Run Automation runbooks on a Hybrid Runbook Worker
Important
- Azure Automation Agent-based User Hybrid Runbook Worker (Windows and Linux) will retire on 31 August 2024 and wouldn't be supported after that date. You must complete migrating existing Agent-based User Hybrid Runbook Workers to Extension-based Workers before 31 August 2024. Moreover, starting 1 November 2023, creating new Agent-based Hybrid Workers wouldn't be possible. Learn more.
- Azure Automation Run As Account will retire on September 30, 2023 and will be replaced with Managed Identities. Before that date, you'll need to start migrating your runbooks to use managed identities. For more information, see migrating from an existing Run As accounts to managed identity to start migrating the runbooks from Run As account to managed identities before September 30, 2023.
Runbooks that run on a Hybrid Runbook Worker typically manage resources on the local computer or against resources in the local environment where the worker is deployed. Runbooks in Azure Automation typically manage resources in the Azure cloud. Even though they are used differently, runbooks that run in Azure Automation and runbooks that run on a Hybrid Runbook Worker are identical in structure.
When you author a runbook to run on a Hybrid Runbook Worker, you should edit and test the runbook on the machine that hosts the worker. The host machine has all the PowerShell modules and network access required to manage the local resources. Once you test the runbook on the Hybrid Runbook Worker machine, you can then upload it to the Azure Automation environment, where it can be run on the worker.
Plan for Azure services protected by firewall
Enabling the Azure Firewall on Azure Storage, Azure Key Vault, or Azure SQL blocks access from Azure Automation runbooks for those services. Access will be blocked even when the firewall exception to allow trusted Microsoft services is enabled, as Automation is not a part of the trusted services list. With an enabled firewall, access can only be made by using a Hybrid Runbook Worker and a virtual network service endpoint.
Plan runbook job behavior
Azure Automation handles jobs on Hybrid Runbook Workers differently from jobs run in cloud sandboxes. If you have a long-running runbook, make sure that it's resilient to possible restart. For details of the job behavior, see Hybrid Runbook Worker jobs.
Service accounts
Windows Hybrid Worker
Jobs for Hybrid Runbook Workers run under the local System account.
Note
- PowerShell 5.1, PowerShell 7.1(preview), Python 2.7, and Python 3.8 runbooks are supported on both extension-based and agent-based Windows Hybrid Runbook Workers. For agent based workers, ensure the Windows Hybrid worker version is 7.3.12960 or above.
- PowerShell 7.2 and Python 3.10 (preview) runbooks are supported on extension-based Windows Hybrid Workers only. Ensure the Windows Hybrid worker extension version is 1.1.11 or above.
Note
To create environment variable in Windows systems, follow these steps:
- Go to Control Panel > System > Advanced System Settings.
- In System Properties select Environment variables.
- In System variables, select New.
- Provide Variable name and Variable value, and then select OK.
- Restart the VM or logout from the current user and login to implement the environment variable changes.
PowerShell 7.2
To run PowerShell 7.2 runbooks on a Windows Hybrid Worker, install PowerShell on the Hybrid Worker. See Installing PowerShell on Windows.
After PowerShell 7.2 installation is complete, create an environment variable with Variable name as powershell_7_2_path and Variable value as location of the executable PowerShell. Restart the Hybrid Runbook Worker after environment variable is created successfully.
PowerShell 7.1
To run PowerShell 7.1 runbooks on a Windows Hybrid Worker, install PowerShell on the Hybrid Worker. See Installing PowerShell on Windows. Ensure to add the PowerShell file to the PATH environment variable and restart the Hybrid Runbook Worker after the installation.
Python 3.10
To run Python 3.10 runbooks on a Windows Hybrid Worker, install Python on the Hybrid Worker. See Installing Python on Windows.
After Python 3.10 installation is complete, create an environment variable with Variable name as python_3_10_path and Variable value as location of the executable Python. Restart the Hybrid Runbook Worker after environment variable is created successfully.
Python 3.8
To run Python 3.8 runbooks on a Windows Hybrid Worker, install Python on the Hybrid Worker. See Installing Python on Windows. Create environment variable PYTHON_3_PATH for Python 3.8 runbooks and ensure to add the location of executable Python as Variable value. Restart the Hybrid Runbook Worker after the environment variable is created successfully.
If the Python executable file is at the default location C:\WPy64-3800\python-3.8.0.amd64\python.exe, then you do not have to create the environment variable.
Python 2.7
To run Python 2.7 runbooks on a Windows Hybrid Worker, install Python on the Hybrid Worker. See Installing Python on Windows. Create environment variable PYTHON_2_PATH for Python 2.7 runbooks and ensure to add the location of executable Python file as Variable value. Restart the Hybrid Runbook Worker after the environment variable is created successfully.
If the Python executable file is at the default location C:\Python27\python.exe, then you do not have to create the environment variable.
Linux Hybrid Worker
Note
- PowerShell 5.1, PowerShell 7.1(preview), Python 2.7, Python 3.8 runbooks are supported on both extension-based and agent-based Linux Hybrid Runbook Workers. For agent-based workers, ensure the Linux Hybrid Runbook worker version is 1.7.5.0 or above.
- PowerShell 7.2 and Python 3.10 (preview) runbooks are supported on extension-based Linux Hybrid Workers only. Ensure the Linux Hybrid worker extension version is 1.1.11 or above.
Note
To create environment variable in Linux systems, follow these steps:
- Open /etc/environment.
- Create a new Environment variable by adding VARIABLE_NAME="variable_value" in a new line in /etc/environment (VARIABLE_NAME is the name of the new Environment variable and variable_value represents the value it is to be assigned).
- Restart the VM or logout from current user and login after saving the changes to /etc/environment to implement environment variable changes.
PowerShell 7.2
To run PowerShell 7.2 runbooks on a Linux Hybrid Worker, install PowerShell file on the Hybrid Worker. For more information, see Installing PowerShell on Linux.
After PowerShell 7.2 installation is complete, create an environment variable with Variable name as powershell_7_2_path and Variable value as location of the executable PowerShell file. Restart the Hybrid Runbook Worker after an environment variable is created successfully.
Python 3.10
To run Python 3.10 runbooks on a Linux Hybrid Worker, install Python on the Hybrid Worker. For more information, see Installing Python 3.10 on Linux.
After Python 3.10 installation is complete, create an environment variable with Variable name as python_3_10_path and Variable value as location of the executable Python file. Restart the Hybrid Runbook Worker after environment variable is created successfully.
Python 3.8
To run Python 3.8 runbooks on a Linux Hybrid Worker, install Python on the Hybrid Worker. Ensure to add the executable Python file to the PATH environment variable and restart the Hybrid Runbook Worker after the installation.
Python 2.7
To run Python 2.7 runbooks on a Linux Hybrid Worker, install Python on the Hybrid Worker. Ensure to add the executable Python file to the PATH environment variable and restart the Hybrid Runbook Worker after the installation.
Configure runbook permissions
Define permissions for your runbook to run on the Hybrid Runbook Worker in the following ways:
- Have the runbook provide its own authentication to local resources.
- Configure authentication using managed identities for Azure resources.
- Specify Hybrid Worker credentials to provide a user context for all runbooks.
Use runbook authentication to local resources
If preparing a runbook that provides its own authentication to resources, use credential and certificate assets in your runbook. There are several cmdlets that allow you to specify credentials so that the runbook can authenticate to different resources. The following example shows a portion of a runbook that restarts a computer. It retrieves credentials from a credential asset and the name of the computer from a variable asset and then uses these values with the Restart-Computer cmdlet.
$Cred = Get-AutomationPSCredential -Name "MyCredential"
$Computer = Get-AutomationVariable -Name "ComputerName"
Restart-Computer -ComputerName $Computer -Credential $Cred
You can also use an InlineScript activity. InlineScript allows you to run blocks of code on another computer with credentials.
Use runbook authentication with managed identities
Hybrid Runbook Workers on Azure virtual machines can use managed identities to authenticate to Azure resources. Using managed identities for Azure resources instead of Run As accounts provides benefits because you don't need to:
- Export the Run As certificate and then import it into the Hybrid Runbook Worker.
- Renew the certificate used by the Run As account.
- Handle the Run As connection object in your runbook code.
There are two ways to use the Managed Identities in Hybrid Runbook Worker scripts.
Use the system-assigned Managed Identity for the Automation account:
Configure a System-assigned Managed Identity for the Automation account.
Grant this identity the required permissions within the Subscription to perform its task.
Update the runbook to use the Connect-AzAccount cmdlet with the
Identityparameter to authenticate to Azure resources. This configuration reduces the need to use a Run As account and perform the associated account management.# Ensures you do not inherit an AzContext in your runbook Disable-AzContextAutosave -Scope Process # Connect to Azure with system-assigned managed identity $AzureContext = (Connect-AzAccount -Identity).context # set and store context $AzureContext = Set-AzContext -SubscriptionName $AzureContext.Subscription -DefaultProfile $AzureContext # Get all VM names from the subscription Get-AzVM -DefaultProfile $AzureContext | Select Name
Note
It is Not possible to use the Automation Account's User Managed Identity on a Hybrid Runbook Worker, it must be the Automation Account's System Managed Identity.
For an Azure VM running as a Hybrid Runbook Worker, use the VM Managed Identity. In this case, you can use either the VM’s User-assigned Managed Identity OR the VM’s System-assigned Managed Identity.
Note
This will NOT work in an Automation Account which has been configured with an Automation account Managed Identity. As soon as the Automation account Managed Identity is enabled, it is no longer possible to use the VM Managed Identity and then, it is only possible to use the Automation Account System-Assigned Managed Identity as mentioned in option 1 above.
Use any one of the following managed identities:
- Configure a System Managed Identity for the VM.
- Grant this identity the required permissions within the subscription to perform its tasks.
- Update the runbook to use the Connect-Az-Account cmdlet with the
Identityparameter to authenticate to Azure resources. This configuration reduces the need to use a Run As Account and perform the associated account management.
# Ensures you do not inherit an AzContext in your runbook Disable-AzContextAutosave -Scope Process # Connect to Azure with system-assigned managed identity $AzureContext = (Connect-AzAccount -Identity).context # set and store context $AzureContext = Set-AzContext -SubscriptionName $AzureContext.Subscription -DefaultProfile $AzureContext # Get all VM names from the subscription Get-AzVM -DefaultProfile $AzureContext | Select Name
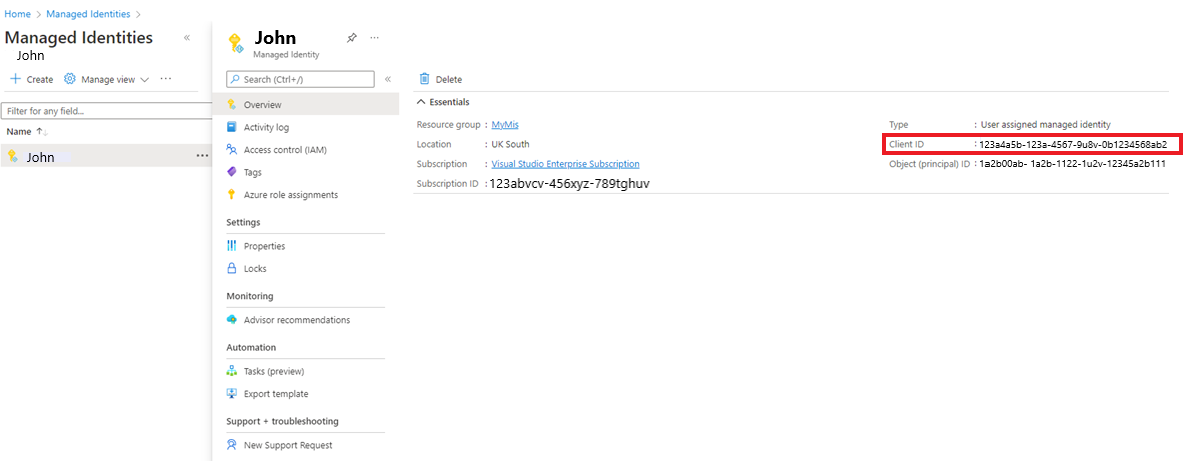
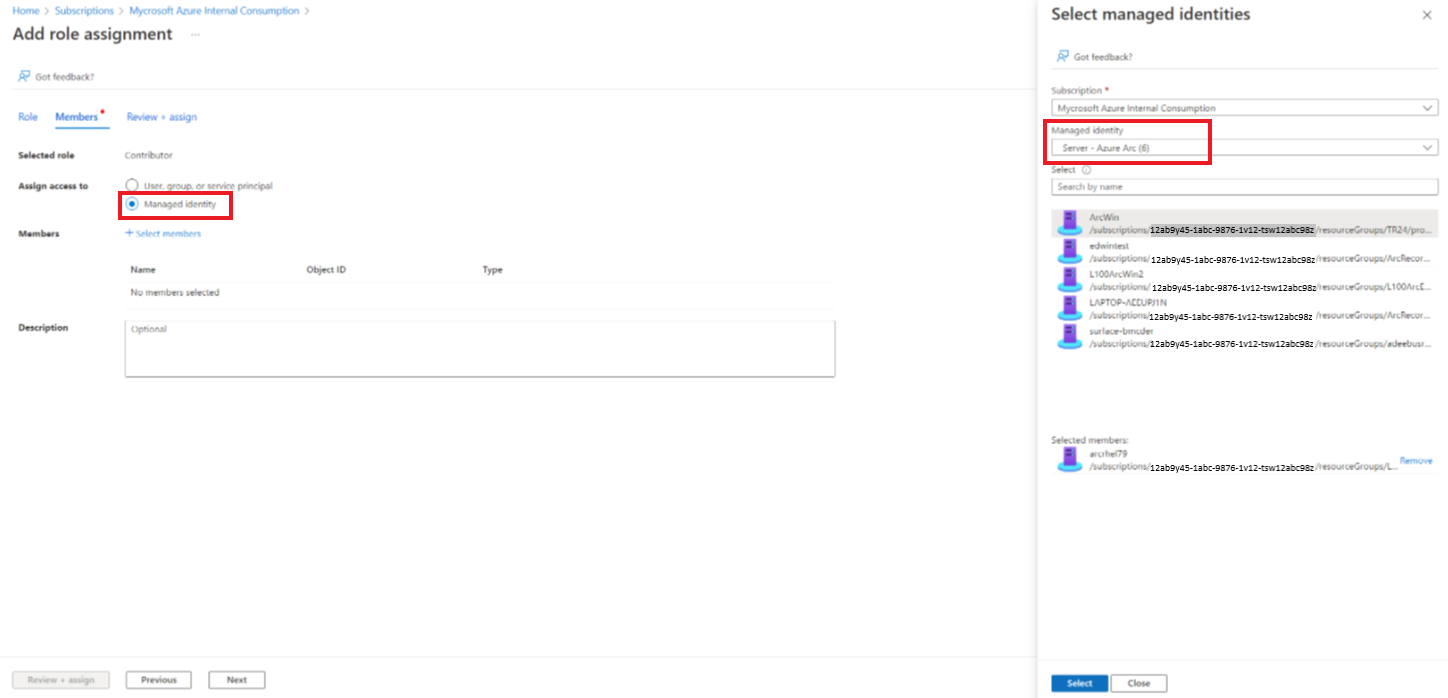
An Arc-enabled server or Arc-enabled VMware vSphere VM running as a Hybrid Runbook Worker already has a built-in System Managed Identity assigned to it which can be used for authentication.
You can grant this Managed Identity access to resources in your subscription in the Access control (IAM) blade for the resource by adding the appropriate role assignment.
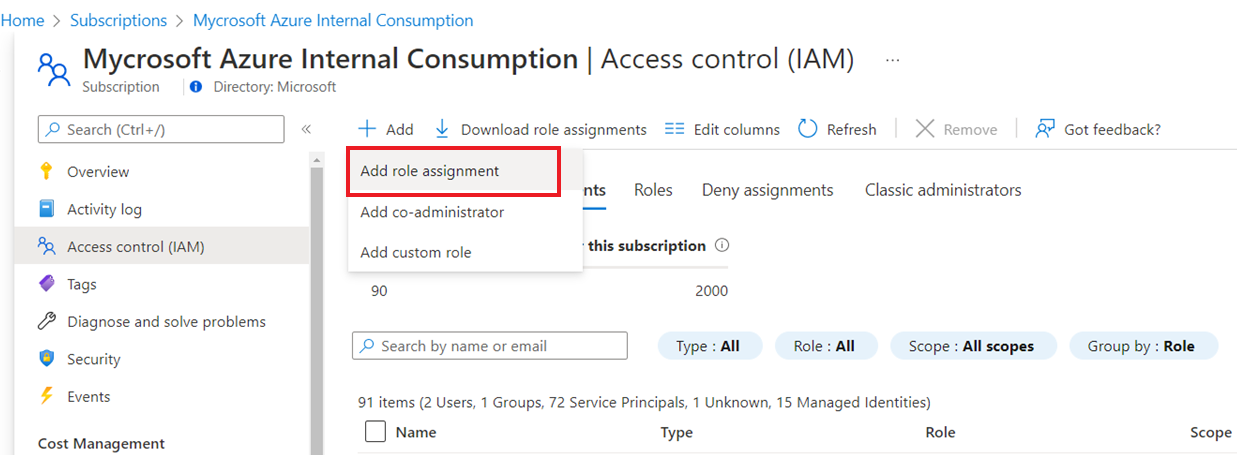
Add the Azure Arc Managed Identity to your chosen role as required.
Note
This will NOT work in an Automation Account which has been configured with an Automation account Managed Identity. As soon as the Automation account Managed Identity is enabled, it is no longer possible to use the Arc Managed Identity and then, it is only possible to use the Automation Account System-Assigned Managed Identity as mentioned in option 1 above.
Note
By default, the Azure contexts are saved for use between PowerShell sessions. It is possible that when a previous runbook on the Hybrid Runbook Worker has been authenticated with Azure, that context persists to the disk in the System PowerShell profile, as per Azure contexts and sign-in credentials | Microsoft Docs.
For instance, a runbook with Get-AzVM can return all the VMs in the subscription with no call to Connect-AzAccount, and the user would be able to access Azure resources without having to authenticate within that runbook. You can disable context autosave in Azure PowerShell, as detailed here.
Use runbook authentication with Hybrid Worker Credentials
Instead of having your runbook provide its own authentication to local resources, you can specify Hybrid Worker Credentials for a Hybrid Runbook Worker group. To specify a Hybrid Worker Credentials, you must define a credential asset that has access to local resources. These resources include certificate stores and all runbooks run under these credentials on a Hybrid Runbook Worker in the group.
The user name for the credential must be in one of the following formats:
- domain\username
- username@domain
- username (for accounts local to the on-premises computer)
To use the PowerShell runbook Export-RunAsCertificateToHybridWorker, you need to install the Az modules for Azure Automation on the local machine.
Use a credential asset for a Hybrid Runbook Worker group
By default, the Hybrid jobs run under the context of System account. However, to run Hybrid jobs under a different credential asset, follow the steps:
- Create a credential asset with access to local resources.
- Open the Automation account in the Azure portal.
- Select Hybrid Worker Groups, and then select the specific group.
- Select Settings.
- Change the value of Hybrid Worker credentials from Default to Custom.
- Select the credential and click Save.
- If the following permissions are not assigned for Custom users, jobs might get suspended.
| Resource type | Folder permissions |
|---|---|
| Azure VM | C:\Packages\Plugins\Microsoft.Azure.Automation.HybridWorker.HybridWorkerForWindows (read and execute) |
| Arc-enabled Server | C:\ProgramData\AzureConnectedMachineAgent\Tokens (read) C:\Packages\Plugins\Microsoft.Azure.Automation.HybridWorker.HybridWorkerForWindows (read and execute) |
Note
Linux Hybrid Worker doesn't support Hybrid Worker credentials.
Start a runbook on a Hybrid Runbook Worker
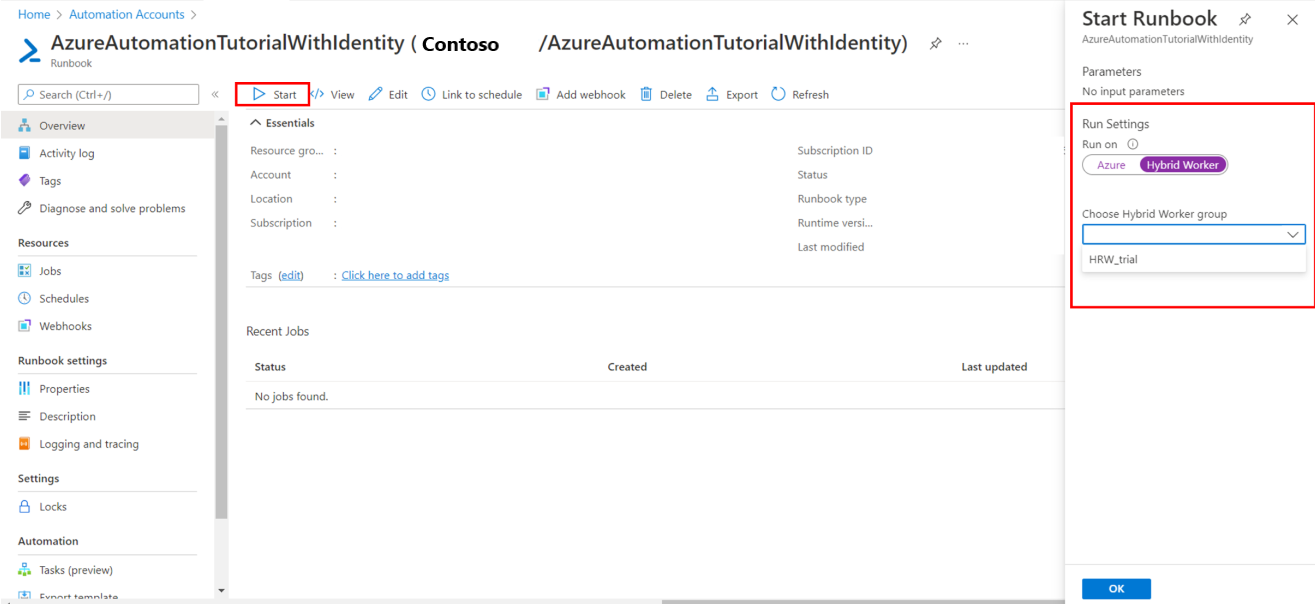
Start a runbook in Azure Automation describes different methods for starting a runbook. Starting a runbook on a Hybrid Runbook Worker uses a Run on option that allows you to specify the name of a Hybrid Runbook Worker group. When a group is specified, one of the workers in that group retrieves and runs the runbook. If your runbook does not specify this option, Azure Automation runs the runbook as usual.
When you start a runbook in the Azure portal, you're presented with the Run on option for which you can select Azure or Hybrid Worker. Select Hybrid Worker, to choose the Hybrid Runbook Worker group from a dropdown.
When starting a runbook using PowerShell, use the RunOn parameter with the Start-AzAutomationRunbook cmdlet. The following example uses Windows PowerShell to start a runbook named Test-Runbook on a Hybrid Runbook Worker group named MyHybridGroup.
Start-AzAutomationRunbook -AutomationAccountName "MyAutomationAccount" -Name "Test-Runbook" -RunOn "MyHybridGroup"
Work with signed runbooks on a Windows Hybrid Runbook Worker
You can configure a Windows Hybrid Runbook Worker to run only signed runbooks.
Important
Once you've configured a Hybrid Runbook Worker to run only signed runbooks, unsigned runbooks fail to execute on the worker.
Note
PowerShell 7.x does not support signed runbooks for Windows and Linux Hybrid Runbook Worker.
Create signing certificate
The following example creates a self-signed certificate that can be used for signing runbooks. This code creates the certificate and exports it so that the Hybrid Runbook Worker can import it later. The thumbprint is also returned for later use in referencing the certificate.
# Create a self-signed certificate that can be used for code signing
$SigningCert = New-SelfSignedCertificate -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine\my `
-Subject "CN=contoso.com" `
-KeyAlgorithm RSA `
-KeyLength 2048 `
-Provider "Microsoft Enhanced RSA and AES Cryptographic Provider" `
-KeyExportPolicy Exportable `
-KeyUsage DigitalSignature `
-Type CodeSigningCert
# Export the certificate so that it can be imported to the hybrid workers
Export-Certificate -Cert $SigningCert -FilePath .\hybridworkersigningcertificate.cer
# Import the certificate into the trusted root store so the certificate chain can be validated
Import-Certificate -FilePath .\hybridworkersigningcertificate.cer -CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\Root
# Retrieve the thumbprint for later use
$SigningCert.Thumbprint
Import certificate and configure workers for signature validation
Copy the certificate that you've created to each Hybrid Runbook Worker in a group. Run the following script to import the certificate and configure the workers to use signature validation on runbooks.
# Install the certificate into a location that will be used for validation.
New-Item -Path Cert:\LocalMachine\AutomationHybridStore
Import-Certificate -FilePath .\hybridworkersigningcertificate.cer -CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\AutomationHybridStore
# Import the certificate into the trusted root store so the certificate chain can be validated
Import-Certificate -FilePath .\hybridworkersigningcertificate.cer -CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\Root
# Configure the hybrid worker to use signature validation on runbooks.
Set-HybridRunbookWorkerSignatureValidation -Enable $true -TrustedCertStoreLocation "Cert:\LocalMachine\AutomationHybridStore"
Sign your runbooks using the certificate
With the Hybrid Runbook Workers configured to use only signed runbooks, you must sign runbooks that are to be used on the Hybrid Runbook Worker. Use the following sample PowerShell code to sign these runbooks.
$SigningCert = ( Get-ChildItem -Path cert:\LocalMachine\My\<CertificateThumbprint>)
Set-AuthenticodeSignature .\TestRunbook.ps1 -Certificate $SigningCert
When a runbook has been signed, you must import it into your Automation account and publish it with the signature block. To learn how to import runbooks, see Import a runbook.
Note
Use only plaintext characters in your runbook code, including comments. Using characters with diacritical marks, like á or ñ, will result in an error. When Azure Automation downloads your code, the characters will be replaced by a question mark and the signing will fail with a "signature hash validation failure" message.
Work with signed runbooks on a Linux Hybrid Runbook Worker
To be able to work with signed runbooks, a Linux Hybrid Runbook Worker must have the GPG executable on the local machine.
Important
Once you've configured a Hybrid Runbook Worker to run only signed runbooks, unsigned runbooks fail to execute on the worker.
You will perform the following steps to complete this configuration:
- Create a GPG keyring and keypair
- Make the keyring available to the Hybrid Runbook Worker
- Verify that signature validation is on
- Sign a runbook
Note
- PowerShell 7.x does not support signed runbooks for agent-based Windows and agent-based Linux Hybrid Runbook Worker.
- Signed PowerShell and Python runbooks aren't supported in extension-based Linux Hybrid Workers.
Create a GPG keyring and keypair
Note
The Create a GPG keyring and keypair are applicable only for the agent-based hybrid workers.
To create the GPG keyring and keypair, use the Hybrid Runbook Worker nxautomation account.
Use the sudo application to sign in as the nxautomation account.
sudo su - nxautomationOnce you are using nxautomation, generate the GPG keypair as root. GPG guides you through the steps. You must provide name, email address, expiration time, and passphrase. Then you wait until there is enough entropy on the machine for the key to be generated.
sudo gpg --generate-keyBecause the GPG directory was generated with sudo, you must change its owner to nxautomation using the following command as root.
sudo chown -R nxautomation ~/.gnupg
Make the keyring available to the Hybrid Runbook Worker
Once the keyring has been created, make it available to the Hybrid Runbook Worker. Modify the settings file home/nxautomation/state/worker.conf to include the following example code under the file section [worker-optional].
gpg_public_keyring_path = /home/nxautomation/run/.gnupg/pubring.kbx
Verify that signature validation is on
If signature validation has been disabled on the machine, you must turn it on by running the following command as root. Replace <LogAnalyticsworkspaceId> with your workspace ID.
sudo python /opt/microsoft/omsconfig/modules/nxOMSAutomationWorker/DSCResources/MSFT_nxOMSAutomationWorkerResource/automationworker/scripts/require_runbook_signature.py --true <LogAnalyticsworkspaceId>
Sign a runbook
Once you have configured signature validation, use the following GPG command to sign the runbook.
gpg --clear-sign <runbook name>
The signed runbook is called <runbook name>.asc.
You can now upload the signed runbook to Azure Automation and execute it like a regular runbook.
Logging
To help troubleshoot issues with your runbooks running on a hybrid runbook worker, logs are stored locally in the following location:
On Windows at
C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\System Center\Orchestrator\<version>\SMA\Sandboxesfor detailed job runtime process logging. High-level runbook job status events are written to the Application and Services Logs\Microsoft-Automation\Operations event log.On Linux, the user hybrid worker logs can be found at
/home/nxautomation/run/worker.log, and system runbook worker logs can be found at/var/opt/microsoft/omsagent/run/automationworker/worker.log.
Next steps
- For more information on Hybrid Runbook Worker, see Automation Hybrid Runbook Worker.
- If your runbooks aren't completing successfully, review the troubleshooting guide for runbook execution failures.
- For more information on PowerShell, including language reference and learning modules, see PowerShell Docs.
- Learn about using Azure Policy to manage runbook execution with Hybrid Runbook Workers.
- For a PowerShell cmdlet reference, see Az.Automation.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for