Apply best practices for application development
In this unit, we'll explore some best practices to apply when developing applications with Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server, which can help to ensure better performance, resilience and security. These best practices include:
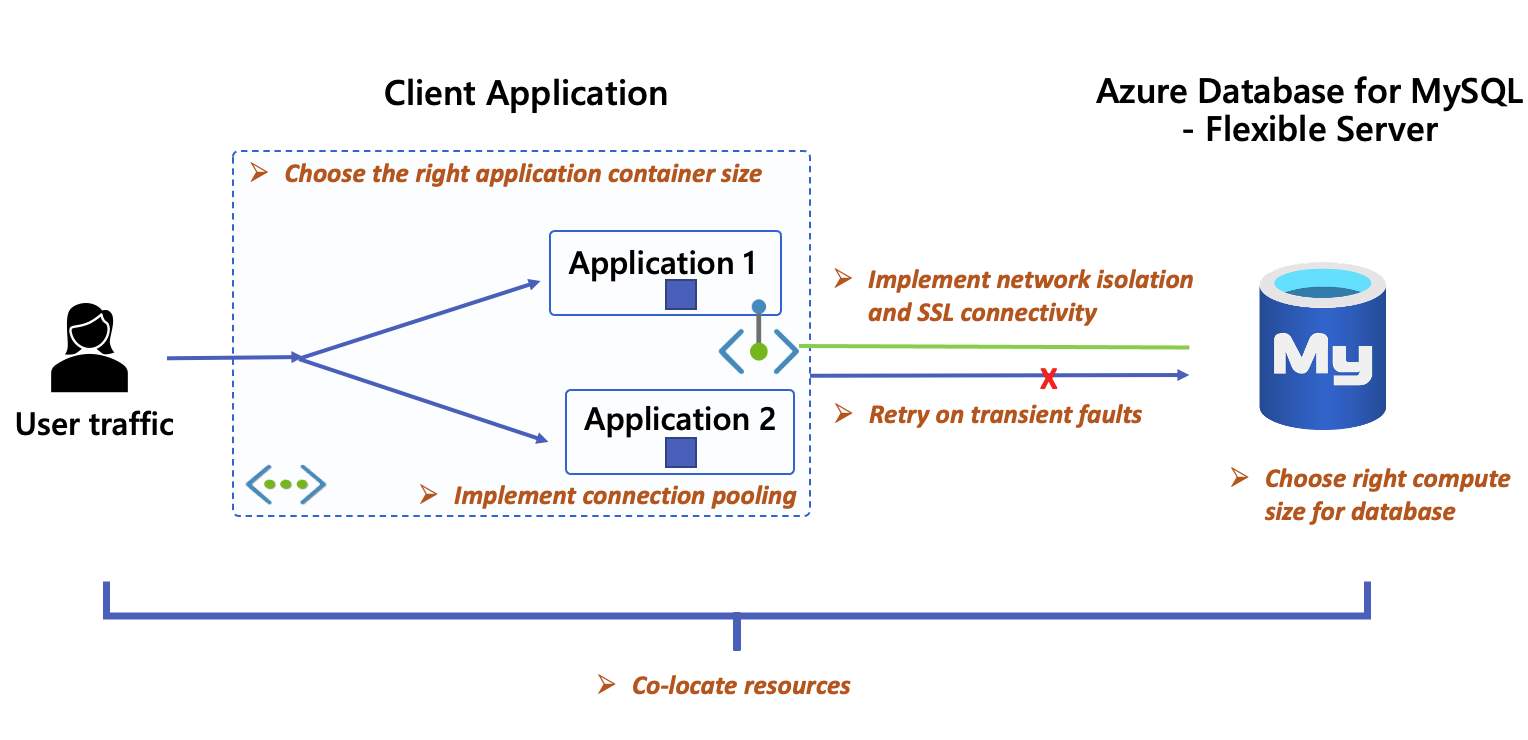
- Co-locating resources.
- Implementing connection pooling.
- Choosing the right application container size.
- Implementing networking isolation and SSL connectivity.
- Implementing retry logic to manage transient faults.
- Choosing the right compute and storage size for database.
Below, you can see where each of these best practices comes into play during the application development process with Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server.
Note
This list of best practices is not exhaustive. Be sure to consult the Azure Database for MySQL documentation for detailed guides on implementing best practices related to networking, security, monitoring, performance optimization, business continuity and disaster recovery, etc.
Co-locate resources
When deploying your application to Azure, ensure that all of your resource dependencies are in the same region. Spreading instances across regions or availability zones creates network latency, which might affect the overall performance of your application.
Implement connection pooling
Managing database connections can significantly impact the overall application performance. To optimize performance, reduce the number of times connections are established and the time taken to establish these connections in key code paths.
To improve application performance and resiliency, consider implementing connection pooling to connect to MySQL - Flexible Server. A connection pooler (like ProxySQL) can decrease the number of idle connections and reuse existing connections.
Choose the right application container size
To ensure optimized performance, verify that your application is allocated sufficient compute and memory resources. Perform load testing with utilities like JMeter to help you size the resources correctly.
Implement network isolation and SSL connectivity
Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server with Virtual Network (VNet) integration (private access connectivity method) provides the benefits of network security and isolation. Virtual Network (VNet) integration enables you to lock down access to the server only to your virtual network infrastructure. You can secure your application and database resources either in a single VNet or across different VNets in the same or different regions (and connected seamlessly with virtual network peering).
It's also recommended to secure data in motion by ensuring that your application connects to MySQL flexible server using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL).
Implement retry logic to manage transient faults
Given that cloud environments are more likely to encounter transient faults like network connectivity interruptions or service timeouts, applications must implement logic to deal with them, typically by retrying requests after a delay.
A good practice is to wait for five seconds before your first retry. Then follow each retry by increasing the wait gradually, up to 60 seconds. After a fixed number of retries, the application can consider the operation failed and you can further investigate the persistent error.
Choose right compute and storage size for database
It's important to analyze your workload and size your Flexible Server instances correctly for an acceptable balance between application performance and costs. You can create a flexible server in one of three compute tiers: Burstable, General Purpose, and Business Critical. As a starting point for choosing the compute tier, consider the detail in the following table.
| Compute tier | Target workloads |
|---|---|
| Burstable | Best for workloads that don’t need the full CPU continuously. Cost-effective for smaller web applications and development workloads. |
| General Purpose | Most business workloads that require balanced compute and memory with scalable I/O throughput. Examples include servers for hosting web and mobile apps and other enterprise applications. |
| Business Critical | High-performance database workloads that require in-memory performance for faster transaction processing and higher concurrency. Examples include servers for processing real-time data and high-performance transactional or analytical apps. |
You can also resize flexible servers after creation. However, you can only scale up or down between the General Purpose or Business Critical tiers.
In terms of storage, you can scale up when you are approaching storage capacity limits. You can also enable the storage auto-grow feature to ensure that the service automatically scales the storage as it nears the storage limits.
To make informed decisions in a timely manner, monitor key Azure Monitor metrics like Host CPU percent, Host Memory percent, Storage percent, IO percent, Active connections, etc. constantly or set up alerts to notify you when the solution approaches the limits of your deployment.