Deploy your application and integrate with other Azure services
Now that you've learned about the different application hosting options on Azure and can determine the best option for your application, we'll take a look at how to deploy MySQL - Flexible Server applications on these services.
In this unit, we'll only explore two of the services: Azure App Service and Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS). We'll also discuss options for automating CI/CD tasks using Azure DevOps and GitHub.
Azure App Service + MySQL - Flexible Server
To deploy your application on Azure App Service and integrate with MySQL - Flexible Server, use one of the following options:
- Option 1: Create a MySQL flexible server and an App Service app individually, and then add the MySQL flexible server's connection information to Application Settings under Configuration Settings in the App Service app.
- Option 2: Use Web App + Database from Azure Marketplace. This option creates a Web App and a MySQL flexible server isolated in a VNet. The flexible server's connection information is automatically added to the App Service app's Configuration Settings, through a Connection String.
After you create the App Service app and database, push your application to Azure from one of the many App Service deployment options such as from a ZIP package, Local Git, Azure Container Registry, GitHub Actions, Azure Pipelines, etc.
We'll explore this in detail by building and deploying a sample PHP application to Azure App Service in the next unit.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) + MySQL - Flexible Server
In general, there are three options for using a MySQL database in your Azure Kubernetes application, as shown in the following image:
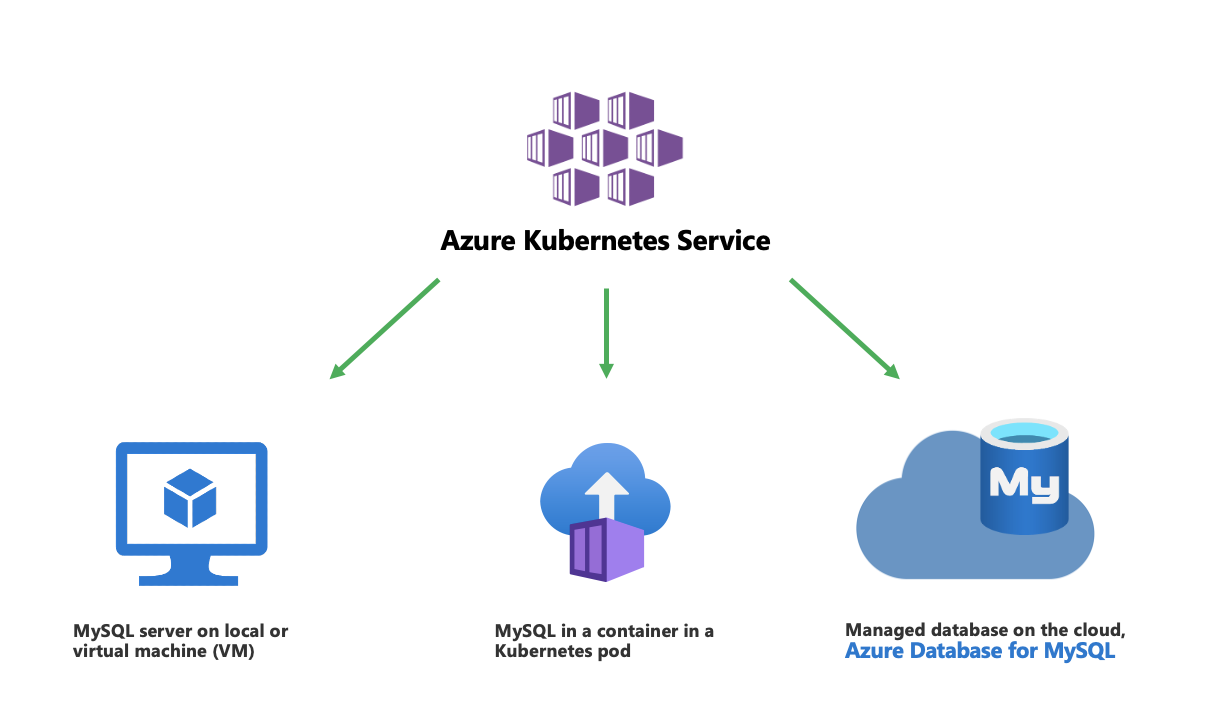
- Use MySQL on Azure VM – Azure VMs are considered an infrastructure as a service offering. This option requires that the user take responsibility for managing and maintaining the MySQL server.
- Run MySQL on Kubernetes – Provision a MySQL database in a container running on a Kubernetes pod. This option has the benefits that Kubernetes provides in terms of automation, but it demands developer efforts to keep the database running together. In addition, given the transient nature of Kubernetes pods, there is a higher likelihood of failovers and restarts which impacts application availability and business continuity.
- Use Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server – Take advantage of this fully managed MySQL service on Azure. This option enhances developer productivity by reducing the operational overhead of managing the MySQL server.
To deploy an application on AKS that integrates Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server in the back end, perform the following five simple steps:
Create a MySQL flexible server using the Azure Portal, the Azure CLI, an ARM/Bicep template, or other Azure tools. Along with choosing the right compute, storage, backup, and high availability options, it’s important to decide the suitable networking option while creating the MySQL flexible server. Based on how you’d want AKS to reach the MySQL flexible server, you can choose either:
- Public Access (allowed IP addresses)
- Private Access (VNet integration)
Unless your scenario only involves small projects or demos, it’s highly recommended to create your server with private access, which will help secure access to your server via VNet integration.
Prepare your application by updating your application code with the following changes:
- To have the application use MySQL flexible server, modify the corresponding configuration file or application properties file to add code indicating the host server URL, database name, username, and password, which will be read from the environment variables (as defined in and passed down from the Kubernetes manifest file).
- Create a DockerFile to build the application docker image.
Create an Azure container registry and push the application to the registry as a Docker image.
Create an AKS cluster and attach the Azure container registry account to the cluster.
Deploy the application to the cluster and then test the deployment. To deploy the application to the AKS cluster, you first need to create a Kubernetes manifest file that defines a desired state for the cluster, such as what container images to run.
In the Kubernetes manifest YAML file, key things to define include:
- Container image name: replace it with your own in the format [registryname].azurecr.io/[image-name]:[tag]
- Environment variables for MySQL flexible server host URL, database name, admin username and password.
- A Service resource to access the application in the cluster. For example, a service of the type “LoadBalancer” will create an external load balancer providing an externally accessible IP address to the application.
After the YAML file is ready, deploy it with kubectl apply or the Kubernetes resource view, via the Azure portal.
Automate database CI/CD tasks with Azure DevOps, GitHub and Azure Service Operator
Deploying an application manually is inefficient and requires testing the changes to the environment. As a result, it is recommended that you automate build and deployment processes to minimize application errors and the time required to release new features. This practice is often referred to as CI/CD - Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery/Deployment (CD). Implementing build and deployment automation enables development teams to rapidly serve small features and fixes in production, rather than having to wait for a single large, error-prone manual deployment.
To automate both application and MySQL flexible server database deployments, you can use the CI/CD tools described in the following sections.
Azure Pipelines
Azure Pipelines is a CI/CD pipeline platform on Azure. It supports code deployments to PaaS services, virtual machines, and container registries in Azure, other cloud platforms, and on-premises.
You can also use Azure Pipelines to deploy your database updates to Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server automatically after every successful build. You can use an Azure CLI task to update the database either with a SQL file or by executing an inline SQL script against the database.
GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions runs automated pipelines after an event occurs, such as when a developer pushes to a repository branch or opens a PR. For example, you can have one workflow that builds and tests pull requests, another workflow that deploys your application every time a release is created, and yet another workflow that adds a label every time someone opens a new issue. You can also configure workflow actions to connect to your MySQL flexible server and deploy databases or database updates.
Azure Service Operator
Azure Service Operator (ASO) helps provision and manage Azure resources from within Kubernetes, integrating infrastructure management into existing Kubernetes release pipelines. With ASO, you can automate deployment and updates to services like Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server without having to leave the Kubernetes control plane.
Other tools
To automate CI/CD tasks for your application, you can also use App Service Deployment Slots, App Service Deployment Center, and open-source tools like Jenkins, etc.