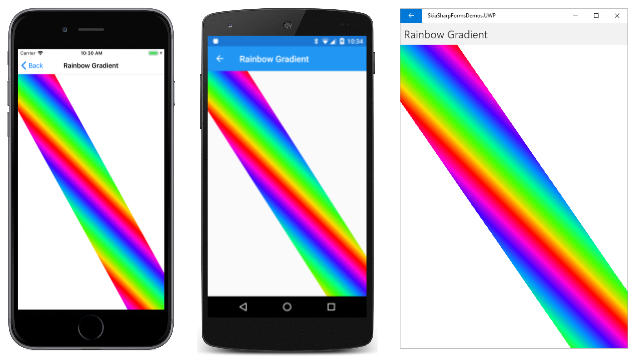
彩虹渐变
“彩虹渐变”页绘制一条从画布左上角连接到右下角的彩虹。 但此彩虹渐变并不像真正的彩虹。 它是直的而不是弯曲的,但它基于八种 HSL(色相-饱和度-亮度)颜色,这些颜色是通过在 0 到 360 之间循环色相值来确定的:
SKColor[] colors = new SKColor[8];
for (int i = 0; i < colors.Length; i++)
{
colors[i] = SKColor.FromHsl(i * 360f / (colors.Length - 1), 100, 50);
}
该代码是如下所示的 PaintSurface 处理程序的一部分。 该处理程序首先创建一条定义从画布左上角延伸到右下角的六边多边形的路径:
public class RainbowGradientPage : ContentPage
{
public RainbowGradientPage ()
{
Title = "Rainbow Gradient";
SKCanvasView canvasView = new SKCanvasView();
canvasView.PaintSurface += OnCanvasViewPaintSurface;
Content = canvasView;
}
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
SKImageInfo info = args.Info;
SKSurface surface = args.Surface;
SKCanvas canvas = surface.Canvas;
canvas.Clear();
using (SKPath path = new SKPath())
{
float rainbowWidth = Math.Min(info.Width, info.Height) / 2f;
// Create path from upper-left to lower-right corner
path.MoveTo(0, 0);
path.LineTo(rainbowWidth / 2, 0);
path.LineTo(info.Width, info.Height - rainbowWidth / 2);
path.LineTo(info.Width, info.Height);
path.LineTo(info.Width - rainbowWidth / 2, info.Height);
path.LineTo(0, rainbowWidth / 2);
path.Close();
using (SKPaint paint = new SKPaint())
{
SKColor[] colors = new SKColor[8];
for (int i = 0; i < colors.Length; i++)
{
colors[i] = SKColor.FromHsl(i * 360f / (colors.Length - 1), 100, 50);
}
paint.Shader = SKShader.CreateLinearGradient(
new SKPoint(0, rainbowWidth / 2),
new SKPoint(rainbowWidth / 2, 0),
colors,
null,
SKShaderTileMode.Repeat);
canvas.DrawPath(path, paint);
}
}
}
}
CreateLinearGradient 方法中的两个渐变点基于定义此路径的两个点:两个点都靠近左上角。 第一个位于画布的上边缘,第二个位于画布的左边缘。 结果如下:
这是一个有趣的图像,但并不是很符合意图。 问题在于,创建线性渐变时,恒定颜色的线条垂直于渐变线。 渐变线基于图形顶部和左侧边的接触点,并且该线条通常不垂直于延伸到右下角的图形边。 仅当画布是正方形时,此方法才有效。
若要创建适当的彩虹渐变,渐变线必须垂直于彩虹的边。 这是一个更复杂的计算。 必须定义一个平行于图形长边的矢量。 该矢量旋转 90 度,以便垂直于该边。 然后乘以 rainbowWidth 将其加长为图形的宽度。 两个渐变点是根据图形一边的点以及该点加上矢量计算得出的。 下面是 SkiaSharpFormsDemos 示例中的“彩虹渐变”页上显示的代码:
public class RainbowGradientPage : ContentPage
{
···
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
···
using (SKPath path = new SKPath())
{
···
using (SKPaint paint = new SKPaint())
{
···
// Vector on lower-left edge, from top to bottom
SKPoint edgeVector = new SKPoint(info.Width - rainbowWidth / 2, info.Height) -
new SKPoint(0, rainbowWidth / 2);
// Rotate 90 degrees counter-clockwise:
SKPoint gradientVector = new SKPoint(edgeVector.Y, -edgeVector.X);
// Normalize
float length = (float)Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow(gradientVector.X, 2) +
Math.Pow(gradientVector.Y, 2));
gradientVector.X /= length;
gradientVector.Y /= length;
// Make it the width of the rainbow
gradientVector.X *= rainbowWidth;
gradientVector.Y *= rainbowWidth;
// Calculate the two points
SKPoint point1 = new SKPoint(0, rainbowWidth / 2);
SKPoint point2 = point1 + gradientVector;
paint.Shader = SKShader.CreateLinearGradient(point1,
point2,
colors,
null,
SKShaderTileMode.Repeat);
canvas.DrawPath(path, paint);
}
}
}
}
现在,彩虹的颜色与图形相符:
无穷大颜色
“无穷大颜色”页中也使用了彩虹渐变。 此页使用三种类型的贝塞尔曲线一文中所述的路径对象绘制无穷大符号。 然后用连续扫过图像的动画彩虹渐变对图像进行着色。
构造函数创建描绘无穷大符号的 SKPath 对象。 创建路径后,构造函数还可以获取路径的矩形边界。 然后它会计算一个名为 gradientCycleLength 的值。 如果渐变基于 pathBounds 矩形的左上角和右下角,则此 gradientCycleLength 值是渐变模式的总水平宽度:
public class InfinityColorsPage : ContentPage
{
···
SKCanvasView canvasView;
// Path information
SKPath infinityPath;
SKRect pathBounds;
float gradientCycleLength;
// Gradient information
SKColor[] colors = new SKColor[8];
···
public InfinityColorsPage ()
{
Title = "Infinity Colors";
// Create path for infinity sign
infinityPath = new SKPath();
infinityPath.MoveTo(0, 0); // Center
infinityPath.CubicTo( 50, -50, 95, -100, 150, -100); // To top of right loop
infinityPath.CubicTo( 205, -100, 250, -55, 250, 0); // To far right of right loop
infinityPath.CubicTo( 250, 55, 205, 100, 150, 100); // To bottom of right loop
infinityPath.CubicTo( 95, 100, 50, 50, 0, 0); // Back to center
infinityPath.CubicTo( -50, -50, -95, -100, -150, -100); // To top of left loop
infinityPath.CubicTo(-205, -100, -250, -55, -250, 0); // To far left of left loop
infinityPath.CubicTo(-250, 55, -205, 100, -150, 100); // To bottom of left loop
infinityPath.CubicTo( -95, 100, - 50, 50, 0, 0); // Back to center
infinityPath.Close();
// Calculate path information
pathBounds = infinityPath.Bounds;
gradientCycleLength = pathBounds.Width +
pathBounds.Height * pathBounds.Height / pathBounds.Width;
// Create SKColor array for gradient
for (int i = 0; i < colors.Length; i++)
{
colors[i] = SKColor.FromHsl(i * 360f / (colors.Length - 1), 100, 50);
}
canvasView = new SKCanvasView();
canvasView.PaintSurface += OnCanvasViewPaintSurface;
Content = canvasView;
}
···
}
构造函数还为彩虹创建 colors 数组和 SKCanvasView 对象。
OnAppearing 和 OnDisappearing 方法的重写执行动画开销计算。 OnTimerTick 方法每两秒将 offset 字段从 0 动画处理为 gradientCycleLength:
public class InfinityColorsPage : ContentPage
{
···
// For animation
bool isAnimating;
float offset;
Stopwatch stopwatch = new Stopwatch();
···
protected override void OnAppearing()
{
base.OnAppearing();
isAnimating = true;
stopwatch.Start();
Device.StartTimer(TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(16), OnTimerTick);
}
protected override void OnDisappearing()
{
base.OnDisappearing();
stopwatch.Stop();
isAnimating = false;
}
bool OnTimerTick()
{
const int duration = 2; // seconds
double progress = stopwatch.Elapsed.TotalSeconds % duration / duration;
offset = (float)(gradientCycleLength * progress);
canvasView.InvalidateSurface();
return isAnimating;
}
···
}
最后,PaintSurface 处理程序呈现无穷大符号。 由于路径包含围绕中心点 (0, 0) 的负坐标和正坐标,因此画布上的 Translate 变换用于将其移动到中心。 平移变换后接一个 Scale 变换,后者应用一个缩放因子,使无穷大符号尽可能大,同时仍保持在画布宽度和高度的 95% 以内。
请注意,STROKE_WIDTH 常量已添加到路径边框的宽度和高度。 将以这种宽度的线条来划路径线,因此渲染的无穷大小在所有四个边上都增加了该宽度的一半:
public class InfinityColorsPage : ContentPage
{
const int STROKE_WIDTH = 50;
···
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
SKImageInfo info = args.Info;
SKSurface surface = args.Surface;
SKCanvas canvas = surface.Canvas;
canvas.Clear();
// Set transforms to shift path to center and scale to canvas size
canvas.Translate(info.Width / 2, info.Height / 2);
canvas.Scale(0.95f *
Math.Min(info.Width / (pathBounds.Width + STROKE_WIDTH),
info.Height / (pathBounds.Height + STROKE_WIDTH)));
using (SKPaint paint = new SKPaint())
{
paint.Style = SKPaintStyle.Stroke;
paint.StrokeWidth = STROKE_WIDTH;
paint.Shader = SKShader.CreateLinearGradient(
new SKPoint(pathBounds.Left, pathBounds.Top),
new SKPoint(pathBounds.Right, pathBounds.Bottom),
colors,
null,
SKShaderTileMode.Repeat,
SKMatrix.MakeTranslation(offset, 0));
canvas.DrawPath(infinityPath, paint);
}
}
}
查看作为 SKShader.CreateLinearGradient 的前两个参数传递的点。 这些点基于原始路径边框。 第一个点是 (–250, –100),第二个点是 (250, 100)。 在 SkiaSharp 内部,这些点受当前画布变换的影响,因此它们与显示的无穷大符号正确对齐。
如果没有 CreateLinearGradient 的最后一个参数,你会看到从无穷大符号的左上角延伸到右下角的彩虹渐变。 (实际上,渐变从边框的左上角延伸到右下角。渲染的无穷大符号在所有边上都比边框大 STROKE_WIDTH 值的一半。由于渐变在起点和终点处都是红色的,并且渐变是使用 SKShaderTileMode.Repeat 创建的,因此差异并不明显。)
使用 CreateLinearGradient 的最后一个参数,渐变模式会连续扫过图像:
透明度和渐变
帮助实现渐变的颜色可以结合透明度。 渐变不是从一种颜色渐变为另一种颜色,而可以从一种颜色渐变为透明。
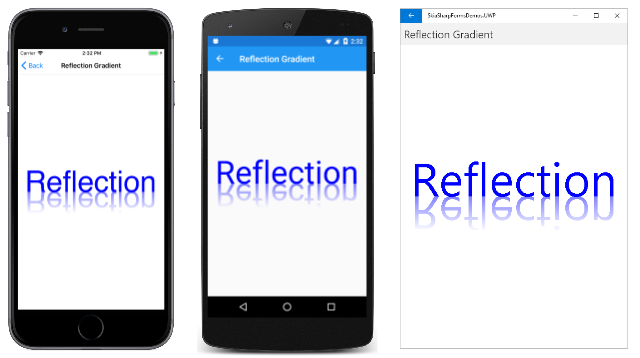
可以使用此技术来获得一些有趣的效果。 经典示例之一显示了一个图形对象及其反射:
倒置的文本采用顶部 50% 透明到底部完全透明的渐变颜色。 这些透明度与 0x80 和 0 的 alpha 值相关联。
“反射渐变”页中的 PaintSurface 处理程序将文本大小缩放至画布宽度的 90%。 然后,它计算 xText 和 yText 值,以将文本水平居中,但位于与页面垂直中心相对应的基线上:
public class ReflectionGradientPage : ContentPage
{
const string TEXT = "Reflection";
public ReflectionGradientPage ()
{
Title = "Reflection Gradient";
SKCanvasView canvasView = new SKCanvasView();
canvasView.PaintSurface += OnCanvasViewPaintSurface;
Content = canvasView;
}
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
SKImageInfo info = args.Info;
SKSurface surface = args.Surface;
SKCanvas canvas = surface.Canvas;
canvas.Clear();
using (SKPaint paint = new SKPaint())
{
// Set text color to blue
paint.Color = SKColors.Blue;
// Set text size to fill 90% of width
paint.TextSize = 100;
float width = paint.MeasureText(TEXT);
float scale = 0.9f * info.Width / width;
paint.TextSize *= scale;
// Get text bounds
SKRect textBounds = new SKRect();
paint.MeasureText(TEXT, ref textBounds);
// Calculate offsets to position text above center
float xText = info.Width / 2 - textBounds.MidX;
float yText = info.Height / 2;
// Draw unreflected text
canvas.DrawText(TEXT, xText, yText, paint);
// Shift textBounds to match displayed text
textBounds.Offset(xText, yText);
// Use those offsets to create a gradient for the reflected text
paint.Shader = SKShader.CreateLinearGradient(
new SKPoint(0, textBounds.Top),
new SKPoint(0, textBounds.Bottom),
new SKColor[] { paint.Color.WithAlpha(0),
paint.Color.WithAlpha(0x80) },
null,
SKShaderTileMode.Clamp);
// Scale the canvas to flip upside-down around the vertical center
canvas.Scale(1, -1, 0, yText);
// Draw reflected text
canvas.DrawText(TEXT, xText, yText, paint);
}
}
}
这些 xText 和 yText 值与用于在 PaintSurface 处理程序底部的 DrawText 调用中显示反射文本的值相同。 不过,紧靠在该代码之前,你会看到对 SKCanvas 的 Scale 方法的调用。 此 Scale 方法将按 1 水平缩放(不执行任何操作),但按 –1 垂直缩放,这实际上会将所有内容倒置。 旋转中心设置为点 (0, yText),其中 yText 是画布的垂直中心,最初计算为 info.Height 除以 2 后的结果。
请记得,Skia 在画布变换之前使用渐变为图形对象着色。 绘制未反射的文本后,textBounds 矩形将发生移动,使其与显示的文本相对应:
textBounds.Offset(xText, yText);
CreateLinearGradient 调用定义从该矩形的顶部到底部的渐变。 从完全透明的蓝色 (paint.Color.WithAlpha(0)) 渐变到 50% 透明的蓝色 (paint.Color.WithAlpha(0x80))。 画布变换将文本上下翻转,因此 50% 透明的蓝色从基线开始,并在文本顶部变得透明。
 下载示例
下载示例