Design for Azure Functions solutions
Azure Functions is a serverless application platform. Functions are used when you want to run a small piece of code in the cloud, without worrying about the infrastructure.
Things to know about Azure Functions
Let's review some benefits and scenarios of Azure Functions that make it a great compute solution for building new workloads.
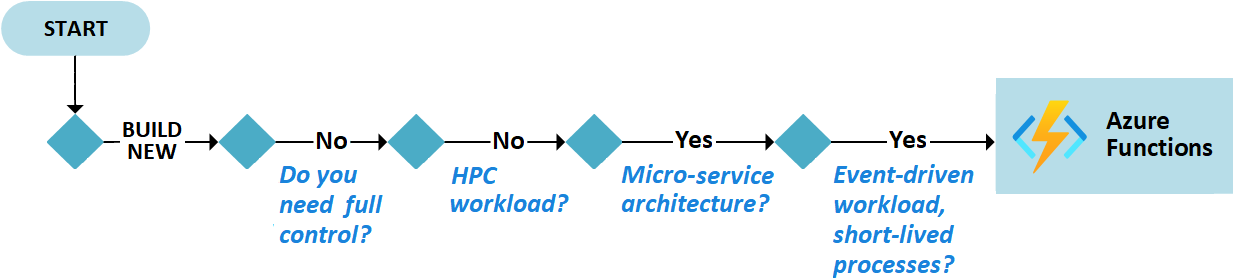
Azure Functions provides intrinsic scalability. You're charged only for the resources you use.
With Azure Functions, you can write your function code in the language of your choice.
Azure Functions supports compute on demand in two significant ways:
Azure Functions lets you implement your system's logic into readily available blocks of code. These code blocks (functions) can run anytime you need to respond to critical events.
As requests increase, Azure Functions meets the demand with as many resources and function instances as necessary. As requests complete, any extra resources and application instances drop off automatically.
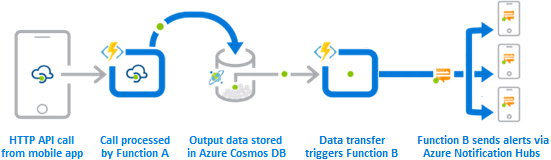
Azure Functions is an ideal solution for handling specific definable actions triggered by an event. A function can process an API call and store the processed data in Azure Cosmos DB. After the data transfer happens, another function can trigger a notification.
Things to consider when using Azure Functions
Let's look at some best practices for using Azure Functions. As you consider these suggestions, think about the advantages to using Azure Functions in the Tailwind Traders infrastructure.
Consider long running functions. Avoid large, long-running functions that can cause unexpected timeout issues. Whenever possible, refactor large functions into smaller function sets that work together and return responses faster. The default timeout is 300 seconds for Consumption Plan functions, and 30 minutes for any other plan.
Consider durable functions. Overcome timeout issues in your configuration with durable functions and smaller function sets. Durable functions let you write stateful functions. Behind the scenes, the function manages the application state, checkpoints, and restarts. An example application pattern for durable functions is function chaining. Function chaining executes a sequence of functions in a specific order. The output of one function is applied to the input of another function.
Consider performance and scaling. Plan how to group functions with different load profiles. Consider a scenario where you have two functions. One function processes many thousands of queued messages and has low memory requirements. The other function is called only occasionally but has high memory requirements. In this scenario, you might want to deploy separate function applications, where each function has its own set of resources. Separate resources means you can independently scale the functions.
Consider defensive functions. Design your functions to handle exceptions. Downstream services, network outages, or memory limits can cause a function to fail. Write your functions so they can continue if a failure occurs.
Consider not sharing storage accounts. Maximize performance by using a separate storage account for each function application. When you create a function app, associate it with a unique storage account. Using a unique storage account is important if your function generates a high volume of storage transactions.
Business application
Take a few minutes to read about other Azure Functions best practices.
You can get more ideas on how to use Azure Functions by checking out the code samples page.