Define GHAS and the importance of its integral features
In this unit we'll be covering:
- Secret scanning
- Code scanning
- Dependabot
- Creating a More Secure Software Development Life Cycle with all 3 Features
Let’s start with a quick review of GHAS.
What is GHAS?
GitHub Advanced Security (or GHAS) is an application security solution that empowers developers. Advanced Security is embedded right into your workflow to help prevent vulnerabilities and credential leaks without slowing development. GitHub Advanced Security is like having your personal security consultant review every line of code with insights from security experts from around the world.
Ensuring the security of applications and the software supply chain has never been more important. Gartner predicts that 45% of global organizations will be impacted by a supply chain attack by 2025. According to the 2022 Verizon Data Breach Investigation Report, applications continue to be a top attack vector and are at the center of more than 40% of all data breaches.
Incorporating security into your software development process may seem like a daunting process, so let's go over 3 key features of GHAS and how they help your team stay on top of the latest security threats: Secret scanning, Code scanning, and Dependabot.
Secret scanning

Secret scanning is a crucial security feature within GitHub Advanced Security (GHAS) designed to identify and mitigate the inadvertent exposure of sensitive information, such as API keys and tokens within the source code.
This scanning process is essential for preventing unauthorized access and safeguarding confidential data. Secret scanning operates by searching for predefined patterns and signatures indicative of sensitive information, ensuring that potential security risks are promptly addressed. By default, secret scanning looks for highly accurate patterns that have been provided by a GitHub Partner, however, custom patterns can be created for other use cases.
Secret scanning includes:
- Push protection proactively prevents secret leaks by scanning code on commit and blocking a push if a secret is present.
- The ability to easily view alerts and remediate them without ever having to leave GitHub.
In a secure software development life cycle, secret scanning plays a pivotal role in preventing unintentional leaks of critical information. By integrating secret scanning into the development process, teams can identify and remediate exposed secrets early, reducing the risk of data breaches and ensuring the confidentiality of sensitive data throughout the entire development life cycle.
Next, let’s review code scanning.
Code scanning

Code scanning is an integral feature of GHAS that analyzes source code for security vulnerabilities and coding errors. It employs static analysis techniques to identify potential issues such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and buffer overflows. By providing automated feedback directly within the pull request workflow, code scanning enables developers to address vulnerabilities early in the development process.
Code scanning enhances the overall security of a software development project by identifying and addressing security vulnerabilities in the codebase before they reach production. By fostering a proactive approach to security, code scanning helps minimize the potential impact of security threats, improves code quality, and accelerates the development cycle by reducing the time spent on post-deployment issue resolution.
Next up, let’s review Dependabot.
Dependabot

Dependabot is an automated dependency management tool, responsible for keeping project dependencies up-to-date. It regularly checks for updates to libraries and frameworks used in a project and automatically opens pull requests to update dependencies to their latest, secure versions. Dependabot contributes to maintaining a secure and stable development environment by addressing vulnerabilities present in outdated dependencies.
In a secure software development life cycle, managing dependencies is crucial to minimizing the risk of exploiting known vulnerabilities. Dependabot streamlines the process of updating dependencies, ensuring that projects benefit from the latest security patches and improvements. By automating this aspect of security, Dependabot contributes to creating a resilient and secure foundation for the entire development process.
With GitHub Advanced Security, Dependabot’s functionality is extended to include Dependency Review, allowing you to check for vulnerable dependencies within a pull request. This check enables you to address vulnerabilities before they are merged into a shared branch.
Where to enable Secret scanning, Code scanning, and Dependabot alerts
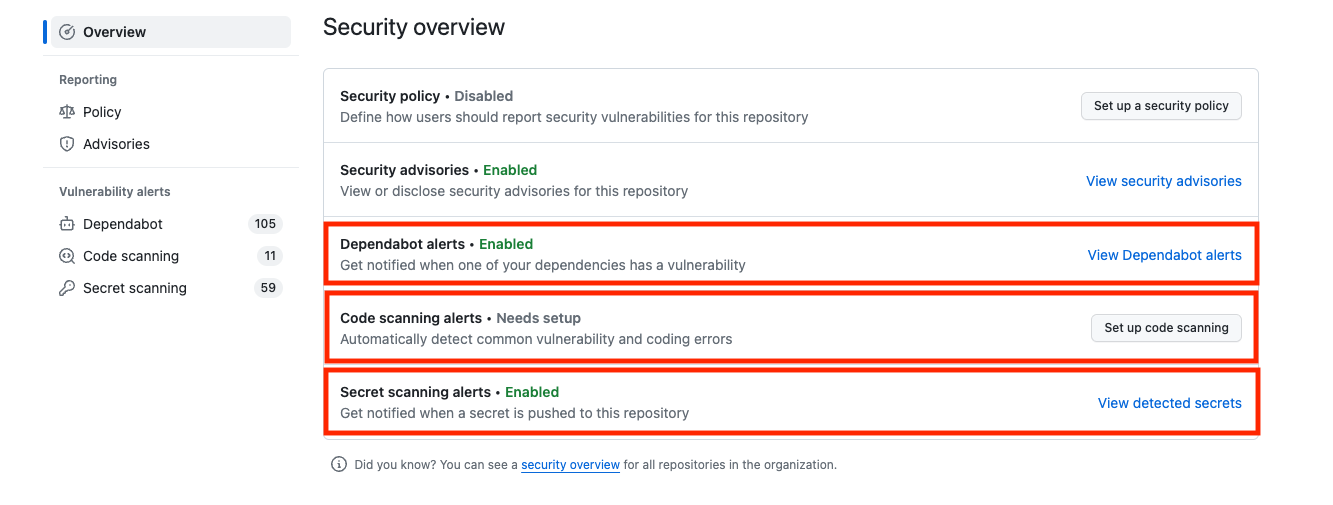
To enable any of the alerts from a repository level first navigate to your repository’s security tab.

Next, enable your alerts in the Security overview.
Now that we’ve reviewed and enabled all 3 of GHAS’s integral features, let's talk about how to implement all of them to create a more secure software development life cycle.
Creating a more secure software development life cycle with all 3 features
Secret scanning, code scanning, and Dependabot collectively contribute to creating a more secure software development life cycle. Secret scanning prevents inadvertent exposure of sensitive information. Code scanning identifies and addresses security vulnerabilities in the codebase. And Dependabot automates dependency management.
By integrating these features, development teams can proactively address security concerns at every stage of the development life cycle. This proactive approach minimizes the likelihood of security incidents reaching production, resulting in a more resilient, secure, and efficient software development process.
The combined impact of these integral features ensures that security is not a standalone consideration but an integral part of the entire development workflow.
Next, let’s review the differences between GitHub’s security features for open-source projects and GHAS on GitHub Enterprise Cloud.
Security features for open source projects
Public projects on GitHub benefit from certain default security features, such as secret scanning and dependency graphs. GitHub automatically scans public repositories for partner patterns and provides alerts to repository administrators. Public projects can also choose to enable code scanning, Dependabot, and Dependency Review without a GitHub Advanced Security license.
However, these features are foundational and may not provide the depth of protection needed for more complex projects or enterprise environments.
When GitHub Advanced Security (GHAS) is paired with GitHub Enterprise Cloud (GHEC), the comprehensive set of security features becomes available for internal and private projects as well:
- Code scanning - Search for potential security vulnerabilities and coding errors in your code.
- Secret scanning - Detect secrets, for example, keys and tokens, that have been checked into private repositories. Secret scanning alerts for users and partners are available and free of charge for public repositories on GitHub.com. If push protection is enabled, it also detects secrets when they are pushed to your repository.
- Dependency review - Show the full impact of changes to dependencies and see details of any vulnerable versions before you merge a pull request. The table below summarizes the availability of GitHub Advanced Security features for public and private repositories.
| Public repository | Private repository without Advanced Security | Private repository with Advanced Security | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Code scanning | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Secret scanning | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Dependency review | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |