Denormalize data in your model
In this unit, you'll look at the product table from your relational database and model it for a NoSQL database. You'll also look at the many-to-many relationship your product table has with product tags.
Model the product entities
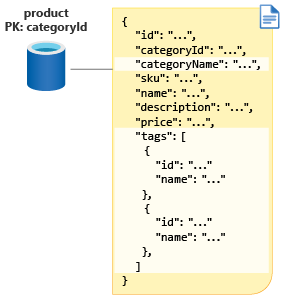
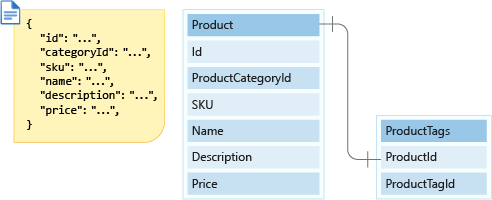
Your initial model for the product table includes only the fields from your relational table. However, your e-commerce application must display the product category name when you display a product page. You'll also want to query for products by product tags within a product category as well. This can be done in either of two ways: you can store products in a product tags container, or you can embed your tags in the product container.
Because there are far fewer tags per product than products per tag, it makes more sense to embed the product tags in the product table. There is a one-to-few relationship between each product and the tags, which makes a good case for embedding. You'll also store your product data with embedded tags in your new product container. So your new product model will appear as shown in the following diagram:
Select a partition key
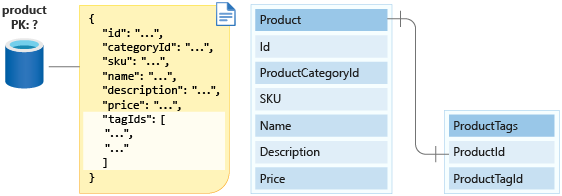
Next, you'll select a partition key for the product container. Again, you need to look at the operations to be performed to decide on a partition key. Your options are either to create a product or edit a product. As customers navigate your e-commerce site, they'll often do so by product category. You need a query that filters products by categoryId to display them to users. To make your query a single-partition query with all products by category, you use categoryId as the partition key for your product container.
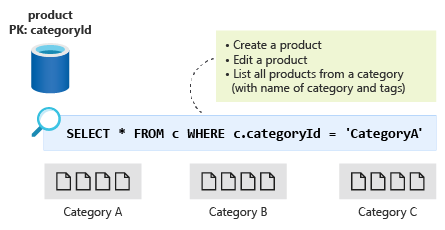
So categoryId is a good partition key that lets you retrieve all products in a category efficiently. By embedding tag IDs, you can get the IDs in your many-to-many relationship between products and tags as well. However, when you query for products, you need not only the product data but you also need to display the category name and the tag names. When you query for products, how can you return the category name for each product and the names for the product tags?
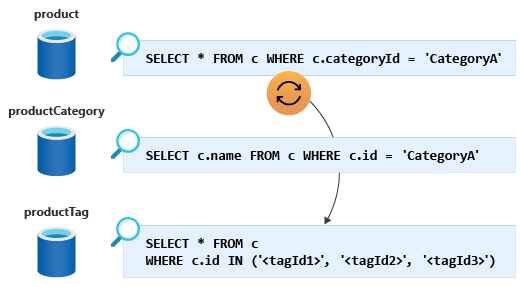
Currently, to display a product page for a category, you would need run the following queries:
- Query the product container to return all the products in a category.
- Query the productCategory container to return the product category's name.
- Then, for every product returned by the first query, run a third query on the productTag container to get each product tag name.
Denormalize product entities
Running all the preceding queries could work for you. However, this approach isn't very scalable. Remember that, in NoSQL databases, there are no joins between containers, so joins aren't an option for you. Also remember that, for NoSQL databases, the objective is to reduce the number of requests by modeling data so that you can fetch your application data in as few requests as possible.
The solution, then, is to denormalize your data. With denormalization, you can optimize your data models to ensure that all the required data for your application is ready to be served by your queries.
To denormalize your data in this instance, you add more properties, such as the name of the category and the name of each tag in your tags array. By adding these properties, you can now retrieve all the data you need to return to your clients in only a single request.