Evaluate and change column data types
When you import a table from any data source, Power BI Desktop automatically starts scanning the first 1,000 rows (default setting) and tries to detect the type of data in the columns. Some situations might occur where Power BI Desktop doesn't detect the correct data type. Where incorrect data types occur, you'll experience performance issues.
You have a higher chance of getting data type errors when you're dealing with flat files, such as comma-separated values (.CSV) files and Excel workbooks (.XLSX), because data was entered manually into the worksheets and mistakes were made. Conversely, in databases, the data types are predefined when tables or views are created.
A best practice is to evaluate the column data types in Power Query Editor before you load the data into a Power BI semantic model. If you determine that a data type is incorrect, you can change it. You might also want to apply a format to the values in a column and change the summarization default for a column.
To continue with the scenario where you're cleaning and transforming sales data in preparation for reporting, you now need to evaluate the columns to ensure that they have the correct data type. You need to correct any errors that you identify.
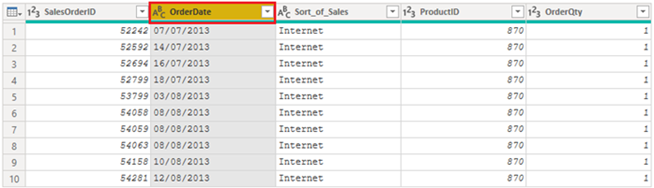
You evaluate the OrderDate column. As expected, it contains numeric data, but Power BI Desktop has incorrectly set the column data type to Text. To report on this column, you need to change the data type from Text to Date.
Implications of incorrect data types
The following information provides insight into problems that can arise when Power BI doesn't detect the correct data type.
Incorrect data types will prevent you from creating certain calculations, deriving hierarchies, or creating proper relationships with other tables. For example, if you try to calculate the Quantity of Orders YTD, you'll get the following error stating that the OrderDate column data type isn't Date, which is required in time-based calculations.
Quantity of Orders YTD = TOTALYTD(SUM('Sales'[OrderQty]), 'Sales'[OrderDate])
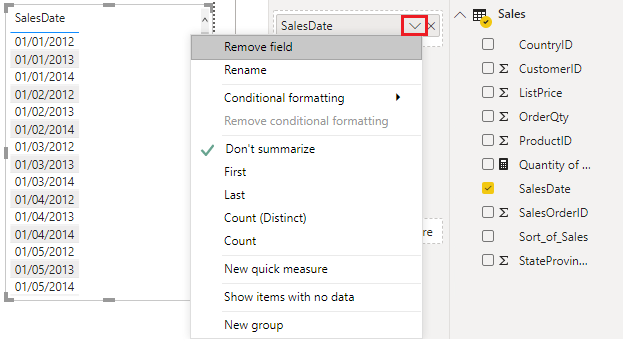
Another issue with having an incorrect data type applied on a date field is the inability to create a date hierarchy, which would allow you to analyze your data on a yearly, monthly, or weekly basis. The following screenshot shows that the SalesDate field isn't recognized as type Date and will only be presented as a list of dates in the Table visual. However, It's a best practice to use a date table and turn off the auto date/time to get rid of the auto generated hierarchy. For more information about this process, see Auto generated data type documentation.
Change the column data type
You can change the data type of a column in two places: in Power Query Editor and in the Power BI Desktop Report view by using the column tools. It is best to change the data type in the Power Query Editor before you load the data.
Change the column data type in Power Query Editor
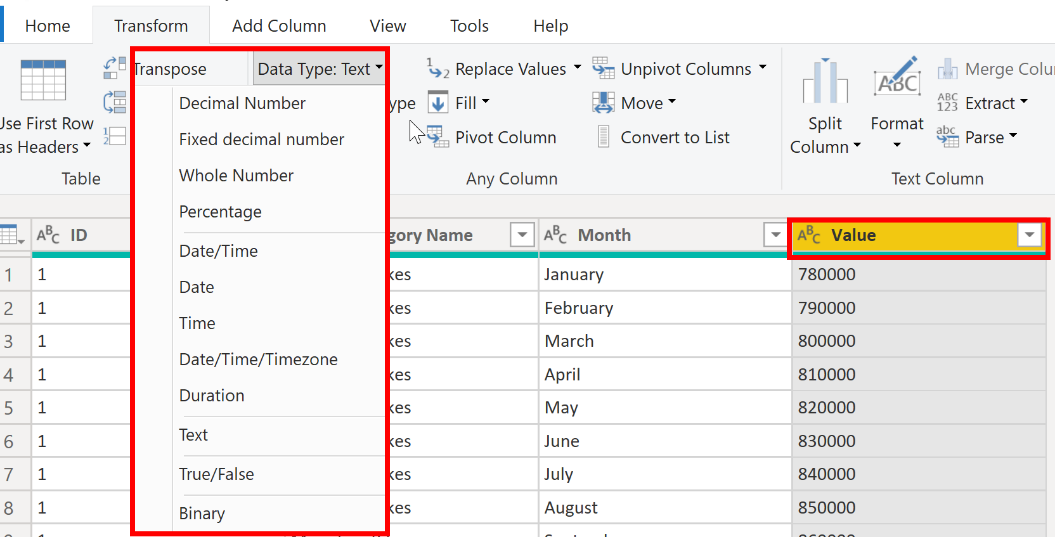
In Power Query Editor, you can change the column data type in two ways. One way is to select the column that has the issue, select Data Type in the Transform tab, and then select the correct data type from the list.
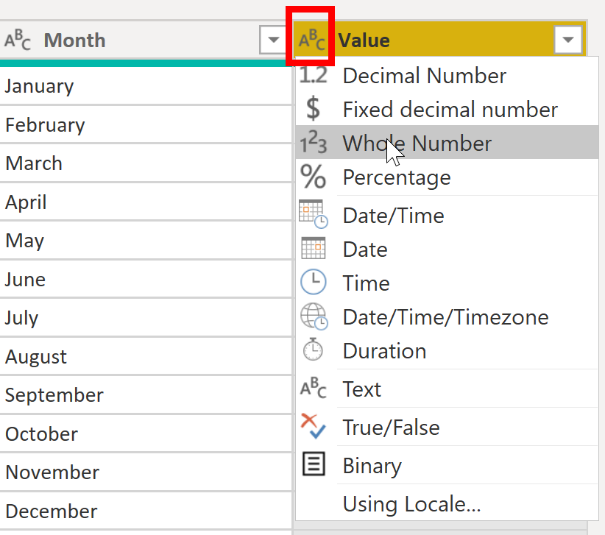
Another method is to select the data type icon next to the column header and then select the correct data type from the list.
As with any other changes that you make in Power Query Editor, the change that you make to the column data type is saved as a programmed step. This step is called Changed Type and it will be iterated every time the data is refreshed.
After you have completed all steps to clean and transform your data, select Close & Apply to close Power Query Editor and apply your changes to your semantic model. At this stage, your data should be in great shape for analysis and reporting.
For more information, see Data types in Power BI Desktop.