Language models
Language models interpret user utterances and trigger the relevant scenario logic in response. They're fundamental components for configuring your Azure Health Bot experience. For example, you can use a language model to trigger scheduling logic when a user enters "How do I schedule an appointment?"
Language models take textual unstructured utterances from users and provide a structured response. This response includes the user's intent combined with a confidence score that reflects the accuracy of the extracted intent.
Multiple models can be used in parallel. When more than one possible intent is identified, the confidence score for each intent is compared. The highest score is used to invoke the mapped scenario. Each intent is unique and mapped to a single built-in or custom scenario.
Confidence score
A score between 0 and 1 reflects the likelihood that a model has correctly matched an intent with the utterance provided. A score of 1 shows a high certainty that the identified intent is accurate.
Types of language models
There are different types of language models. Some language models are built in to your bot and come out of the box. By default, the built-in models are used to trigger the built-in scenarios. Built-in models can be repurposed and mapped to your own custom scenarios by changing their configuration. You can also build your own custom models for tailored language understanding.
Regular Expression models
Regular Expression (RegEx) models are great for optimizing performance when you need to understand simple and predictable commands from users. They extract a single intent from an utterance by matching the utterance to a RegEx pattern. For example, the RegEx pattern /.help./I matches the utterance "I need help".
For more information, see Regular Expressions.
The confidence score is calculated based on the number of characters in the matched part and the full length of the utterance. The longer the match, the higher the confidence score from the RegEx model.
LUIS models
LUIS models are great for natural language understanding. They understand broader intentions and improve recognition. They also require an HTTPS call to an external service. LUIS models return a confidence score based on mathematical models used to extract the intent.
LUIS is deeply integrated into Health Bot and supports multiple LUIS features, such as:
- Bing Speller: Provide your Bing Speller subscription key in the endpoint URL to pass all utterances through a spell check before undergoing processing by the LUIS application. For more information, see Bing Speller.
- Staging: Use the staging version of your LUIS application if you want to prevent testing from affecting the learning of your production LUIS application. For more information on publishing your LUIS application, see Production and Staging slots.
- Verbose responses: Typically, the response from your LUIS application includes only the highest scoring intent for the model. To include all intents and their respective scores in the response, use the Verbose setting.
When you create a LUIS model, you need an account with the LUIS.ai service.
System models
System models use proprietary recognition methods. They're not open for editing, but you can override the default intent mapping. For example, you can use the medical complaint recognizer to trigger your own symptom-checking scenarios.
The built-in medical models provide language understanding that's tuned for medical concepts and clinical terminology. All medical language models use system recognition methods. Some of them include:
- Medical complaints: This model understands when a user is making a medical complaint. It extracts key information, such as the medical concept, age, gender, and other information that's required to diagnose a complaint, and triggers the built-in triage protocols.
- Medical information requests: This model understands when a patient is asking for information about a medical concept. For example, the user can ask about symptoms or complications of a given condition. It then triggers a scenario that displays relevant information from a medical database.
- Drugs and medication: This model understands when a user is asking for information about the type or brand of a drug. It invokes a scenario that presents information about the drug in question.
Which models should you use?
Different models use different language recognition methods. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. When you plan your implementation, use a combination of recognition types best suited to the type of scenarios and capabilities you need.
Add a RegEx model to your health bot
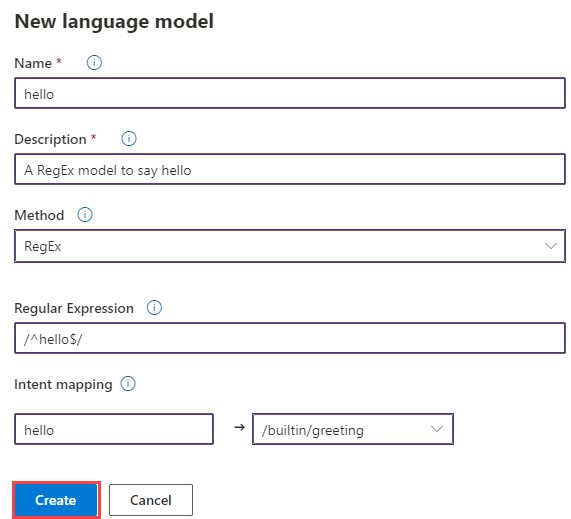
Go to the home page of your health bot. In the left pane, under Language select Models. Select the New option near the top of the page.
In the New model pane that appears on the right side of the page:
Under Method, select RegEx. Enter a name and description for your RegEx language model.
Under Regular Expression, enter the RegEx pattern for your language model, which in this case is /^hello$/.
Under Intent mapping, name your RegEx model with a unique intent that isn't used by another model. Name it hello for now, and map it to the builtin/greeting scenario in the dropdown menu. Select Create.
After you've successfully created your RegEx language model, test it in Web Chat.
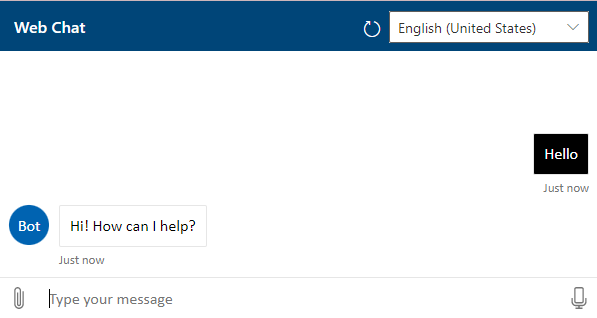
After you're finished, exit Web Chat. Scroll through the various language models and find the Greetings language model.
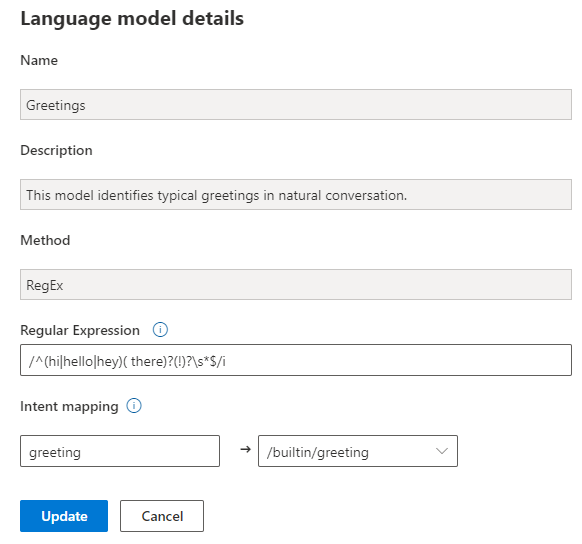
The language model that we added earlier was a simpler version of the built-in Greetings language model.
Select Cancel after you're finished viewing the Greetings language model.
