Describe the production elements of a production process
Although each company’s manufacturing processes are unique, depending on the nature of the production environment, the core conceptual elements that are used in the production control module are often similar.
Creating a production order is a request to start manufacturing the quantity of items specified on the order. All information associated with the item that is to be produced is contained in the production order. Production orders have either a list of raw materials from the BOM or a formula that might contain coproducts and by-products, the required resources, the routes, and the operations.
Whether the company produces items that are made to order, made to stock, or engineered to order, the production control module enables the manufacturing facility to change production orders so that they're streamlined to their specific production requirements.
The core concepts in the Production control module are the following:
Calendars
Resources
Resource types
Resource capabilities
Bill of materials (BOM)
Routes and operations
Formula
Value streams
Production flow models
Production units
Production groups
Production pools
Allocation keys
Kanban functionality
Resources
Resources are the company’s total working resources. They can be anything that is used to create, produce, or deliver a good and/or service over and beyond the materials consumed in the process. Resources can be of different types, including machines, tools, people, vendors, or locations.
Resource types
You create resource types in the Organization administration module. They're used in production, along with the calendar, to manage the overall capacity of a company's equipment and resources. Each resource can be associated with a resource type, and one or multiple resources can exist in any given resource type.
The following resource types are available in Supply Chain Management:
Vendor - Use this type for operations or tasks performed by an outside resource or subcontractor. A vendor number can be associated with this kind of resource to help with scheduling and tracking.
Human resources - Use this type to define when personnel or a group of employees conduct an operation.
Machine - Use this type to tie an individual machine or group of machines with a resource. It's the most frequently used type of resource.
Tool - Use this type to control and schedule the reservations of a tool. Use this type only when capacity is limited.
Location - Use this type to control and schedule the reservations of a specific location.
Facility - A building or fixed structure that is required to perform an activity.
The following is a screenshot of resource types in a dropdown list.
Resource capabilities
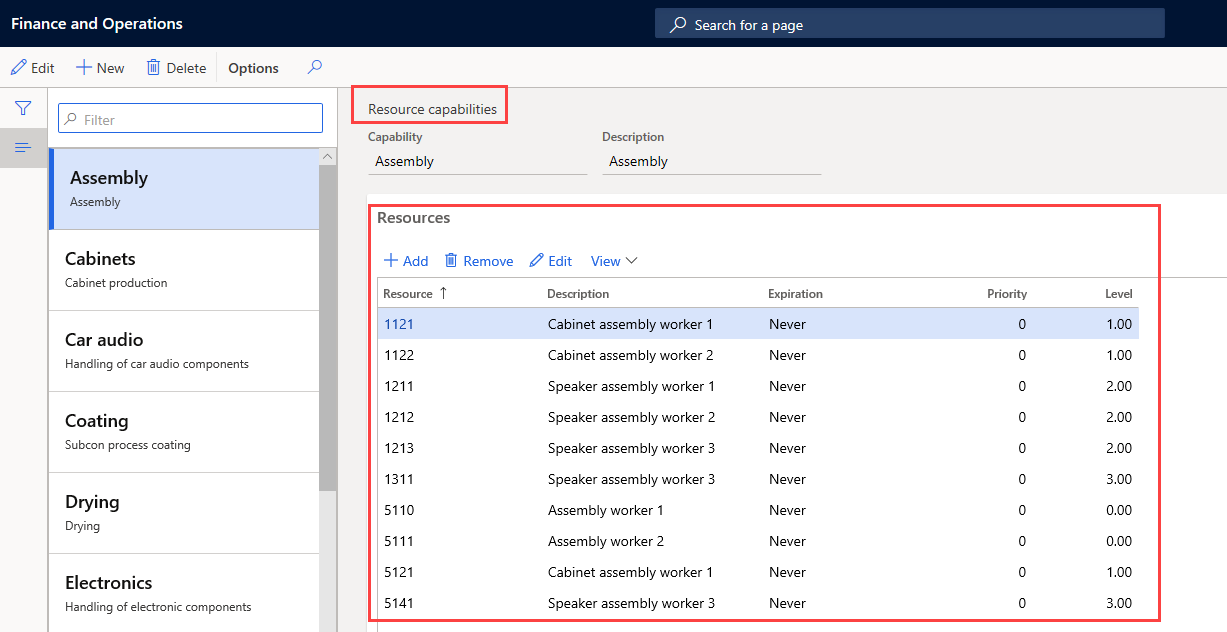
You assign resource capabilities to an operation’s resource. A resource can have more than one capability assigned to it, and a capability can be assigned to more than one resource.
You can also assign capabilities to resources on a temporary basis by defining a start date and expiration date on the capability assignment. Capabilities that expired on a resource prevents the resource from being scheduled for production if the production requires that capability, but it can later be renewed if necessary.
When defining resource requirements for a production route, you can specify one or more capabilities as requirements. When production scheduling is performed, the capabilities that are defined in the resource requirements on the route operation are matched with the capabilities that are defined for the resources.
The resources with capabilities that satisfy the requirements are then selected. When defining capabilities for different resources, you should set up capabilities so that different processing speeds are set up as different capabilities.
The following screenshot displays the list of resources for the selected capability of Assembly.
Bill of materials
The bill of materials (BOM) is one of the most important elements in a manufacturing company. Before a company can produce a product, it must know what components will be included and how many of these components are needed to make the product. The BOM has all the ingredients, components, parts, or raw materials necessary to make one finished product.
Routes and operations
The route determines the process steps that are needed to produce a finished product.
The BOM defines the materials needed, the resource defines where the item is produced, and the route determines the sequence of events to build the finished product.
Operations are the tasks or work processes that are put together with a route to produce a specific product. Each task is associated with a time allotment to complete the individual task.
Companies can also set up optional settings that control the production process if these are relevant to their production environments.
The optional settings are:
Production groups - Set up production groups to establish relationships between the production order and ledger accounts. The ledger accounts are used to post or to group orders for reporting.
Production pools - Create production pools to group production orders for processing urgent production orders or for deleting and posting groups of orders.
Properties - Define properties to create special attributes that you can assign to your resources for use in the scheduling process. These attributes are connected to the working time template.
Resource capabilities - Create resource capabilities in case resources need to perform the various operations in the route that can be expressed as the set of resource capabilities. This allows the allocation of resources to be deferred until production is scheduled.
Production control integration with other modules in Supply Chain Management
The Production control module is integrated with the following modules in Supply Chain Management:
Inventory management
Warehouse management
General ledger
Master planning
Organization administration
Project accounting
Product information management
This integration supports the information flow needed to complete the manufacturing of a finished item. The production of items follows a sequential production lifecycle.
The lifecycle reflects the actual steps taken to manufacture an item. It begins with creating a production order and ends with a finished, manufactured item that is ready for the customer.
Each step in the lifecycle requires different kinds of information. When a step in the lifecycle is completed, the production order signals this by a change in the production status. If any of the mandatory steps (or updates) are skipped, the steps are performed automatically before the production order is moved to the next step.
Production lifecycle and statuses
Production orders are assigned a status that reflects where it is in the production lifecycle. The status of the orders is as follows:
Create
Estimate
Schedule
Release
Start
Report as finished
End
A parameter setting in each stage allows a user to configure each step. The setting can be set up for a single user or for all users.
Continue to the next unit to learn about item tracking and tracing processes.