Resolve data import errors
While importing data into Power BI, you may encounter errors resulting from factors such as:
- Power BI imports from numerous data sources.
- Each data source might have dozens (and sometimes hundreds) of different error messages.
- Other components can cause errors, such as hard drives, networks, software services, and operating systems.
- Data often can't comply with any specific schema.
The following sections cover some of the more common error messages that you might encounter in Power BI.
Query timeout expired
Relational source systems often have many people who are concurrently using the same data in the same database. Some relational systems and their administrators seek to limit a user from monopolizing all hardware resources by setting a query timeout. These timeouts can be configured for any timespan, from as little as five seconds to as much as 30 minutes or more.
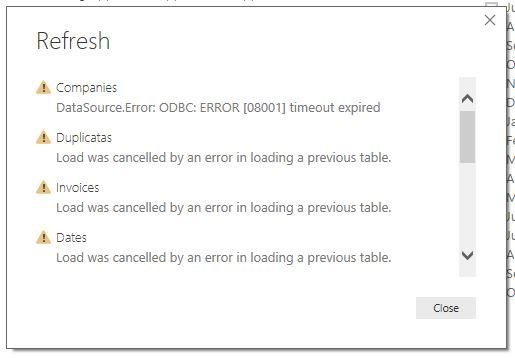
For instance, if you’re pulling data from your organization’s SQL Server, you might see the error shown in the following figure.
Power BI Query Error: Timeout expired
This error indicates that you’ve pulled too much data according to your organization’s policies. Administrators incorporate this policy to avoid slowing down a different application or suite of applications that might also be using that database.
You can resolve this error by pulling fewer columns or rows from a single table. While you're writing SQL statements, it might be a common practice to include groupings and aggregations. You can also join multiple tables in a single SQL statement. Additionally, you can perform complicated subqueries and nested queries in a single statement. These complexities add to the query processing requirements of the relational system and can greatly elongate the time of implementation.
If you need the rows, columns, and complexity, consider taking small chunks of data and then bringing them back together by using Power Query. For instance, you can combine half the columns in one query and the other half in a different query. Power Query can merge those two queries back together after you're finished.
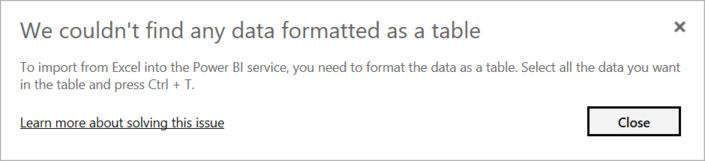
We couldn't find any data formatted as a table
Occasionally, you may encounter the “We couldn’t find any data formatted as a table” error while importing data from Microsoft Excel. Fortunately, this error is self-explanatory. Power BI expects to find data formatted as a table from Excel. The error even tells you the resolution. Perform the following steps to resolve the issue:
Open your Excel workbook, and highlight the data that you want to import.
Press the Ctrl-T keyboard shortcut. The first row will likely be your column headers.
Verify that the column headers reflect how you want to name your columns. Then, try to import data from Excel again. This time, it should work.
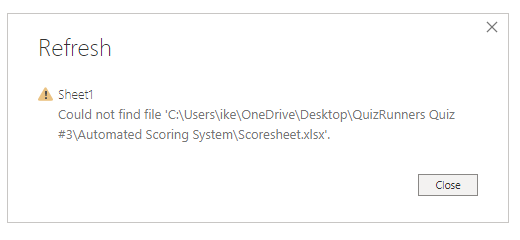
Couldn't find file
While importing data from a file, you may get the "Couldn't find file" error.
Usually, this error is caused by the file moving locations or the permissions to the file changing. If the cause is the former, you need to find the file and change the source settings.
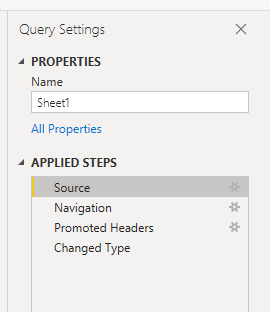
Open Power Query by selecting the Transform Data button in Power BI.
Highlight the query that is creating the error.
On the left, under Query Settings, select the gear icon next to Source.
Change the file location to the new location.
Data type errors
Sometimes, when you import data into Power BI, the columns appear blank. This situation happens because of an error in interpreting the data type in Power BI. The resolution to this error is unique to the data source. For instance, if you're importing data from SQL Server and see blank columns, you could try to convert to the correct data type in the query.
Instead of using this query:
SELECT CustomerPostalCode FROM Sales.Customers
Use this query:
SELECT CAST(CustomerPostalCode as varchar(10)) FROM Sales.Customers
By specifying the correct type at the data source, you eliminate many of these common data source errors.
You may encounter different types of errors in Power BI that are caused by the diverse data source systems where your data resides.
If you experience an error not covered, you can search Microsoft documentation for the error message, and the resolution you need.