Exercise - Implement Azure App Service on Kubernetes with Azure Arc
In this exercise, you'll implement App Service on the Azure Arc enabled Kubernetes cluster. This will allow you to deply an App Service web app's in the next exercise. Your implementation will integrate with an Azure Log Analytics workspace that you'll create in this exercise. The exercise consists of the following tasks:
- Prepare for implementing App Service on the Azure Arc enabled Kubernetes cluster.
- Create an Azure Log Analytics workspace.
- Install the Application services extension on the Azure Arc enabled Kubernetes cluster.
- Create a custom location for the Azure Arc enabled Kubernetes cluster.
- Register an App Service Kubernetes environment into the custom location.
This is the fourth in this module's sequence of exercises. These exercises guide you through implementing Azure App Service web apps on Kubernetes with Azure Arc. The sequence consists of the following exercises:
- Prepare the lab environment.
- Set up a Kubernetes cluster.
- Connect the Kubernetes cluster to Azure Arc.
- Implement App Service on the Azure Arc enabled Kubernetes cluster.
- Deploy an App Service web app to the Azure Arc enabled Kubernetes cluster.
- Clean up the lab environment.
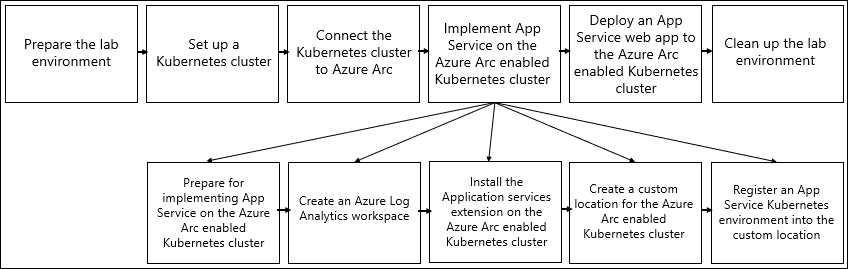
Task 1: Prepare for implementing App Service on the Azure Arc enabled Kubernetes cluster
There is information you must collect that's required for implementation steps in this unit, including installing the Application services extension, creating a custom location, and setting up a Kubernetes environment.
Use the following steps to collect the required information:
In the browser window that displays the Bash session in the Azure Cloud Shell pane, run the following commands. These commands set variable values for the names of the resource group that's hosting the AKS cluster, the AKS cluster, the resource group that contains the Arc resources, and the Azure Arc-connected cluster resource:
K8S_CLUSTER_RG_NAME=k8sAKS-RG K8S_CLUSTER_NAME=$(az aks list -g $K8S_CLUSTER_RG_NAME --query "[0].name" -o tsv) K8S_ARC_PREFIX=k8sArc ARC_RG_NAME="${K8S_ARC_PREFIX}-RG" ARC_CLUSTER_NAME="${K8S_ARC_PREFIX}-cluster"Run the following command to set the variable value that designates the name of the custom location that will host resources you deployed to the Azure Arc-connected Kubernetes cluster:
CUSTOM_LOCATION_NAME="${K8S_ARC_PREFIX}-location"Run the following commands to set the values of the variables that designate the name of the extension you're installing in the Azure Arc-connected cluster and the corresponding Kubernetes environment:
EXTENSION_NAME="${K8S_ARC_PREFIX}-kube" KUBE_ENV_NAME="${K8S_ARC_PREFIX}-env-$RANDOM"Run the following command to set the variable value that designates the name of the Kubernetes namespace that hosts the App Service resources:
APP_SERVICE_NAMESPACE_NAME=appservice-ns
Task 2: Create an Azure Log Analytics workspace
You can leverage Log Analytics to store and analyze application logs for your cluster's App Service. This step is optional but recommended. Once you configure this functionality, application logs for all web apps deployed on the cluster will be stored in the Log Analytics workspace.
Note
This task is applicable only if you intend to use Log Analytics to store and analyze application logs for App Service resources that your Kubernetes cluster hosts.
Use the following steps to create an Azure Log Analytics workspace:
Run the following commands to set values of the variables that represent the names of the resource group that contains the AKS cluster infrastructure resources and the Azure Log Analytics workspace:
K8S_INFRA_RG_NAME=$(az aks show -g $K8S_CLUSTER_RG_NAME -n $K8S_CLUSTER_NAME --query nodeResourceGroup -o tsv) LA_WORKSPACE_NAME=k8sAKS-workspaceRun the following command to create an Azure Log Analytics workspace:
az monitor log-analytics workspace create -g $K8S_INFRA_RG_NAME -n $LA_WORKSPACE_NAMENote
Wait for the workspace provisioning to complete. This should take about 2 minutes.
Run the following commands to set the values of the variables that designate the name of the Log Analytics workspace and its shared key:
LA_WORKSPACE_NAME=k8sAKS-workspace LA_WORKSPACE_ID=$(az monitor log-analytics workspace show --resource-group $K8S_INFRA_RG_NAME --workspace-name $LA_WORKSPACE_NAME --query "customerId" -o tsv) LA_WORKSPACE_ID_ENC=$(printf %s $LA_WORKSPACE_ID | base64) LA_WORKSPACE_KEY=$(az monitor log-analytics workspace get-shared-keys --resource-group $K8S_INFRA_RG_NAME --workspace-name $LA_WORKSPACE_NAME --query "secondarySharedKey" -o tsv) LA_WORKSPACE_KEY_ENC_WITH_SPACE=$(printf %s $LA_WORKSPACE_KEY | base64) LA_WORKSPACE_KEY_ENC=$(echo -n "${LA_WORKSPACE_KEY_ENC_WITH_SPACE//[[:space:]]/}")
Task 3: Install the Application services extension on the Azure Arc enabled Kubernetes cluster
Now you're ready to install the Application services extension. Cluster extensions provide an Azure Resource Manager-based functionality for installation and lifecycle management of Azure resources on Azure Arc enabled Kubernetes clusters. A cluster-extension instance is an extension of the Azure Resource Manager resource (Microsoft.KubernetesConfiguration/extensions) that's on top of the Azure Arc-connected Kubernetes resource (represented by Microsoft.Kubernetes/connectedClusters).
Use the following steps to install the Application services extension on your Azure Arc enabled Kubernetes cluster:
In the browser window that displays the Bash session in the Azure Cloud Shell pane, run the following command to verify the registration state of the Microsoft.KubernetesConfiguration resource provider. This enables you to create the Application services extension in the region you selected for the resource group that hosts the Azure Arc-enabled services:
az provider show -n Microsoft.KubernetesConfiguration --query "[registrationState,resourceTypes[?resourceType=='extensions'].locations]"Run the following command to install the extension, including support for Log Analytics:
Important
Do you plan to use Log Analytics to store logs of App Service web apps that are hosted on an Azure Arc enabled Kubernetes cluster? You must reference the workspace when installing the Application services extension. There currently isn't support for implementing this functionality after the Application services extension is installed.
az k8s-extension create -g $ARC_RG_NAME --name $EXTENSION_NAME --cluster-type connectedClusters -c $ARC_CLUSTER_NAME --extension-type 'Microsoft.Web.Appservice' --release-train stable --auto-upgrade-minor-version true --scope cluster --release-namespace $APP_SERVICE_NAMESPACE_NAME --configuration-settings "Microsoft.CustomLocation.ServiceAccount=default" --configuration-settings "appsNamespace=${APP_SERVICE_NAMESPACE_NAME}" --configuration-settings "clusterName=${KUBE_ENV_NAME}" --configuration-settings "buildService.storageClassName=default" --configuration-settings "buildService.storageAccessMode=ReadWriteOnce" --configuration-settings "envoy.annotations.service.beta.kubernetes.io/azure-load-balancer-resource-group=${K8S_CLUSTER_RG_NAME}" --configuration-settings "customConfigMap=${APP_SERVICE_NAMESPACE_NAME}/kube-environment-config" --configuration-settings "logProcessor.appLogs.destination=log-analytics" --configuration-protected-settings "logProcessor.appLogs.logAnalyticsConfig.customerId=${LA_WORKSPACE_ID_ENC}" --configuration-protected-settings "logProcessor.appLogs.logAnalyticsConfig.sharedKey=${LA_WORKSPACE_KEY_ENC}"Note
To install the extension without support for Log Analytics, use the following command:
az k8s-extension create -g $ARC_RG_NAME --name $EXTENSION_NAME --cluster-type connectedClusters -c $ARC_CLUSTER_NAME --extension-type 'Microsoft.Web.Appservice' --release-train stable --auto-upgrade-minor-version true --scope cluster --release-namespace $APP_SERVICE_NAMESPACE_NAME --configuration-settings "Microsoft.CustomLocation.ServiceAccount=default" --configuration-settings "appsNamespace=${APP_SERVICE_NAMESPACE_NAME}" --configuration-settings "clusterName=${KUBE_ENV_NAME}" --configuration-settings "buildService.storageClassName=default" --configuration-settings "buildService.storageAccessMode=ReadWriteOnce" --configuration-settings "envoy.annotations.service.beta.kubernetes.io/azure-load-balancer-resource-group=${K8S_CLUSTER_RG_NAME}" --configuration-settings "customConfigMap=${APP_SERVICE_NAMESPACE_NAME}/kube-environment-config"Run the following command to validate the installed extension's status:
az k8s-extension show --cluster-type connectedClusters -c $ARC_CLUSTER_NAME -g $ARC_RG_NAME --name $EXTENSION_NAMENote
Rerun the command until the value of the installState property changes to Installed. This should take about 5 minutes.
Run the following command to store the extension's id property value in a variable:
EXTENSION_ID=$(az k8s-extension show --cluster-type connectedClusters -c $ARC_CLUSTER_NAME -g $ARC_RG_NAME --name $EXTENSION_NAME --query id -o tsv)Note
You'll need this value in the next task of this exercise.
Task 4: Create a custom location for the Azure Arc enabled Kubernetes cluster
Azure Resource Manager provides the location extension. This extension allows you to designate Azure Arc enabled Kubernetes clusters as target locations. Use these locations for deploying instances of Azure Arc enabled services, such as App Services web apps, Azure Functions, and Azure Logic Apps. A custom location maps extensions to a Kubernetes namespace that's hosting pods. These pods implement the functionality of the corresponding resources.
Use the following steps to create a custom location.
In the browser window that displays the Bash session in the Azure Cloud Shell pane, run the following command to verify the registration state of the Microsoft.ExtendedLocation resource provider. This provider allows you to create a custom location in the region you selected for the resource group that's hosting the Azure Arc enabled services:
az provider show -n Microsoft.ExtendedLocation --query "[registrationState,resourceTypes[?resourceType=='customLocations'].locations]"Run the following command to store the value of the connected cluster's id property in a variable:
CONNECTED_CLUSTER_ID=$(az connectedk8s show -n $ARC_CLUSTER_NAME -g $ARC_RG_NAME --query id -o tsv)Run the following command to create a custom location:
az customlocation create -g $ARC_RG_NAME -n $CUSTOM_LOCATION_NAME --host-resource-id $CONNECTED_CLUSTER_ID --namespace $APP_SERVICE_NAMESPACE_NAME -c $EXTENSION_IDNote
Wait for the provisioning process to complete. This should take about 1 minute.
Note
Review the output of the command, and verify the value of the provisioningState property is Succeeded".
Run the following command to store the custom location's value of the id property in a variable:
CUSTOM_LOCATION_ID=$(az customlocation show -g $ARC_RG_NAME -n $CUSTOM_LOCATION_NAME --query id -o tsv)Note
You'll use this value in the next task of this exercise.
Task 5: Register an App Service Kubernetes environment into the custom location
After you create a custom location, you can proceed to register an App Service Kubernetes environment into that location. An App Service Kubernetes Environment enables configuration common across apps.
Note
You can create only one Kubernetes environment resource per custom location.
Use the following steps to create an App Service Kubernetes environment:
In the browser window that displays the Bash session in the Azure Cloud Shell pane, run the following command to verify the registration state of the Microsoft.Web resource provider. You then can create a kubeEnvironment resource in the Azure region hosting the resource group containing the Azure Arc connected cluster and the custom location:
az provider show -n Microsoft.Web --query "[registrationState,resourceTypes[?resourceType=='kubeEnvironments'].locations]"Run the following commands to create the App Service Kubernetes environment:
az appservice kube create -g $ARC_RG_NAME -n $KUBE_ENV_NAME --custom-location $CUSTOM_LOCATION_IDRun the following command to validate the status of the Kubernetes environment:
az appservice kube show -g $ARC_RG_NAME -n $KUBE_ENV_NAMENote
Rerun the command until the value of the provisioningState property changes to Succeeded
Congratulations! You've completed the fourth exercise of this module. You've implemented the Application services extension on your Azure Arc enabled Kubernetes cluster. This prepares it for deployment of an App Service web app in the next exercise.