Define extended replication
As the Contoso Windows Server administrator, you should understand how to provide an additional solution in case there are two site outages. You'll investigate extended replication with Hyper-V Replica to determine if that's a potential solution.
Extended replication
To provide additional disaster recovery protection by preparing for the outage of both the primary and replica sites, Hyper-V Replica supports the replication to a third server. This third server can be at a third site, separate from the locations of the primary and replica servers. With this setup, you can replicate a running VM to two independent servers which could be in different geographic locations, providing additional options for recovering a failed VM. This configuration is known as Extended replication. The replication doesn't happen from the primary server to two other replica servers. Instead, the primary server replicates to the replica server, which in turn replicates to the extended replica server, in a daisy chain as depicted in the following image.
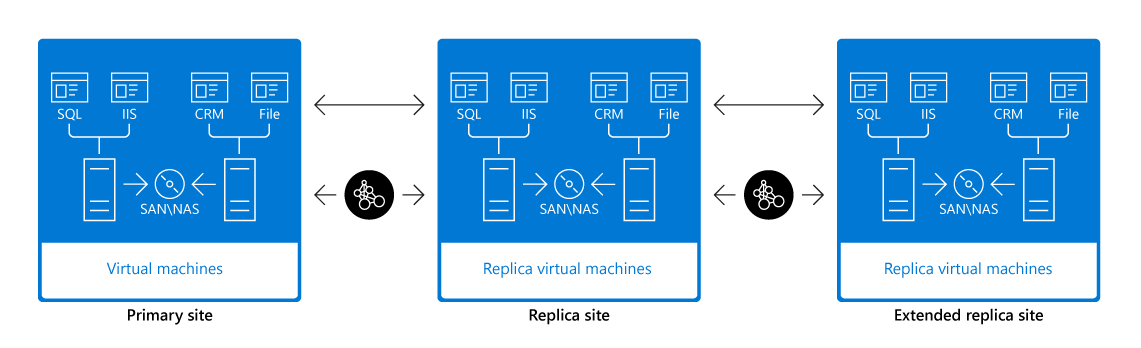
Note
The option to create an extended replica is only available on the replica VM; it isn't available from the primary VM.
Create an extended replica
To create an extended replica in Hyper-V Manager:
- Select the replica VM.
- Select Replication > Extend Replication to start the Extend replication for <VMName> wizard.
- In the Extend replication for <VMName> wizard, select the following:
- Select the replica server that will act as the extended replica server.
- Select whether to compress the data that's transmitted over the network.
- Select the frequency at which changes will be sent to the extended replica server. You can select an interval greater than (but not less than) the initial replication frequency.
- Select the option to maintain only the latest recovery points or create additional hourly recovery points.
- Select an initial replication method and schedule.
- Complete the wizard, and then the extended replication will initiate.
To create an extended replica by using Windows PowerShell:
On the replica server, open a Windows PowerShell console with elevated permissions and use the following cmdlets, which are the same Windows PowerShell cmdlets that you used for enabling replication:
Enable-VMReplication –VMName -ReplicaServerName <extended_server_name> -ReplicaServerPort <Auth_port> -AuthenticationType <Certificate/Kerberos> -ReplicationFrequencySec <300/900>On the extended replica server, examine the state, health, size and other details of the extended replica VM by running the following Windows PowerShell command:
Measure-VMReplication -ReplicationRelationshipType Extended
Limits of extended replication configuration
Extended replication has the following configuration limits:
- Replication frequency can be 5 minutes or 15 minutes only.
- Replication frequency can't be lower than the initial replication. For example, if the initial replication frequency is 15 minutes, you can't set the extended replication to 5 minutes.
- You can't change the authentication type.