Calculations for product configuration models
Calculations can be used for arithmetic or logical operations. They complement expression constraints in product configuration models. You can define calculations on the Constraint-based product configuration model details page and then build expressions for the calculations in the expression editor.
A calculation is an element that you can use in a product configuration model. Calculations complement constraints by letting you use decimal numbers to calculate values when you configure a product. Additionally, calculations have a larger set of available operators than constraints have.
Like a constraint, a calculation is associated with a specific component in a product configuration model and can't be reused by or shared with another component. One important difference between calculations and constraints is that calculations are imperative (unidirectional), whereas constraints are declarative (bi-directional).
A calculation consists of a target attribute and a calculation expression.
Target attribute
A target attribute is an attribute that receives the result of the calculation expression.
In the following expression, the target attribute is a tablecloth measurement:
Expression: If [decimalAttribute1 <= decimalAttribute2, True, False]
DecimalAttribute1 is the table length and decimalAttribute2 is the tablecloth length. The expression returns the value True to the target attribute if decimalAttribute2 is greater than or equal to decimalAttribute1. Otherwise, the expression returns False. Therefore, the tablecloth measurement is acceptable if the tablecloth length is the same as or exceeds the length of the table.
All attribute types that the product configurator supports can be set to target attributes except text without a fixed list.
The value of a target attribute cannot restrict the values of the input attributes because calculations are unidirectional. Therefore, the value of the target attribute is set based on changes in the value of the input attributes, but a change in the value of the target doesn't affect the value of the input attributes. This behavior differs from the behavior for constraints. Constraints occur in both directions.
Example:
In the following expression, the target for the calculation is the length of a power cord and the input value is a color.
Expression: [If Color == "Green", 1.5, 1.0]
When you configure the item, the length of the power cord is set to 1.5 if you specify Green as the value of the color attribute. If you specify any other color, the length is set to 1.0. However, because calculations are unidirectional, the calculation doesn't set the value of the color attribute to Green if you specify a length of 1.5.
If a target attribute is of the integer type, but a calculation generates a decimal number, only the integer part of the calculated result is returned, the decimal part is removed, and the result isn't rounded. For example, a result of 12.70 is shown as 12.
Calculations occur when a value has been provided for all input attributes. You can overwrite the value that is calculated for the target attribute unless the target attribute is set as hidden or read-only.
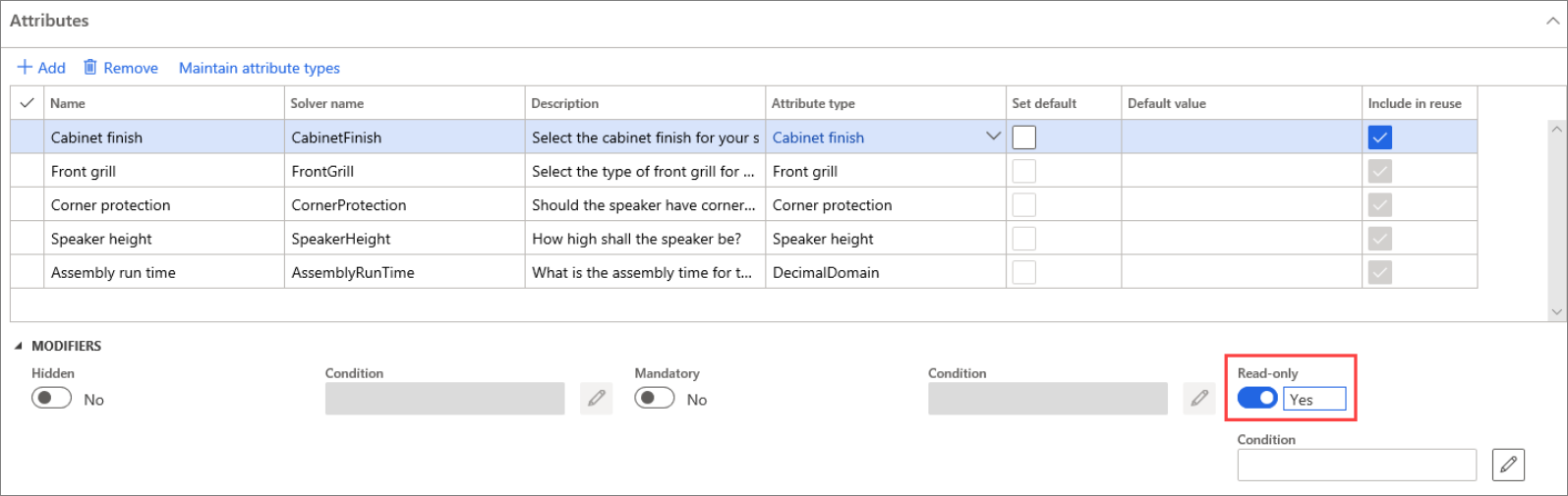
Set up a target attribute as hidden or read-only
To set an attribute as hidden or read-only, follow these steps.
Select Product information management > Products > Product configuration models.
Select a product configuration model and then, on the Action Pane, select Edit.
On the Constraint-based product configuration model details page, select the attribute to use as a target attribute.
On the Attributes FastTab, select Hidden or Read-only.
A calculation cannot overwrite the values that you set. The values that you set when you configure a product are the values that are used. The calculation that occurs when the input values in a calculation are changed can't overwrite the values that you provide for a specific attribute.
If you remove an input value in a calculation, the value of the target attribute is also removed.
Error message - Model is in contradiction
The Model is in contradiction error message is shown when a calculation includes an error or when a contradiction exists in one or more constraints.
Situations where errors can occur in calculations are when:
A value is divided by 0 (zero).
A conflict exists between the following two elements:
The values that are available for an attribute and are limited by a constraint
A value that is generated by a calculation
The values that are returned by the calculation are outside the domain of the attribute, for example, an integer from [1..10] that is calculated to 0.
Error message - After successfully validating a product model
If you receive the After successfully validating a product model error message, calculations are not included in the validation. You must test the product configuration model to find errors in calculations. To test a product configuration model, follow these steps:
Select Product information management > Products > Product configuration models.
Select a product configuration model and then, on the Action Pane, in the Run group, select Test.