Explore Storage Spaces
Storage Spaces is a storage virtualization technology in Windows and Windows Server that can help protect your data from drive failures. It is conceptually similar to RAID, but implemented in software. You can use Storage Spaces to group three or more drives together into a storage pool and then use capacity from that pool to create Storage Spaces. These typically store extra copies of your data so if one of your drives fails, you still have an intact copy of your data. If you run low on capacity, just add more drives to the storage pool.
Storage Spaces is available for NTFS and ReFS volumes, providing redundancy and pooled storage for numerous internal and external drives of differing sizes and interfaces. You can use Storage Spaces to add physical disks of any type and size to a storage pool, and then create highly available virtual disks from the storage pool. The primary advantage of Storage Spaces is that you do not have to manage single disks, but can manage multiple disks as one unit.
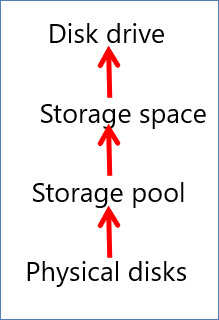
To create a highly available virtual disk, you need the following:
Physical disk. Physical disks are disks such as Serial ATA (SATA) or Serially Attached SCSI (SAS) disks. If you want to add physical disks to a storage pool, the disks need to satisfy the following requirements:
- Creating a storage pool requires one physical disk.
- Creating a resilient mirror virtual disk requires a minimum of two physical disks.
- Creating a virtual disk with resiliency through parity requires a minimum of three physical disks.
- Three-way mirroring requires at least five physical disks.
- Disks must be blank and unformatted; no volume must exist on them.
- Disks attachment can use a variety of bus interfaces including SAS, SATA, small computer system interface (SCSI), and USB.
Storage pool. A storage pool is a collection of one or more physical disks that you can use to create virtual disks. You can add all nonformatted physical disks and disks that do not have an attachment to another storage pool to a storage pool.
Storage space. This is similar to a physical disk from the perspective of users and programs. However, storage spaces are more flexible because they include thin provisioning or just-in-time (JIT) allocations, and they include resiliency to physical disk failures with built-in functionality such as mirroring.
Disk drive. You can access this volume from your Windows operating system, for example, by using a drive letter.
Note
Storage Spaces Direct is for creating highly scalable storage solutions. Unlike Storage Spaces, which is intended to create storage pools for the local client, Storage Spaces Direct is designed to configure local drives on a server, performing a role similar to traditional SAN or NAS arrays at a lower cost. This feature is not designed for client, and is only available on Windows Server, only available in Windows Server Datacenter edition.