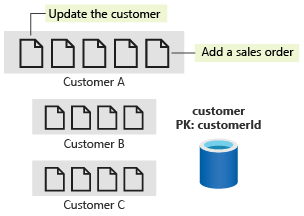
Denormalize aggregates in the same container
Before your new model is complete, one last operation to look at is to query your top 10 customers by the number of sales orders. In your current model, you first do a group by on each customer and sum for sales orders in your customer container. You then sort in descending order and take the top 10 results. Even though customers and sales orders sit in the same container, this type of query is not something you can currently do.
The solution here is to denormalize the aggregate value in a new property, salesOrderCount, in the customer document. You can get the data you want by using this property in a query such as the one shown in the following diagram:
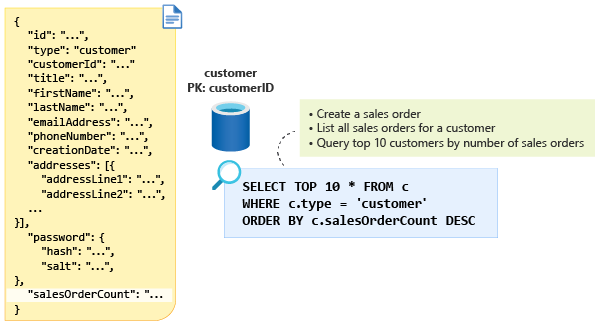
Now, every time a customer creates a new sales order and a new sales order is inserted into your customer container, you need a way to update the customer document and increment the salesOrderCount property by one. To do this, you need a transaction. Azure Cosmos DB supports transactions when the data sits within the same logical partition.
Because customers and sales orders reside in the same logical partition, you can insert the new sales order and update the customer document within a transaction. There are two ways to implement transactions in Azure Cosmos DB: by using stored procedures or by using a feature called transactional batch, which is available in both .NET and Java SDKs.