Define application lifecycle management
Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) is a common practice in development even if you're not familiar with the term. Enterprises use ALM to continually develop and maintain applications with minimal effort. By applying this same concept to Power BI, you'll create consistency, integrity, and improved customer experience with your reports.
What is Application Lifecycle Management?
The application lifecycle is the cyclical software development process that involves these areas:
- Plan and track
- Develop
- Build and test
- Deploy
- Operate
- Monitor and learn
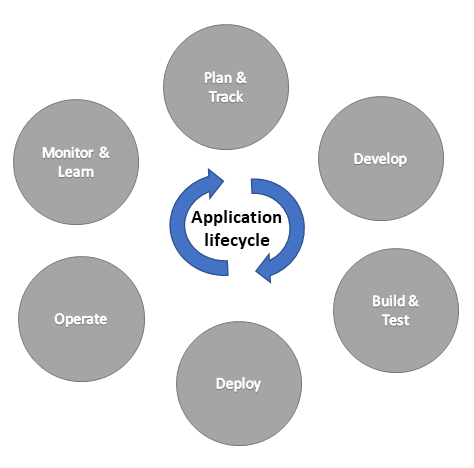
Application lifecycle management (ALM) specifically manages the lifecycle of an application. There are three key aspects to ALM: governance, development, and maintenance.
Governance
- Requirements and resource management
- System administration, such as:
- Data security and user access
- Change tracking
- Review and audit
- Deployment control
- Rollback planning
Development
- Identifying current problems
- Planning and design
- Building and testing the application
Maintenance
- Deployment of the application
- Maintenance of dependent technologies
Continuous integration and continuous delivery
Another popular aspect in ALM is Continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD), which refers to an automated process to build, test, and deploy your application.
- Continuous integration includes the build, test, and integration of changes into a code repository.
- Continuous delivery includes the staging and delivery of code changes to production-ready environments for deployment.
CI/CD doesn't automatically deploy the code changes, and is dependent on approval for deployment. The term continuous deployment refers to automated deployment of code changes to production without approval.
What next?
Now that you know what ALM is, let's determine how to implement ALM in your organization. First, determine where code will be stored and how you'll govern different versions. We'll dive into this topic more in the next unit, Recommend a source control strategy. Then, you'll want to determine your deployment strategy, which we cover as well in the Design a deployment strategy unit later.