Explore Elastic jobs
One of the reasons why many DBAs became so familiar with Azure Automation is that Azure SQL Database initially lacked capabilities for scheduled jobs.
Elastic jobs feature allows you to run a set of T-SQL scripts against a collection of servers or databases as a one-time job, or by using a defined schedule. Elastic jobs work similarly to SQL Server Agent jobs, except that they're limited to executing T-SQL. The jobs work across all tiers of Azure SQL Database. SQL Agent jobs continue to be used for task automation in SQL Server and are also included with Azure SQL Managed Instances.
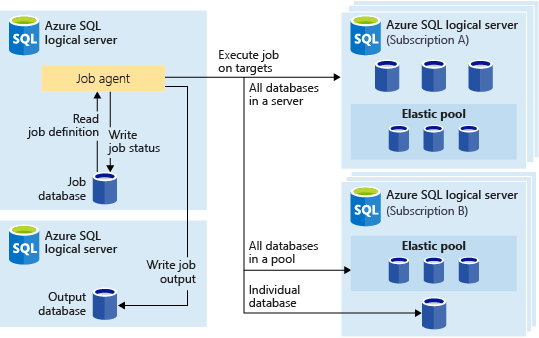
To configure Elastic Jobs, you need a Job agent and database dedicated to managing your jobs. The recommended service tier for the job database is S1 or higher, and the optimum service tier will be dependent on the number of jobs you're executing and the frequency of those jobs.
Let's review the elastic jobs components:
- Elastic Job agent - your Azure resource for running and managing jobs.
- Job database - a database dedicated to manage your jobs.
- Target group - a collection of servers, elastic pools, and single databases in which a job will be run.
- Job - one or more T-SQL scripts that compose a job step.
If a server or elastic pool is the target, a credential within the master database of the server or pool should be created so that the job agent can enumerate the databases within. For a single database, a database credential is all that is needed. Credentials should have the least privileges necessary to perform the job step.
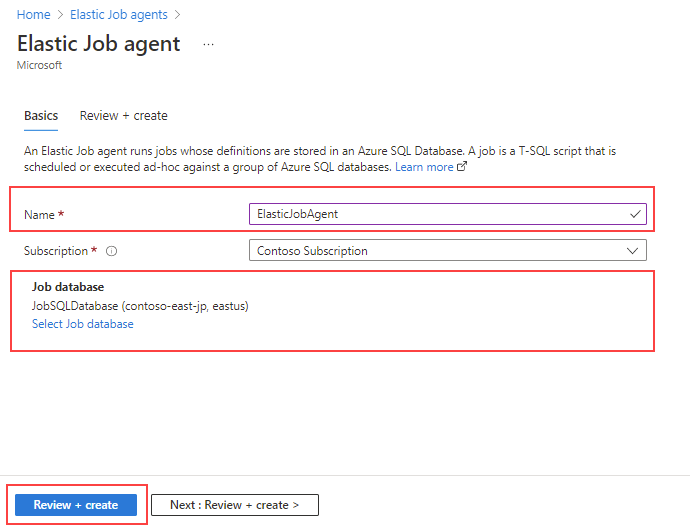
You can create an elastic job agent through the Azure portal. On the Elastic Job agent page, make sure you provide a name for your agent, and specify a SQL database for your job database.
You can create a target group by using either PowerShell or T-SQL. The following snippet creates MyServerGroup target group including all databases that exist on the server at the time of execution. This code snipped assumes that the variable $jobAgent and the variable $targetServerName were previously provided.
# create MyServerGroup target group
$serverGroup = $jobAgent | New-AzSqlElasticJobTargetGroup -Name 'MyServerGroup'
$serverGroup | Add-AzSqlElasticJobTarget -ServerName $targetServerName -RefreshCredentialName $masterCred.CredentialName
The code snipped below creates an elastic job, and add job steps using PowerShell. The Step1 is responsible to create the MyTable table if it does exist.
Write-Output "Creating a new job..."
$jobName = "MyFirstElasticJob"
$job = $jobAgent | New-AzSqlElasticJob -Name $jobName -RunOnce
Write-Output "Creating job steps for $($jobName) job..."
$sqlText1 = "IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.tables WHERE object_id = object_id('MyTable')) CREATE TABLE [dbo].[MyTable]([Id] [int] NOT NULL);"
$job | Add-AzSqlElasticJobStep -Name "Step1" -TargetGroupName $serverGroup.TargetGroupName -CredentialName $jobCred.CredentialName -CommandText $sqlText1
As we can see above, T-SQL scripts being executed by elastic jobs should be idempotent, which means if the job is run multiple times, whether accidentally or because of job failure, the job won’t fail or produce unintended results. You should be able to run the same script multiple times without failure.
Finally, run the elastic job MyFirstElasticJob using PowerShell.
Write-Output "Start the job..."
$jobExecution = $job | Start-AzSqlElasticJob
$jobExecution
Use case scenarios
Elastic jobs can be used in the following scenarios:
- Automate management tasks to run on a specific schedule
- Deploy schema changes
- Data movements
- Collect, and aggregate data for reporting or other purposes
- Load data from Azure Blob storage
- Configure jobs to execute across a collection of databases on a recurring basis, such as during off-peak hours
- Data processing over a large number of databases, for instance, telemetry collection. Results are then compiled into a single destination table for further analysis.